In today’s digital era, managing IT security threats stands as an imperative cornerstone in safeguarding organizational assets and ensuring operational continuity. As cyber threats continue to evolve in complexity and frequency, a proactive approach to IT security risk management becomes paramount. Welcome to our comprehensive guide on Navigating IT Security Threats, where we delve into the critical aspects of risk management in the ever-changing landscape of cybersecurity. Throughout this guide, we’ll explore key strategies, best practices, and actionable insights designed to fortify your defenses and mitigate potential risks. Join us as we navigate through the essentials of securing your digital infrastructure and combating emerging threats.

Defining IT Security Threat Management
Understanding the landscape of IT security threats involves acknowledging the dynamic and multifaceted nature of contemporary cyber risks. From sophisticated phishing attacks and ransomware to data breaches and insider threats, the spectrum of potential dangers is vast and continually evolving. These threats not only compromise sensitive data but also pose severe disruptions to business operations, tarnishing reputations and incurring substantial financial losses.
Identifying the need for proactive threat management is essential in mitigating these risks. Reactive approaches are no longer sufficient in combating the agility and sophistication of modern cyber threats. Proactive threat management involves staying ahead of potential risks by implementing robust security measures, conducting regular assessments, and fostering a culture of vigilance within an organization. Embracing a proactive stance empowers businesses to anticipate, prevent, and swiftly respond to looming security threats, ultimately fortifying their resilience in the face of ever-evolving cyber dangers.
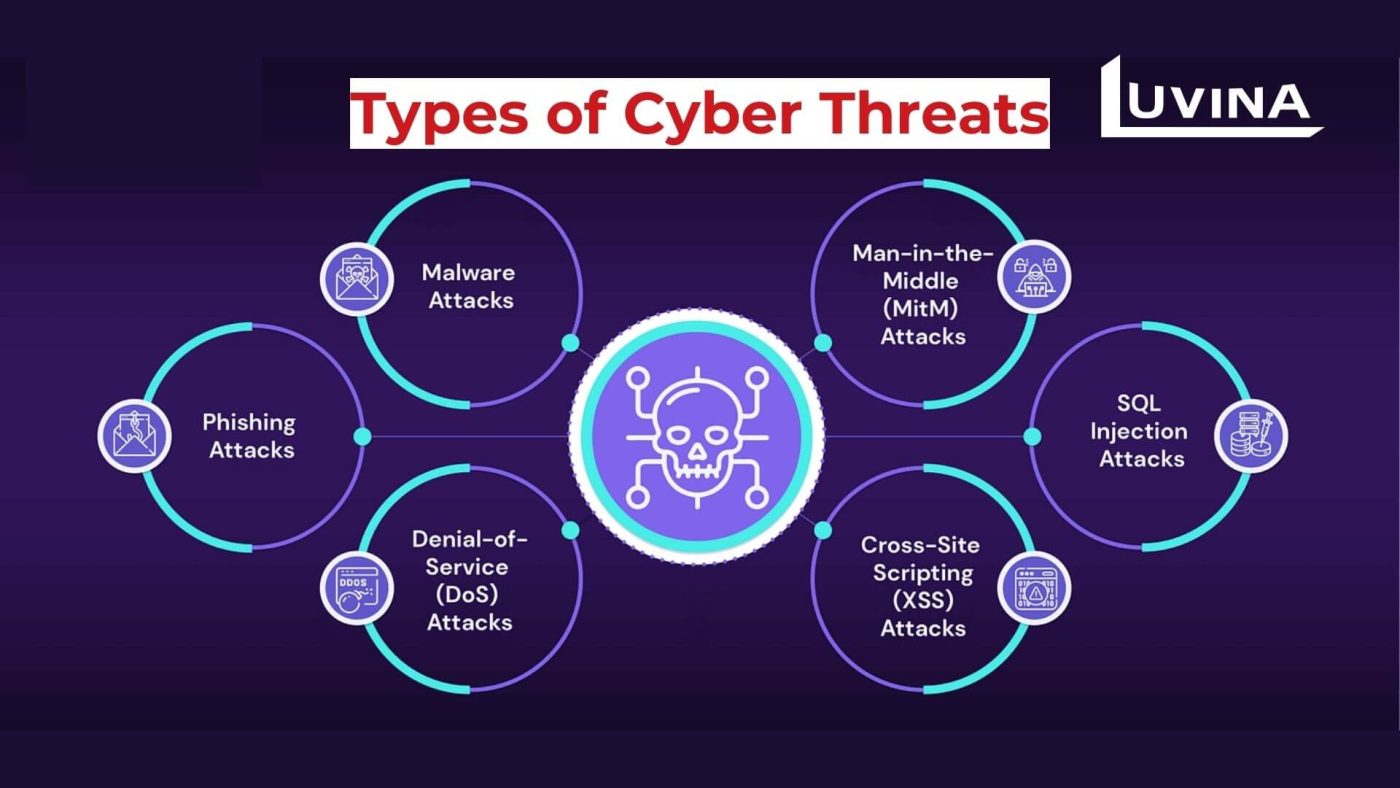
Strategies for IT Security and Risk Management
Strategies for effective IT Security and Risk Management encompass several crucial steps aimed at fortifying an organization’s defense against potential threats:
1. Developing a Risk Management Framework
Establishing a robust risk management framework involves outlining clear objectives, defining risk tolerance levels, and implementing structured methodologies to identify, assess, and mitigate risks. This framework serves as a guideline for systematically managing risks, ensuring a proactive approach to security.
2. Prioritizing and Categorizing IT Security Risks
Categorizing risks based on their severity, potential impact, and likelihood of occurrence helps in prioritizing mitigation efforts. By classifying risks such as high, medium, or low impact, organizations can allocate resources efficiently, focusing on addressing critical vulnerabilities that pose significant threats to their systems and data. This approach ensures that efforts are concentrated where they can have the most substantial impact on reducing risk.
Managed IT Services: Strengthening Security Measures
Managed IT Services play a pivotal role in fortifying an organization’s security measures by leveraging specialized expertise, cutting-edge technologies, and round-the-clock vigilance. Their contribution to mitigating security threats is multifaceted:

1. Leveraging Managed Services for Enhanced Security
Managed IT Security Services providers offer a suite of security-focused solutions, including continuous monitoring, threat detection, and incident response capabilities. Their expertise spans various areas like network security, endpoint protection, data encryption, and compliance management, providing organizations with comprehensive security coverage.
2. Role of Managed Services in Mitigating Security Threats
These services act as a proactive defense mechanism against evolving cyber threats. By employing sophisticated tools and methodologies, managed service providers constantly monitor networks, detect anomalies or potential breaches, and respond swiftly to security incidents. Their proactive approach helps in identifying and neutralizing threats before they escalate, reducing the likelihood of successful cyber attacks and minimizing potential damage to systems and data. Additionally, managed services offer regular updates, patch management, and compliance adherence, ensuring a robust security posture aligned with industry standards and best practices.
IT Security Vulnerability Management
IT Security Vulnerability Management is crucial in maintaining a resilient security posture within an organization:
1. Importance of Identifying and Addressing Vulnerabilities
Identifying vulnerabilities is essential as they represent potential entry points for cyber threats. Addressing these weaknesses prevents exploitation by malicious actors, safeguarding systems, networks, and sensitive data. It’s crucial to proactively manage vulnerabilities to mitigate risks and prevent potential security breaches or system compromises.
2. Strategies for Vulnerability Assessment and Management
Implementing a robust vulnerability management program involves continuous assessment, prioritization, and remediation. This includes conducting regular vulnerability scans and assessments using automated tools to identify weaknesses in systems, applications, and infrastructure. Once vulnerabilities are identified, prioritization based on severity and potential impact guides the remediation process. Timely patching, system updates, configuration changes, and implementing security best practices are crucial steps in managing vulnerabilities effectively. Additionally, ongoing monitoring and periodic reassessment ensure that the IT environment remains resilient against emerging threats.
Incident Management in IT Security
Incident Management in IT Security is pivotal for effectively responding to and mitigating the impact of security incidents:

1. Understanding and Preparing for Security Incidents:
Organizations must comprehend the types of security incidents they might face, such as data breaches, malware attacks, or unauthorized access attempts. Preparing involves creating incident response plans, defining roles and responsibilities, establishing communication protocols, and conducting regular drills or simulations to ensure readiness. Understanding potential threats and having a well-defined incident response framework helps in swift and efficient mitigation when incidents occur.
2. Incident Response and Resolution Strategies:
Once a security incident is detected, a predefined incident response plan guides the organization’s actions. This includes immediate containment of the incident, forensics analysis to understand the scope and impact, notifying relevant stakeholders, and initiating remediation steps. An effective incident response strategy involves coordinated efforts among IT teams, legal departments, management, and relevant authorities (if necessary). Learning from incidents is crucial for improving response strategies, updating security measures, and preventing similar incidents in the future. Constant refinement and adaptation of incident response plans ensure an organization’s ability to handle and recover from security incidents efficiently.
>> Also read: Top 10 IT Security Companies
Implementation and Best Practices
Key considerations when implementing risk management strategies involve several critical aspects:
1. Comprehensive Risk Assessment
Start by conducting a thorough risk assessment across the organization’s systems, networks, and data. Identify potential threats, vulnerabilities, and their potential impact on business operations. Understanding the organization’s risk landscape forms the foundation for effective risk management.
2. Establish Clear Objectives and Goals
Define clear objectives and goals for risk management aligned with the organization’s overall business objectives. This involves setting risk tolerance levels, outlining specific risk management strategies, and determining acceptable levels of risk in different areas of operation.
3. Engage Stakeholders
Collaboration and communication among stakeholders are crucial. Involve key stakeholders from different departments – IT, legal, compliance, finance – to ensure a comprehensive understanding of risks and establish a unified approach to risk management.
4. Adopt a Layered Security Approach
Implement a multi-layered security approach that includes preventive, detective, and corrective measures. This strategy ensures that security measures cover various aspects, including network security, endpoint protection, access controls, and data encryption, among others.
5. Regular Monitoring and Review
Continuously monitor the risk landscape to identify changes or emerging threats. Regularly review and update risk management strategies and measures to adapt to evolving risks and technology changes. Consistent evaluation ensures that risk management remains effective and aligned with the organization’s changing needs and industry standards.
>> Also read: Enhancing IT Security Operations
Conclusion
Robust IT security and risk management are pivotal shields safeguarding organizations against evolving threats in today’s digital landscape. Proactive measures in fortifying defenses, conducting comprehensive risk assessments, and adopting multi-layered security approaches are imperative to mitigate potential risks effectively. Embracing continual vigilance, adaptation, and enhancement in security measures is crucial as IT security landscapes continuously evolve. Organizations must stay agile, regularly reassess their security postures, and foster a culture of resilience to tackle emerging threats and ensure sustained protection of valuable assets and operations.









Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter
Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter