The application of machine learning in business has shifted from a competitive differentiator to an operational imperative. In a 2024 Rackspace Technology report, over a third of IT leaders cited ML adoption as a top strategic priority, with this figure increasing as organizations strive for smarter, faster, and more scalable solutions.
Machine learning (ML), once a futuristic idea, is now the hidden engine driving data-informed decision-making, automated workflows, and personalized customer engagement across industries. This article highlights some of the top real-world applications of machine learning in business that are changing the businesses we run today. Organizations are not only building machine learning system to remain competitive, but also to transform the definition of efficiency, innovativeness, and growth as we enter the intelligent automation era.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine learning is an area of artificial intelligence (AI) that allows a system to learn from data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention. It emulates the way in which humans learn from their experiences, and has algorithms and statistical models that improve in accuracy as it learns. While the concept itself was first articulated in 1959, the application of machine learning in business has become a movement in today’s data-driven age.
Business machine learning comes from the ability to move from merely analyzing the past and transforming unstructured raw data into strategic insight to inform the decision-making process, optimizing the performance of the enterprise, and ultimately creating a long-term, transformative effect at scale.
In essence, the application of machine learning in business gives companies the capability to do away with relying on their instinct, being predictive intelligence, and create a future where data-driven strategy becomes the definition of competitive advantage and success. Machine learning replaces gut-feel decisions with predictive insights, as seen in Amazon’s demand forecasting.
Top applications of Machine Learning in business
Business activities are being significantly changed by the application of machine learning in business. Its applications span across industries – marketing, finance, manufacturing, healthcare, and others – using data, machine learning is taking what has been a process defined by our standard way of thinking and redesigning it as an intelligent system that learns and adapts along the way.
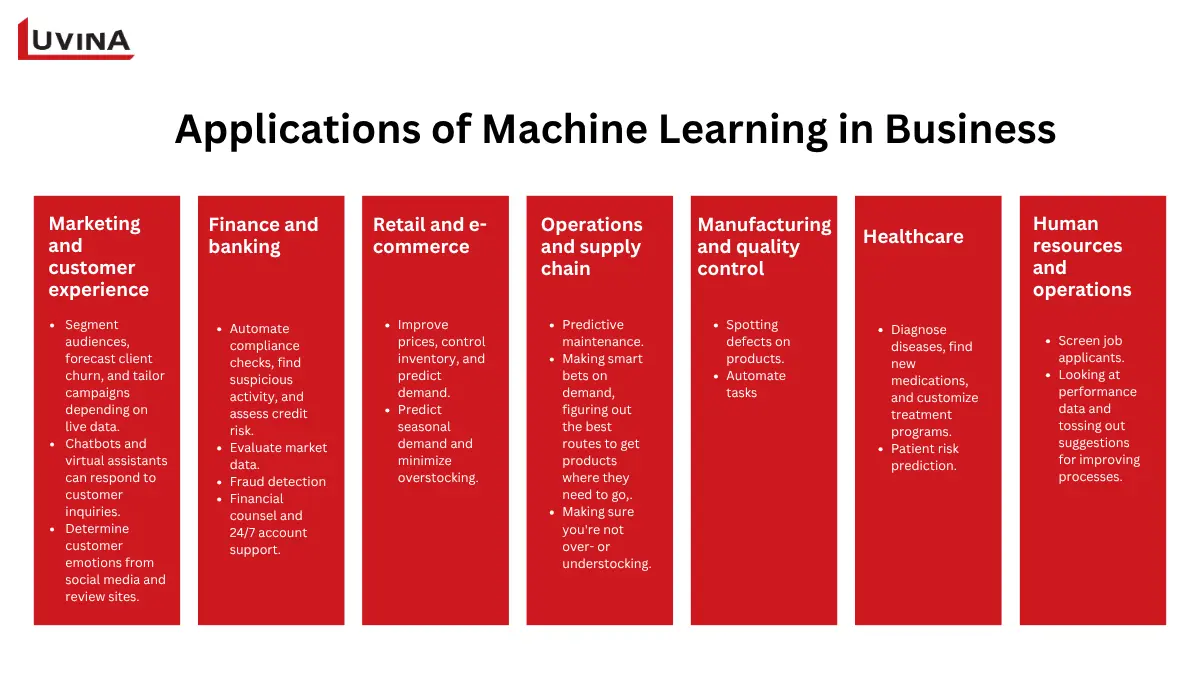
1. Machine learning in marketing and customer experience
Among the fast-developing domains of application in machine learning for business is marketing. ML helps businesses segment audiences, forecast client churn, and tailor campaigns depending on live data. Recommendation systems seen on Netflix or Amazon examine user behavior to recommend material or products suited to personal preferences.
Using the ability of natural language processing (NLP), chatbots and virtual assistants – the application of machine learning in business – can respond to customer inquiries instantly and personalize the response to enhance satisfaction at minimal operating expense. Using sentiment analysis tools, brands can determine customer emotions from social media and review sites to inform communication strategies and brand positioning.
2. Machine learning in finance and banking
Financial institutions depend heavily on machine learning to increase security and precision. Predictive algorithms automate compliance checks, find suspicious activity, and assess credit risk. Machine learning also drives algorithmic trading, in which models evaluate market data in milliseconds to support wise financial choices.
One of the most used application of machine learning in business in the financial sector is fraud detection. ML algorithms detect abnormalities more efficiently than conventional rule-based approaches by constantly learning from fresh transaction patterns. Financial counsel and 24/7 account support that chatbots provide also help to raise retention and customer engagement.
3. Machine learning in retail and e-commerce
The application of machine learning in business is used by retailers to improve prices, control inventory, and predict demand. Real-time product price adjustments are made using dynamic pricing models in response to consumer behavior, market developments, and competition. By improving customisation, recommendation systems increase loyalty and conversion rates.
While predictive analytics helps companies predict seasonal demand and minimize overstocking, ML-driven visual search lets customers locate items utilizing photographs rather than words. Business process uses of machine learning enable retail companies to become more customer-focused and nimble.
4. Machine learning in operations and supply chain
Operational efficiency is one of the biggest advantages of getting into application of machine learning in business. Predictive maintenance systems keep a close eye on machinery and give techs a heads up before it’s about to throw a wrench, which means a lot less downtime and a lot less stress.
When it comes to supply chain management, machine learning is all about making smart bets on demand, figuring out the best routes to get products where they need to go, and making sure you’re not over- or understocking – that’s key when you’re competing in a pretty cutthroat market.
5. Machine learning in manufacturing and quality control
Manufacturers use the application of machine learning in business to really ramp up precision and reliability. Computer vision does a way faster job than humans of spotting defects on products, and machine learning does a great job of sniffing out equipment wear from sensor data.
This is all about being able to predict when equipment is going to give up the ghost, which means you can keep it running longer – and that’s better for safety and production consistency all around. Plus – using machine learning to automate tasks really reduces waste and gets you producing more, which is a big step forward in the direction of Industry 4.0.
6. Machine learning in healthcare
To diagnose diseases, find new medications, and customize treatment programs, healthcare providers use the application of machine learning in business. Models developed on medical images have astounding accuracy in detecting anomalies like tumors, hence facilitating quicker and more precise diagnoses.
Furthermore, aiding hospitals in resource allocation is machine learning helps with patient risk prediction. Wearable technologies additionally employ ML to keep tabs on vital signs and warn consumers early on of any possible health problems, hence allowing preventative treatment.
7. Machine learning in human resources and operations
Businesses are diving into using application of machine learning in business in their HR and internal management, too. They’re using algorithms to actually screen job applicants, predict how likely an employee is to quit, and help their managers come up with better workforce plans. In the trenches of daily operations, machine learning comes in handy by looking at performance data and tossing out suggestions for improving processes that can actually make a difference.
These tools don’t just save time for companies, they also help them build a data-driven culture – one that really does boost productivity and long-term growth.
Integrating Machine Learning into business processes
Integrating AI and machine learning in business is a pretty big shift – it helps to turn raw data into real predictions and automates the dull, grind-it-out tasks that eat up so much of our time. The result is a more streamlined operation all round – departments are optimised and performance is lifted because of it. To get the best results out of the application of machine learning in business, you need to go through a careful process – one that makes sure they’re getting the technical side just right and also that it all fits in with their overall strategy.
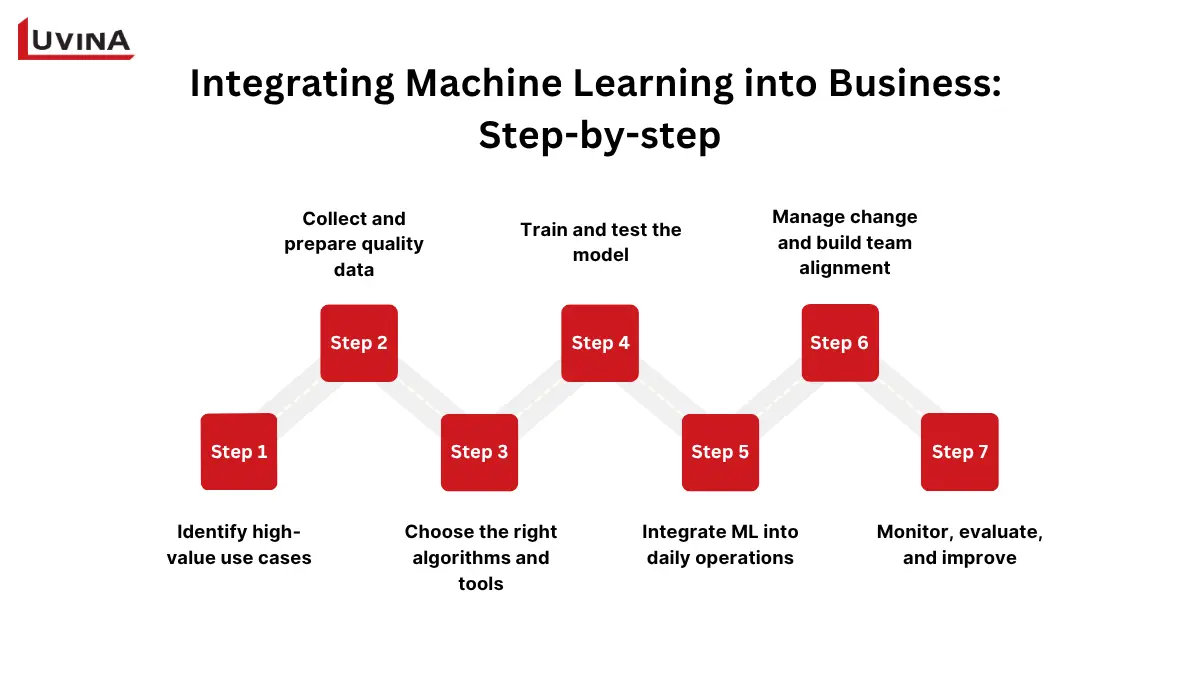
Step 1: Identify high-value use cases
Adoption of the application of machine learning in business starts with identifying areas where it might have a visible effect. So instead of throwing ML at something just because it’s shiny, get really specific about the business problems you want to solve with it – like cutting costs, getting more out of customer relations, or making your inventory management more efficient. Think about a retailer who wants to use ML to predict seasonal demand or a bank that wants to use it to stay one step ahead of scammers.
Doing this up front means you can make sure your ML strategy really lines up with what your business is trying to do, and that makes adoption a whole lot more straightforward and likely to stick.
Step 2: Collect and prepare quality data
The application of machine learning in business is only as good as the data it gets to learn from. So collect all sorts of data from places like customer records, transaction history, social media, or all those IoT sensors, and make sure it’s in good shape – clean, structured, and relevant. How you clean and get that data ready for use is going to affect how well your models work.
We often find out at this stage just how much work goes into getting your data in order – it’s not a one-off project, it’s an ongoing effort. But if you get your data governance right, you’ll end up with ML results you can actually trust.
Step 3: Choose the right algorithms and tools
The smartest algorithm choice is essential to bringing the power of application of machine learning in business in line with your business challenge. Different algorithms like linear regression, random forests, and neural networks are designed for various applications. To illustrate, a regression model may be used to forecast sales, whereas a classification algorithm would be employed to figure out which customers are at risk of leaving.
Besides this, organizations should look at the scalability, computational cost, and the integration process when deciding on ML frameworks and platforms. This step forms the technical foundation of machine learning with business applications.
Step 4: Train and test the model
Training about the application of machine learning in business starts when algorithms are chosen. This entails feeding the model labeled data so it can detect patterns and forecast. Measure the model’s performance on unknown data by dividing your dataset into training and testing groups.
The aim is to strike a balance between generalizing and accuracy. An overtrained model may do well on historical data but fall short in actual situations. Frequent testing guarantees that as corporate dynamics change, your ML model adjusts appropriately.
Step 5: Integrate ML into daily operations
After deployment, put your AI and machine learning to work in business. In marketing, we see how the application of machine learning in business improves from which is the basis of customer segmentation, predictive maintenance and demand forecasting. Also, for instance, marketing teams use ML-based insights to tweak campaigns as they go live and at the same time, logisticians use predictive analysis to better put together delivery routes.
Successful integration also requires cross-disciplinary work between data scientists, IT professionals, and business managers. These teams see to it that machine learning results are practical, reliable, and integrated into everyday processes.
Step 6: Manage change and build team alignment
The application of machine learning in business usually calls for organizational and cultural change. Interpreting data insights or operating automated systems could call for new skills from employees. An organized change management process helps smooth this transition by defining roles, resolving opposition, and matching personnel with long-term ML objectives.
Incorporating machine learning into the DNA of the firm depends on training initiatives, straightforward communication, and leadership assistance that will help to guarantee adoption and excitement across departments.
Step 7: Monitor, evaluate, and improve
Dynamic systems are machine learning models. They develop along with corporate information. Models must be kept accurate and efficient; therefore, ongoing monitoring is critical. Develop dashboards to monitor performance statistics and revalidate models on a regular basis. Setting up frequent review cycles lets companies detect drift, retrain models, and improve algorithms to keep accuracy over time.
Core Technologies and Algorithms behind business ML solutions
Machine learning systems rely on a mix of programming languages, frameworks, libraries, and computing resources. These technologies form the backbone that enables scalable ML solutions for modern businesses.
1. Core technologies in machine learning
Every machine learning system rests on a mix of frameworks, languages, libraries, and computing resources. These technologies make up the environment that allows the application of machine learning in business.
Programming languages
Building effective ML solutions starts with selecting the best programming language. Every language offers particular advantages; the selection depends on project scale, infrastructure, and deployment objectives.
– Python: The most popular choice for its simplicity, vast library ecosystem, and strong community. Used by Google, Netflix, and Spotify.
– R: Ideal for heavy data analysis and visualization, common in finance and research (e.g., JPMorgan).
– Java & C++: Offer speed and scalability; often used for fraud detection and computer vision at companies like IBM and PayPal.
– Julia: Combines Python’s simplicity with C++-level performance, adopted in scientific and energy sectors.
– Scala: Works seamlessly with Apache Spark for big data processing, used by Twitter and LinkedIn.
– JavaScript: Enables web-based ML with TensorFlow.js, popular among web platforms like Airbnb.
Frameworks and libraries
Frameworks and libraries speed up research by means of reusable code and prebuilt models.
– TensorFlow by Google and PyTorch by Meta dominate deep learning tasks such as image recognition and NLP.
– Scikit-Learn and Keras simplify traditional ML and neural network prototyping.
– Apache MXNet, Caffe, and H2O support scalable model training and distributed computing.
– MLlib incorporates machine learning features into large data environments via Apache Spark.
These tools let developers concentrate on optimization and correctness instead of starting from scratch to create algorithms. Additionally, promoting smooth integration into already present corporate settings, they improve the application of machine learning in business.
Computational resources
Computational power determines much of the success of the application of machine learning in business. GPUs and TPUs enable parallel data processing, while AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure offer on-demand scalability without large upfront costs.
2. Algorithms powering machine learning
Machine learning’s brain is algorithms. They forecast, spot patterns, and interpret data. Various algorithmic types fulfill various goals.
Supervised learning
Supervised learning relies on labeled data to train models for prediction and classification.
– Linear regression projects sales or pricing among numerical values.
– Decision trees and random forests look for structured data for medical diagnostics or credit scoring.
– Logistic regression forecasts binary results, including churn probability.
– Support vector machines (SVMs) identify images, detect fraud, and categorize text.
Many predictive and diagnostic tools used in corporate settings are built on these algorithms.
Unsupervised learning
Unsupervised algorithms find trends in unlabelled data, which is most helpful when outcomes are not set in advance.
– K-Means clustering divides customers according to buying habits.
– Hierarchical clustering shows relationships in biological data or social networks.
– Principal component analysis (PCA) reduces the dimension of the data for visualization or risk tools.
These sorts of approaches allow businesses to segment clients, simplify complex data and open up new market opportunities.
Reinforcement learning
In adversity, reinforcement learning is forced to experiment to optimise invariant decisions. Q-Learning and Monte Carlo-type algorithms are used in Robotics, gaming and automated trading. And good for helping computers find strategies that maximize the long-term reward, making them great candidates for process optimization and automation.
Deep learning
Deep learning represents the most advanced form of ML, powered by multi-layered neural networks inspired by the human brain.
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) handle image and video recognition for security, healthcare, and autonomous driving.
Recurrent neural Networks (RNNs) and Transformers process sequential data for speech recognition and language translation.
Generative adversarial networks (GANs) create realistic images, videos, or synthetic data for creative and analytical purposes.
Deep learning algorithms drive innovation in personalization, predictive maintenance, and intelligent automation – key areas of the application of machine learning in business today.
Business benefits and ROI of Machine Learning
Firms increase profitability and productivity with the application of machine learning in business to derive insights from data, enhance business performance, and generate better outcomes for customers. As well as combinations of automating and analyzing data, machine learning provides long-term opportunities for growth and signals competitive positioning.
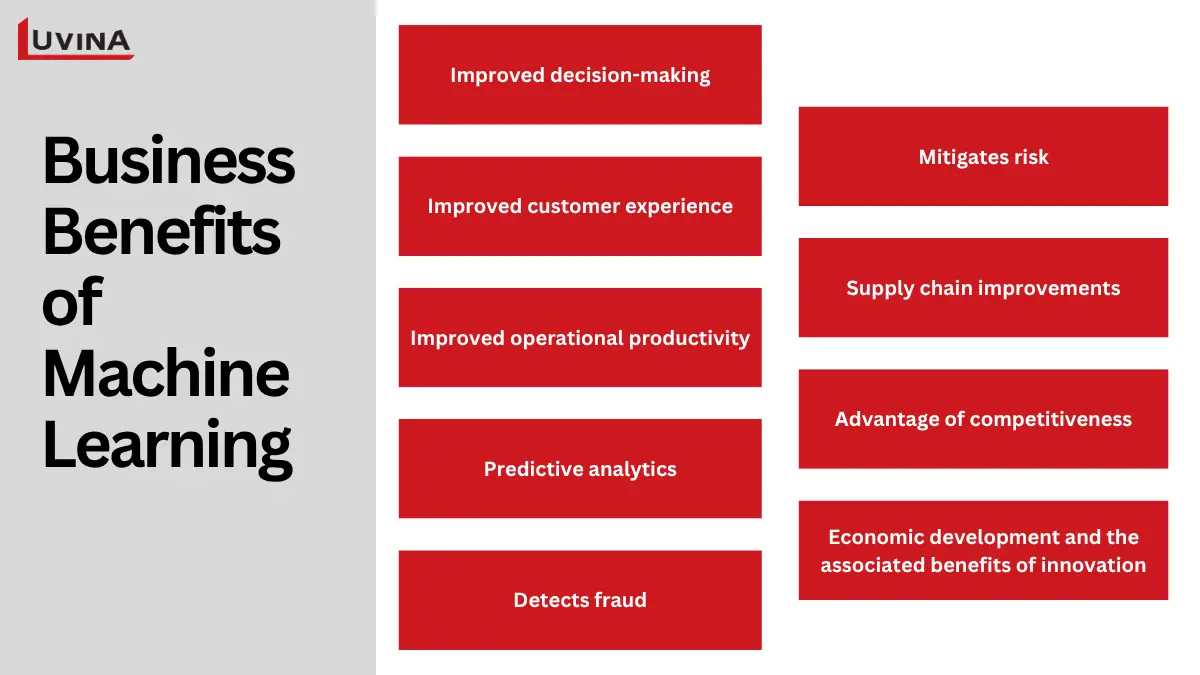
Improved decision-making: The application of machine learning in business helps make quicker and more correct business decisions by examining vast datasets to discover patterns and insights.
Improved customer experience: Machine learning with business applications allows for personalized suggestions and offers, focused discounts, and predictive engagement, all of which improve satisfaction and loyalty.
Improved operational productivity: The application of machine learning in business reduces repetitive work, saves transaction time and reduces errors induced from manual efforts.
Predictive analytics: Machine learning is able to predict customer behavior, demand, and sales, as well as improve planning and risk management.
Detects fraud: The advanced machine learning approaches identify difficult patterns and will quickly flag outliers as potentially questionable transactions to protect assets and reputations.
Mitigates risk: The machine learning models will identify unusual vulnerabilities and measure such vulnerabilities to avoid operational, cybersecurity, or financial risk.
Supply chain improvements: With real-time assessment, the application of machine learning in business improves logistics and associate mapping and delivery accuracy.
Advantage of competitiveness: Through the value-based adoption of machine learning solutions throughout their operations, firms acquire the agility to innovate more quickly and differentially.
Economic development and the associated benefits of innovation: A 2017 report by PwC forecasted that application of machine learning in business and artificial intelligence would unlock 14% of global GDP growth, or $15.7 trillion added to global GDP by 2030. As a result, it is reasonable to think of both as novel and transformative sources of corporate value.
Key challenges and how to overcome them
A lot of businesses struggle with practical obstacles that prevent them from deriving the full value from the application of machine learning in business. Here are the most common hurdles and pragmatic approaches to addressing them.
1. Data challenges
While data is still the underpinning of every machine learning system, a variety of problems surrounding data availability, quality, and labeling still stymie progress. Customers who are using the application of machine learning in business struggle with data collection because datasets tend to be small, relevant, and inaccurate; regulations such as GDPR and CCPA also limit access to proprietary and sensitive data. When datasets are incomplete or inconsistent, there is a greater chance a model’s accuracy will be impacted negatively, not to mention the exorbitant expense of manual labeling.
Solution: A clearly defined data management framework will help facilitate service and support the latter gap. Now, to be more specific, this means closing gaps that have to do with the collection, cleaning, verification, and storage of data. If problems are to be solved and restrictions observed, synthetic data generation, automated labeling, and secure data-sharing agreements are all fine options to help bridge data gaps.
2. Technical and infrastructure challenges
Modern ML models are computationally intensive and frequently challenging to incorporate with obsolete or siloed systems. Scalability, model deployment, and system compatibility may be problems for groups slowing uptake and adding to maintenance loads when using application of machine learning in business.
Solution: Progressive modernizing of IT infrastructure and use of cloud-based solutions for scalability and adaptability. APIs and microservices let companies link fresh ML elements without having to replace whole legacy systems.
3. Cost and resource constraints
Setting up infrastructure, model training, and data processing for the application of machine learning in business can entail significant initial expenditures. Particularly for smaller businesses, continuing costs for model changes and surveillance put financial stress.
Solution: The solution is to initiate pilot projects with very specific goals in high-impact areas before scaling them. Employ open-source frameworks and cloud computing, so startup costs are low and you have access to scale. The adoption of machine learning can yield more sustainable outcomes from automation of retraining and monitoring systems that deliver model accuracy with a minimal amount of manual intervention.
4. Ethical and regulatory challenges
The widespread application of machine learning in business raises legal and ethical questions about fairness, bias, and responsibility. Datasets that are slanted may lead to unfair decisions; models that are black boxes will make it hard to communicate predictions straightforwardly. Another complexity is that by following worldwide data protection laws.
Solution: Implement fairness testing, bias detection, and explainable AI methods to ensure transparency and trust. Establishing internal governance policies and collaborating with legal experts can also help align AI initiatives with ethical and regulatory expectations, building user confidence and minimizing risk.
5. Skill and expertise gaps
The key barrier to the application of machine learning in business is the shortage of skilled individuals. In spite of demand, skillful data scientists who have ML expertise and industry knowledge are hard to find – and even with recognized skills, the right amount of counseling can hinder projects from achieving production implementation.
Solution: Through specific training initiatives and ongoing learning, invest in their staff members’ development. Cross-functional teams, including both ML and domain specialists, help close the information gap.
Collaborating with seasoned artificial intelligence vendors or consulting companies can speed deployment even more while knowledge is transferred inside for long-term capability development. They can help choose the best algorithms, lower infrastructure expenses, and build effective data pipelines.
Businesses get end-to-end support from a team of hundreds of experienced professionals by working with a dependable partner like Luvina. Our thorough knowledge of machine learning for corporate uses enables companies to maximize actual value, increase operational efficiency, and generate quantifiable return on investment. Reach Luvina right now to discuss smart, data-driven solutions that might speed up digital transformation for your company.
Contact our team to discuss tailored solutions!
Real-World case studies: Successful ML implementations
The application of machine learning in business is transforming industries by improving decision-making, increasing productivity, and creating new avenues for creativity. These real-world examples illustrate how businesses are utilizing machine learning along with business applications to achieve quantifiable outcomes.
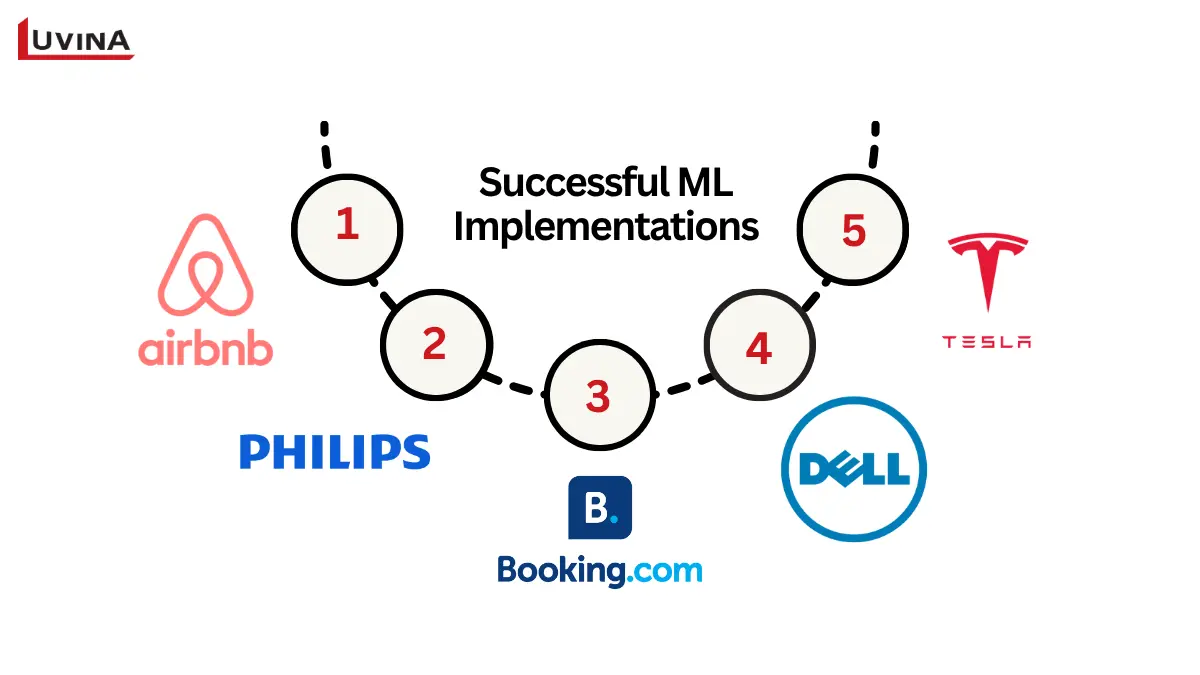
1. Airbnb: Automated document processing in customer communications
Companies like Airbnb, which handle a lot of consumer correspondence, frequently find it challenging to properly manage structured and unstructured data. Using AWS EMR and Airflow, Airbnb created a strong data infrastructure that handled more than 50GB of information per day. The company’s custom ML platform, Metis, aided automated data validation to provide more accurate suggestions and dynamic pricing strategies, therefore raising occupancy rates and customer happiness.
2. Philips: AI-powered medical imaging
By improving the speed and accuracy of diagnostic procedures, the application of machine learning in business has changed medical imaging. ML models trained on huge quantities of imaging data can detect abnormalities and patterns not easily discernible to the human eye.
Philips simplified model deployment and upgrades by using MLOps-backed artificial intelligence-driven imaging. This solution guaranteed consistent performance across various imaging datasets, lowered interpretation time, and improved diagnostic accuracy.
By using this application of machine learning in business, healthcare professionals may provide quicker, more accurate diagnoses and so improve patient outcomes.
3. Booking.com: AI scaling for e-commerce personalization
Personalization is essential for customer loyalty and interaction in e-commerce. Managing ML deployment over 150 customer-facing applications, Booking.com incorporated MLOps. Through data-driven recommendations, this strategy increased the accuracy of personalization systems, raised customer happiness, and produced better conversion rates.
4. Dell: Data-driven marketing optimization
Dell has implemented the application of machine learning in business marketing to enhance customer engagement and fully maximize campaign performance. Through its collaboration with Persado, Dell tied data analysis to linguistic analyses based on AI to see what tones, terminology, and phrases were most appealing to the various target groups.
As a result of the collaboration, Dell saw a 50% higher click rate and a 22% lift in page views. Now, the company’s email, social, and digital advertising are powered by machine learning, allowing the company to make innovative decisions with data.
5. Tesla: Advancing autonomous driving
One of the most recognized examples of the application of machine learning in business in the automotive industry is Tesla. Semi-autonomous driving functions such as lane centering, adaptive cruise control, and automatic braking all rely on its Autopilot software, which in a unified fashion, requires data from cameras, sensors, and neural networks.
Tesla improves the accuracy and safety of its system over time by continuously gathering training on real-world driving data. It is even looking to use ML in its battery management solutions to optimize performance, make more efficient charging decisions, and extend battery life as part of enhanced efficiency and sustainability goals.
Future trends of AI and Machine Learning in business
The application of machine learning in business will be used more throughout sectors as technology develops, therefore allowing quicker, more scalable innovation. Some main trends influencing machine learning with business applications now and in the next few years are listed below:
Generative AI expansion: Beyond words, generative models now produce images, movies, and music, therefore fueling personalization, automation, and content efficiency.
Smaller language models (SLMs): Compact, affordable models enable mobile, IoT, and localized business uses of artificial intelligence.
Quantum and edge computing: With their immediate computing power, quantum force, when combined with edge processing, will enhance speed and accuracy while also aiding in real-time decision-making in critical industries.
Automated and no-code ML: AutoML and no-code platforms will accelerate business and modeling innovation while reducing waste and cost by accelerating the build and deployment of machine learning models.
Multimodal reinforcement learning: Systems that use combinations of visual, text and/or audio inputs will be able to tackle complex problem-solving human adaptations.
Ethical and explainable AI: Models that can guarantee transparency, fairness and compliance in decision-making by considering multiple factors in a model.
MLOps adoption: Training, monitoring and scaling MLOps machine learning models will enhance achievable reliability and long-term return on investment.
Conclusion
The application of machine learning in business to propel real, measurable results rather than just being a buzzword has become a reality. But success really relies on having strong foundation data, good, skilled builders, and a clear strategy for implementation. Those who move now will be best positioned to thrive in the future data economy.
Resources
- https://www.adaglobal.com/resources/insights/benefits-of-machine-learning-in-business
- https://coralogix.com/ai-blog/machine-learning-for-business-use-cases-and-5-steps-to-success/
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchenterpriseai/feature/Top-12-machine-learning-use-cases-and-business-applications
https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/machine-learning-use-cases - https://www.intuition.com/machine-learnings-business-impact-by-the-numbers/
- https://www.adaglobal.com/resources/insights/benefits-of-machine-learning-in-business
- https://coralogix.com/ai-blog/machine-learning-for-business-use-cases-and-5-steps-to-success/
- https://integrio.net/blog/technologies-algorithms-used-for-developing-ml-solutions
- https://www.intuition.com/machine-learnings-business-impact-by-the-numbers/
- https://www.adaglobal.com/resources/insights/benefits-of-machine-learning-in-business
- https://research.aimultiple.com/mlops-case-study/
- https://www.projectpro.io/article/machine-learning-case-studies/855









Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter
Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter