Behind seemingly stable applications, old schemas, replicated records, and inconsistent data rules silently restrict scalability and slow down change. Software engineers progressively wonder what data re-engineering in software engineering and why it is now more vital than ever to overcome this concealed difficulty.
Teams can free the complete worth of their software investments, lower technical debt, and increase system dependability by rethinking how data is arranged and used. From a software engineering viewpoint, this article examines data re-engineering more closely, including its function, methods, actual uses, and future developments.
What is data re-engineering in software engineering?
Data re-engineering in software engineering focuses on redesigning and restructuring existing data assets so they remain reliable, consistent, and compatible with modern systems. Within the broader software reengineering process, it does not rebuild data systems from scratch, but rather transforms legacy data into improved structures that integrate smoothly with current software components, enabling better analytics, reporting, and long-term data usability without compromising critical historical value.
What is data re-engineering in software engineering?
Data re-engineering is characterized by several essential concepts:
– Legacy data assessment: To spot quality problems, redundancies, and structural constraints, one must examine current schemas, data types, and dependencies as well as databases.
– Data restructuring and transformation: Enhancing consistency, correctness, and use while maintaining business meaning by means of data cleaning, normalizing, and reorganization.
– Data model renovation: Redefining data models to more clearly represent existing corporate operations, performance requirements, and system design.
– System adaptation: Refactoring or modifying software parts to run effectively with re-engineered data structures.
– Controlled data migration: The transfer of transformed data into fresh storage systems with the least disturbance to current activities.
– Preserving data lineage: Clear insight into how data comes from, changes, and moves over both legacy and contemporary systems.
– Governance, security, and quality controls: Enforcing access restrictions, compliance requirements, and continuous data quality validation throughout the re-engineering project.
The Role of Data Re-engineering in Software Re-engineering
Improvement of code structure or system architecture in software re-engineering projects seldom fixes persistent operational problems on its own. This is why data re-engineering in software engineering plays a central role in guaranteeing software modernization.
Usually, when businesses revamp old systems, move to fresh platforms, or grow apps to manage growing data volume and variety, data re-engineering is needed. Data must be cleaned, validated, standardized, and consolidated during software re-engineering so it can enable new architectures and changing business needs.
Organizations can realize real business and technical advantages by including data re-engineering in software engineering into the general re-engineering initiative:
– Enhanced data accuracy and consistency among all systems
– Superior backing of data-driven decision-making
– More adaptability and scalability for future expansion
– Increased data analysis and reporting efficiency
– Lower data-related technical debt in upgraded systems
For example, a 200-engineer EPC firm struggled with recurring cost overruns because late design changes were not consistently reflected across CAD, BOM, and ERP systems. Data re-engineering standardized data models and synchronization rules, reducing rework and improving cost visibility across projects.
Data Reengineering Use Cases
Data re-engineering in software engineering enables any business to re-engineer its current data and use it for modern use cases that require real-time processing/integration and advanced analytics. The table below contains examples of typical data re-engineering use cases by industry and their business benefits.
| Industry | Use case | Business impact |
| e-Commerce | Customer segmentation and real-time product recommendations | Higher conversion rates and increased customer lifetime value |
| Healthcare | Integration of patient records and predictive diagnostics | Improved patient outcomes and better operational efficiency |
| Finance | Fraud detection and real-time transaction monitoring | Reduced financial losses and stronger compliance |
| Manufactoring | IoT data analysis for predictive maintenance | Minimized downtime and optimized supply chains |
| Marketing | Campaign performance analysis and lead scoring | More targeted outreach and improved ROI |
Some use cases of data re-engineering across different industries
Core Techniques and Approaches to Data Reengineering
Successful data re-engineering requires both practical techniques and clear approaches that define how legacy data is improved and aligned with modern systems. In data re-engineering in software engineering, these techniques focus on fixing data quality and structure issues, while the approaches guide how data changes are carried out within larger modernization initiatives, including major software migration projects.
1. Key Techniques in Data Reengineering
These techniques address common problems found in legacy data and data-related code. Each one contributes to making existing data easier to use, maintain, and scale within data re-engineering in software engineering.
| Technique | Description |
| Data cleaning and standardization | Fixing errors, inconsistencies, and format differences in data. |
| Data modeling and mapping | Redesigning data structures and mapping old schemas to new ones. |
| ETL processes | Extracting data, transforming it, and loading it into target systems. |
| Reverse engineering | Understanding existing data structures and logic in legacy systems. |
| Data enrichment | Adding useful data to improve context and analysis. |
| Code refactoring | Improving data-related code without changing system behavior. |
Techniques used in data re-engineering
2. Key Approaches
These approaches help teams lower risk and guarantee long-term scalability via data re-engineering in software engineering by specifying how data re-engineering is designed and implemented across systems.
| Approach | Description |
| Data restructuring and redesign | Improving data architecture and standardizing definitions. |
| Database migration | Moving data from legacy databases to modern platforms. |
| Data integration | Enabling smooth data sharing between old and new systems. |
| Data flow analysis | Analyzing how data moves and is used within the system. |
| Model-driven re-engineering | Redesigning data using conceptual models and rules. |
| Iterative re-engineering | Modernizing data gradually through controlled changes. |
Approaches to data re-engineering
>>> Read more: Guide on data migration from legacy systems
Related Concepts
To better understand the scope and value of reengineering in software engineering, it is important to place it alongside other closely related concepts commonly used in software modernization initiatives. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they serve different purposes and address different levels of change.
| Data re-engineering | Data migration | Schema migration | ETL | Refactoring | |
| Purpose | Redesign data to support modern systems and business needs | Move data from one system to another | Update or change the database schema | Prepare data for reporting and analytics | Improve internal structure without changing behavior |
| What’s changed? | Data models, data quality rules, relationships, and usage logic | Data location and storage platform | Table structures, columns, constraints | Data format and aggregation for consumption | Code and logic, not data meaning |
| Level of data transformation | High – data is cleaned, restructured, enriched, and aligned with new architectures | Low to medium – structure often remains the same | Medium – schema-level only | Medium – focused on transformation for analysis | Low – data remains unchanged |
| Typical use cases | Legacy system modernization, analytics enablement, platform transformation | Cloud migration, system replacement | DB upgrades, application changes | Data warehouses, BI pipelines | Reducing technical debt in existing applications |
Comparison table of data re-engineering with other related concepts
Practical Steps in a Data Re-engineering Project
To lower risk and guarantee long-term value, a data re-engineering project should follow a systematic and well-thought-out path of implementation. Three main transformation levels – schema conversion, data conversion, and software program conversion. – In theory, define data re-engineering in software engineering. Practically speaking, though, these changes are realized via a series of tangible, iterative actions that help teams from the first evaluation to steady operation.
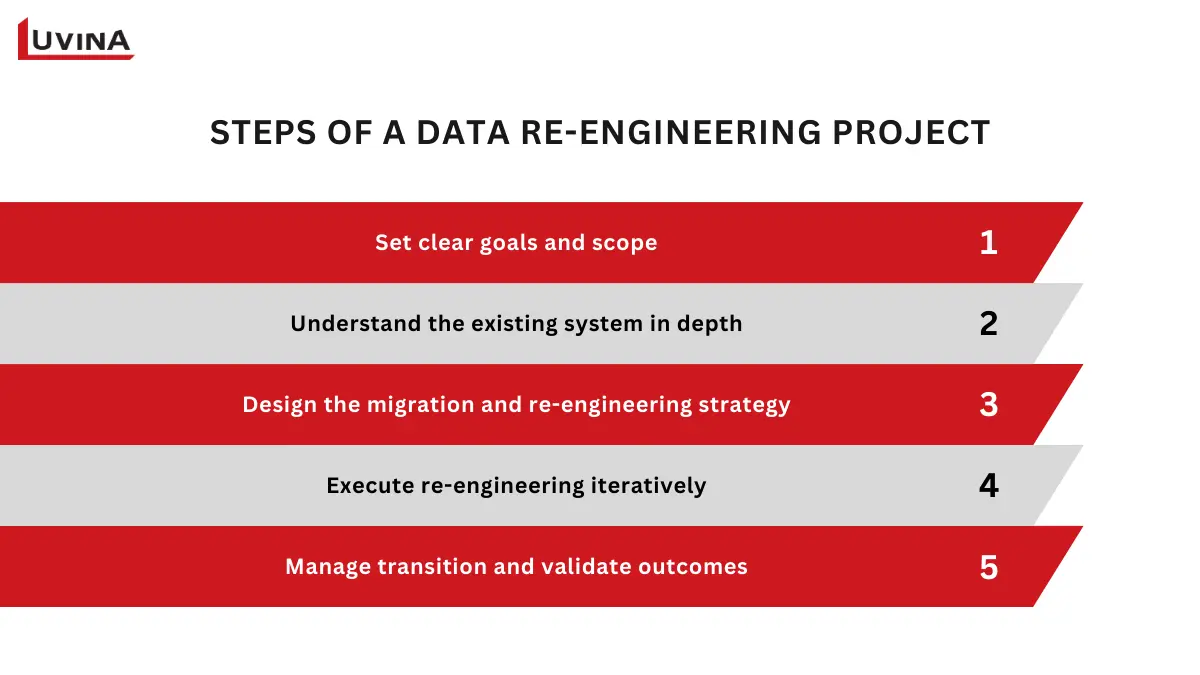
5-step process for executing data re-engineering projects
Step 1- Set clear goals and scope
Teams must specify the issues they want to address, be it subpar data quality, limited scalability, or exorbitant upkeep costs. These objectives steer technical decisions throughout the project and assist in ranking what should be re-engineered first. Data re-engineering initiatives risk expanding out of control or providing little business value without this clarity.
Step 2 – Understand the existing system in depth
This stage includes examining data flows, database schemas, available documentation, and dependency identification between application logic and data. Hidden rules and unrecorded systems are sometimes revealed by reverse engineering methods. Data re-engineering in software engineering starts with this study, which underpins every design change and migration choice.
Step 3 – Design the migration and re-engineering strategy
Teams develop a plan based on the results from systems analysis that specifies target data models, transformation rules, tools, and responsibilities. Choices regarding whether to refactor, rearrange, or gradually modernize data assets guide judgments. This approach also specifies how schema transformation, data conversion, and application conversion will be carried out in line with more general software re-engineering objectives.
Step 4 – Execute re-engineering iteratively
Rather than undertaking a high-risk, one-time transformation, data re-engineering is best done in gradual phases. Data is transformed and validated, schemas are changed, and systems slowly adjust to the new structures. This cyclical approach enables ongoing testing, early detection of problems, and regulated growth. Iteration greatly minimizes operational disturbance in data re-engineering in software engineering.
Step 5 – Manage transition and validate outcomes
Legacies and re-engineered systems can run simultaneously during the transition phase. Before completely converting to the new database, one must meticulously verify data consistency, system performance, and functional behavior. Rigorous testing and monitoring guarantee the stability of company processes and that the re-engineered data underpins current and future system needs.
Tools & Technologies for Data Reengineering
Data re-engineering in software engineering is not handled by a single platform but by a combination of tools, each addressing a specific stage of the re-engineering lifecycle. The table below groups commonly used tools into major categories:
| Tools group | Representative | Role |
| Reverse engineering and system analysis | Decompilers, disassemblers, code analysis tools | Understand legacy data and logic |
| Documentation and modeling | UML modeling tools, documentation platforms | Visualize and document data structures |
| Data engineering and processing | Python, SQL, Scala, Spark, Kafka | Build and process data pipelines |
| Data platforms and operations | Databricks, Snowflake | Store and manage re-engineered data |
| Refactoring and development | IDEs with refactoring features, automated refactoring tools | Restructure code and data logic |
| Migration and integration | Fivetran, Airbyte, and software migration platforms | Move and connect data systems |
| Testing and quality assurance | Unit testing frameworks, static code analysis, and code coverage tools | Ensure data and system reliability |
| Monitoring and optimization | Profiling tools, monitoring, and logging platforms | Maintain performance and stability |
Some essential tools for data re-engineering
Challenges, Risks & Best Practices
Data re-engineering rarely goes according to plan in practical projects. Data re-engineering in software engineering usually uncovers unseen dependencies, quality problems, and organizational constraints that were not readily apparent at first when used at scale. When teams have to juggle modernization objectives with everyday system stability, these difficulties get even more complicated.
Common difficulties are summarized at a high-level below, together with thorough justifications and best-practice solutions for each.
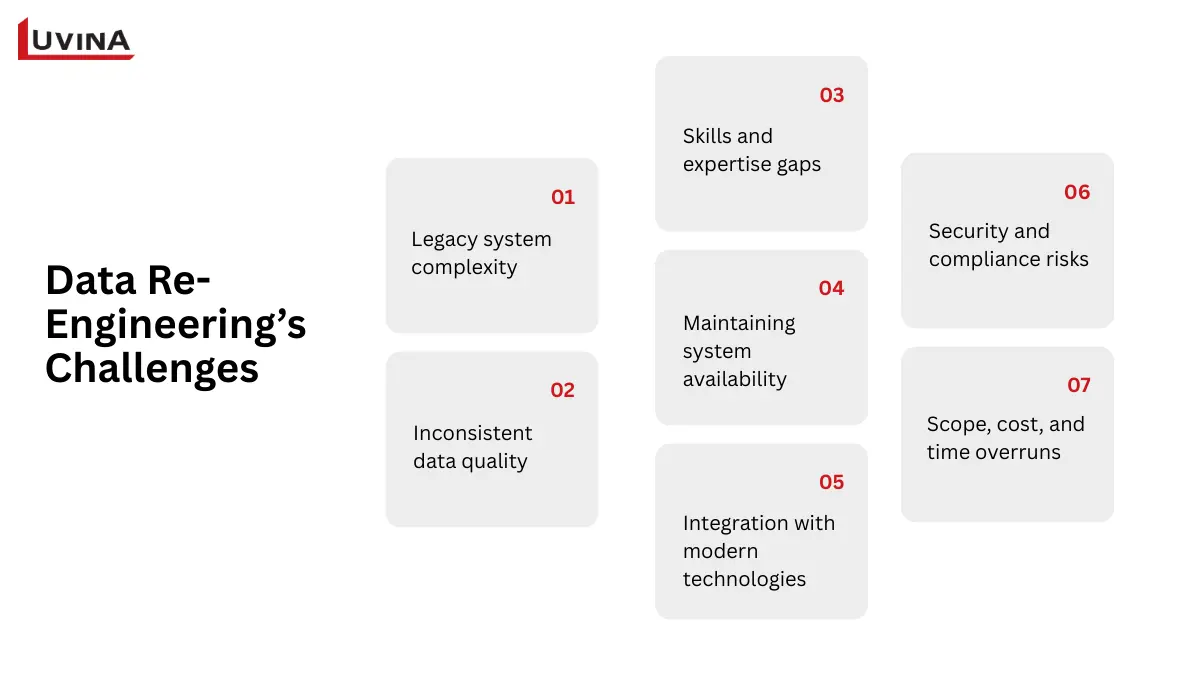
Facing challenges when implementing data re-engineering
Legacy system complexity
Old data structures, unwritten schemas, and tightly linked dependencies abound in legacy systems, therefore complicating analysis and transformation.
Best practice: Before restructuring, use reverse engineering methods to create data models and clearly record data relationships.
Inconsistent data quality
In data re-engineering in software engineering projects, data inconsistencies like duplication, missing values, and unsuitable formats can impair transformation accuracy.
Best practice: Early data profiling and standardization help to find and solve quality problems prior to migration.
Skills and expertise gaps
Effective data reengineering demands familiarity with contemporary data architectures as well as legacy systems, which several teams lack.
Best practice: To minimize reliance on limited expertise, integrate cross-functional teams with automation technologies.
Maintaining system availability
While data systems are being revamped, several businesses cannot afford downtime.
Best practice: To guarantee operational continuity, best practice calls for phased execution, parallel systems, and progressive cutoff techniques.
Integration with modern technologies
Rebuilt data has to interface perfectly with APIs, analytics solutions, and cloud services.
Best practice: Modular data layers and clear interfaces are the best design for integration and future scalability.
Security and compliance risks
Increased exposure to security threats and regulatory concerns in data reengineering projects in software engineering comes from data movement and transformation.
Best practice: Across all data pipelines, put strong access restrictions, data masking, and continuous monitoring into action.
Scope, cost, and time overruns
Scope creep and delays can result from hidden dependencies and underestimated complexity.
Best practice: Take an iterative one with well-defined goals, frequent evaluations, and quantifiable results.
Measuring Success: KPIs & Metrics
To evaluate whether data re-engineering delivers real value, teams should focus on a compact set of KPIs that reflect data quality, system stability, delivery efficiency, and business impact. Tracking too many overlapping metrics often adds noise rather than insight, especially in large-scale data re-engineering in software engineering initiatives.
| KPI group | Included metrics | What does it measure? |
| Delivery speed | Cycle time, lead time for changes, deployment frequency | How quickly do data changes move from design to production |
| Data and system Quality | Defect rate, code quality, code coverage | Reliability and correctness of re-engineered data assets |
| Change stability | Change failure rate (CFR), code churn | Risk introduced by data and schema changes |
| System reliability | MTTR, MTBF, average downtime | Resilience of data platforms after re-engineering |
| Flow efficiency | Cumulative flow, throughput | Smoothness and balance of data engineering workloads |
| Cost and resource Efficiency | Effort allocation, capacity utilization | How effectively engineering resources are used |
| Delivery predictability | Project completion rate, release burndown | Ability to meet data re-engineering milestones |
| Stakeholder impact | Developer experience, customer satisfaction | Sustainability and business value of the initiative |
Key KPIs and metrics for measuring success
Future Trends in Data Reengineering
Data re-engineering in software engineering is more and more shaped by automation, cloud-first design, and the need for quicker, more governed data distribution instead of just data restructuring.
– Data engineering processes are more automated; CI/CD, monitoring, and operational discipline built into data pipelines to achieve this.
– Cloud-native and ELT-first designs: Cloud solutions and ELT models now serve by default to allow for scalable storage, in-warehouse transformations, and quicker iteration.
– Real-time and event-driven data processing: Low-latency analytics and near real-time decision-making increasingly benefit from streaming pipelines.
– Governance by design: Built directly into reengineered data systems are data lineage, access control, and compliance with privacy rules.
– AI-enabled data workflows: AI and machine learning are enabling automation in data preparation and driving more sophisticated analytics applications in AI-enabled data workflows.
– Distributed data architectures: Data mesh and data fabric techniques are starting to be used in major businesses to increase ownership and scalability.
– Self-service analytics enablement: Data reengineering projects now concentrate on accurate, well-modeled data readily usable by business users.
FAQ
1. What are the biggest risks in data re-engineering projects?
Data loss, system downtime, and misalignment with business requirements are the most common risks.
2. Is data re-engineering the same as data transformation?
No. Data transformation is only one activity within data re-engineering in software engineering, which also covers restructuring, optimization, and integration.
3. When should a company consider data re-engineering instead of incremental fixes?
When legacy data structures block scalability, performance, or integration with modern systems, data re-engineering in software engineering becomes a more sustainable option.
4. Does data re-engineering require rebuilding the entire system?
Not necessarily. It can be executed incrementally, focusing only on critical datasets and pipelines.
Conclusion
SQL and NoSQL are complementary, not competing technologies.
The best choice depends on how your data evolves, how your Modernizing data assets, enhancing reliability, and matching legacy systems with present corporate and technical needs are all made possible through data re-engineering in software engineering.
Data re-engineering helps lower technical debt, improve data quality, and allow for easier integration with contemporary architectures when used with well-defined goals, the proper tools, and reasonable execution plans. More importantly, it helps to guarantee that information stays a strategic resource instead of an increasing obstacle.
Successful data re-engineering is a long-term investment in system sustainability, operating efficiency, and the capacity of the company to grow and change in a data-driven environment.
Glossaries
Data re-engineering: The process of redesigning and restructuring existing data systems to improve quality, performance, and compatibility with modern architectures.
Legacy system: An older data or software system that is still in use but built with outdated technologies, often difficult to maintain or integrate.
Reverse engineering: The practice of analyzing existing systems or data structures to understand their design, logic, and behavior when documentation is limited or missing.
ETL/ ELT: Data integration approaches where data is extracted, transformed, and loaded (ETL), or extracted, loaded, then transformed inside the target system (ELT).
Resources
- https://medium.com/@tvs_next/how-to-reengineer-data-to-make-better-decisions-16c8d1b1363a
- https://www.dremio.com/wiki/data-re-engineering/
- https://sixthsense.rakuten.com/blog/Top-Data-Engineering-Concepts-and-Architectures-You-Need-to-Know
- https://www.cloudera.com/resources/faqs/data-engineering.html
- https://www.eicta.iitk.ac.in/knowledge-hub/data-science/future-of-data-engineering-trends-and-predictions
- https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/65207
- https://mobidev.biz/blog/how-to-build-effective-software-reengineering-strategy#h3
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/4000826_Strategies_for_data_reengineering
- https://jellyfish.co/blog/engineering-kpis/
- https://weje.io/blog/software-re-engineering









Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter
Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter