Studies show that students retain 75% of what they experience in VR, compared to only 10% from reading. The application of AR and VR in education is revolutionizing the learning experience. The interactive and experiential learning provided by these immersive technologies enhances understanding and recall. While there are some issues around their impact—especially on younger learners—research suggests that carefully designed AR and VR can provide safe, effective, and highly interactive learning experiences. But what are the real benefits? What are the obstacles to be overcome? And how can teachers maximize the use of AR and VR in education? Let’s discuss these points in detail.
The Key Differences Between VR and AR in Education
There is a massive revolution taking place in the education world with the incorporation of new technology. Among these, AR VR technology in education is quickly becoming a platform to underpin the way students learn and interact with study material. Two such new technologies being leveraged across most institutions of learning are augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), offering unique avenues for an immersive learning experience.
Although both possess the capability of creating interactive, engaging environments, they differ enormously in the way they affect students’ interaction with their environment. To help clarify the distinctions between AR and VR, we’ll first take a quick look at how these technologies compare across key features and their applications in education.
| Aspect | Augmented reality (AR) | Virtual Reality (VR) |
| Environment interaction | Enhances the real world with digital elements | Immerses users in a completely digital environment |
| Devices used | Smartphones, tablets, and AR glasses | Specialized hardware, such as VR headsets and motion sensors |
| User experience | Overlays digital information onto physical objects or environments | Completely replaces the physical world with a virtual one |
| Learning applications | Interactive textbooks, virtual tours, and hands-on learning | Virtual labs, historical explorations, and immersive simulations |
| Technology focus | Integrates both worlds | Focuses solely on creating a virtual environment |
Augmented Reality in the education sector
AR in education technology is transforming how students interact with the world around them by overlaying digital content in physical environments. Unlike Virtual Reality, which immerses users in entirely new worlds, augmented reality in education and training enhances real-world experiences.
For example, using a device’s camera, students can see interactive educational content superimposed onto textbooks, maps, or historical sites. This form of immersive learning offers immediate and relevant information that complements physical learning objects, such as interactive textbooks or virtual tours of historical locations.
This approach enriches learning, making it more contextualized, effective, and enjoyable. The use of AR VR in education offers immersive learning experiences that are accessible and affordable to learning institutions.
Use of Virtual Reality in education
On the other hand, virtual reality (VR) offers a fully immersive educational experience by transporting students into entirely new digital worlds. With the help of VR headsets and motion sensors, students can engage with environments and situations that would otherwise be inaccessible.
For instance, VR can mimic virtual laboratories, recreate complex scientific experiments, or allow students to walk through history. This kind of virtual and augmented reality in education approach provides interactive, experiential learning experiences that are highly interactive and not restricted by spatial limitations.

VR immerses students in a 360-degree world, creating a powerful experiential learning tool. As augmented and virtual reality in education continues to evolve, VR will stand at the front line of changing learning.
Key Differences Between AR and VR in Education
The basic difference between AR and VR in education is how they approach immersing and interacting with the user and the surroundings. AR VR education has complementary and contrasting roles to play. AR extends the real world by projecting digital data onto real-world objects, thereby increasing students’ interaction with their real-world environment. It is hardware-based, like smartphones or tablets, which are easily accessible and affordable by classrooms.
On the other hand, VR creates an entirely virtual environment, cutting people off from the real world and putting them into an entirely new virtual one. VR relies on dedicated hardware such as headsets and motion sensors, which are more expensive and less portable than AR hardware. While AR can be used in a variety of environments and is well suited to layering information, VR is ideally suited to simulations where complete immersion is beneficial.
>> Read more: Virtual learning management system
Benefits and Applications of VR and AR in Education
AR and VR are revolutionizing education by making learning more immersive, interactive, and engaging. These technologies provide new opportunities for both students and teachers. These technologies, in which the physical and virtual worlds merge, are transforming the way we experience and interact with the learning content, creating new opportunities for personalized learning as well as experiential learning. Below are some of the most significant benefits and applications of AR VR for education:
- Personalized learning: The use of virtual reality in education makes it possible to customize content by personal needs and facilitates students to progress at their pace. This personalized learning supports different learning styles and independent learning.
- Increased engagement and motivation: Augmented reality in education examples demonstrate how AR can make learning more engaging. Whether it’s through virtual field trips, gamified apps, or interactive simulations, these technologies motivate students to participate actively in their lessons.
- Improved academic performance: Academic work validates that AR and VR’s experience of engagement contributes to better scholarly performance. Interactional and interactive exposure makes classroom teaching more susceptible to memory, for a higher rate of retaining material.
- Simplified complex concepts: Applications of augmented reality in education make abstract concepts more tangible. AR and VR can visualize processes like the movement of electricity or the internal workings of a machine, allowing students to grasp difficult concepts that would be hard to visualize otherwise.
- Enhanced collaboration: Augmented reality in classroom education promotes collaboration among students. Interactive AR lessons allow students to work on group projects together, fostering collaboration and peer learning.
- Virtual field trips and simulations: The use of virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) creates virtual field trips to historical sites or science laboratories. VR also offers simulation training, e.g., performing surgery or flying aircraft, so students have actual-world experience in a safe, controlled setting.
- Interactive textbooks and learning resources: Augmented reality in education sector applications can bring textbooks to life by overlaying 3D models, animations, and interactive elements, converting passive study material into active, engaging content.
- Broader educational access: Augmented reality used in education provides access to experiences that are otherwise inaccessible, like practicing complex procedures or exploring historical events through immersive VR environments. This is particularly valuable in fields like medicine and engineering.

Challenges and Solutions for VR AR in Education
While AR and VR in education yield many groundbreaking benefits, their integration presents many obstacles to overcome to harness the technologies appropriately in school systems. From the costs of implementing these technologies to where new ones are inserted into old-fashioned curriculums, these are some of the most critical challenges and their potential solutions.
1. High costs and limited accessibility
One of the biggest hurdles to the incorporation of augmented reality and education is the expense of the hardware, particularly virtual reality. The expense of VR headsets can be so prohibitive as to be out of reach, particularly for those institutions with smaller budgets. Fortunately, there are affordable alternatives in the form of mobile VR headsets that one can use in conjunction with their smartphone, as well as cloud-based VR systems that do away with the use of costly hardware.
For augmented reality in educational settings, using the available hardware of tablets and smartphones makes AR a more affordable option by maintaining initial investments for schools lower.
2. Learning curve and technological familiarity
Both teachers and students also have anxiety about the curve of learning needed to embrace augmented reality in the classroom. Not many are aware of these technologies, and it is challenging to negotiate cyberspace or interact with digital content. This could slow down the acceptance of AR/VR applications in education. Users have to be made accustomed to the technologies and seamlessly fit them into their learning cycles; therefore, teacher and student training programs as well as user-friendly interfaces are required.
3. Effective curriculum integration
Placing augmented reality on education tools alone is not enough. Teachers have to design lesson plans that blend AR and VR seamlessly into existing curricula. Virtual and augmented experiences have to map to learning objectives and be built to foster exploration and inquiry. One solution is to scaffold learning experiences, enabling students to accumulate knowledge gradually through interactive and immersive content so that it is more applicable to real-life situations.
4. Privacy concerns and data security
The collection of personal data by AR and VR technologies also raises concerns about student privacy. Ensuring proper protection and management of data collected by augmented reality in healthcare education or other education AR/V purposes is critical. The school should adhere to privacy policies and ensure that all the apps used comply with the specified standards for data security and student privacy.
5. Ensuring quality content
The success of VR and AR experiences depends to a large extent on the content. Teachers need to select VR and AR content carefully for use in the classroom to ensure that they are educationally valid and curriculum-based. To help students take advantage of these technologies, information should be current, pertinent, and of appropriate age. For example, augmented reality in medical education and training must provide realistic simulations and real information to ensure the learning process is worthwhile.
Best virtual reality and augmented reality in education examples
The potential of AR and VR in the classroom is expanding at a breakneck pace, and some revolutionary examples are showcasing how these technologies are revolutionizing education. From virtual field trips in class to totally immersive learning, below are some of the most impressive examples of virtual reality in education and how they are revolutionizing the future of education.
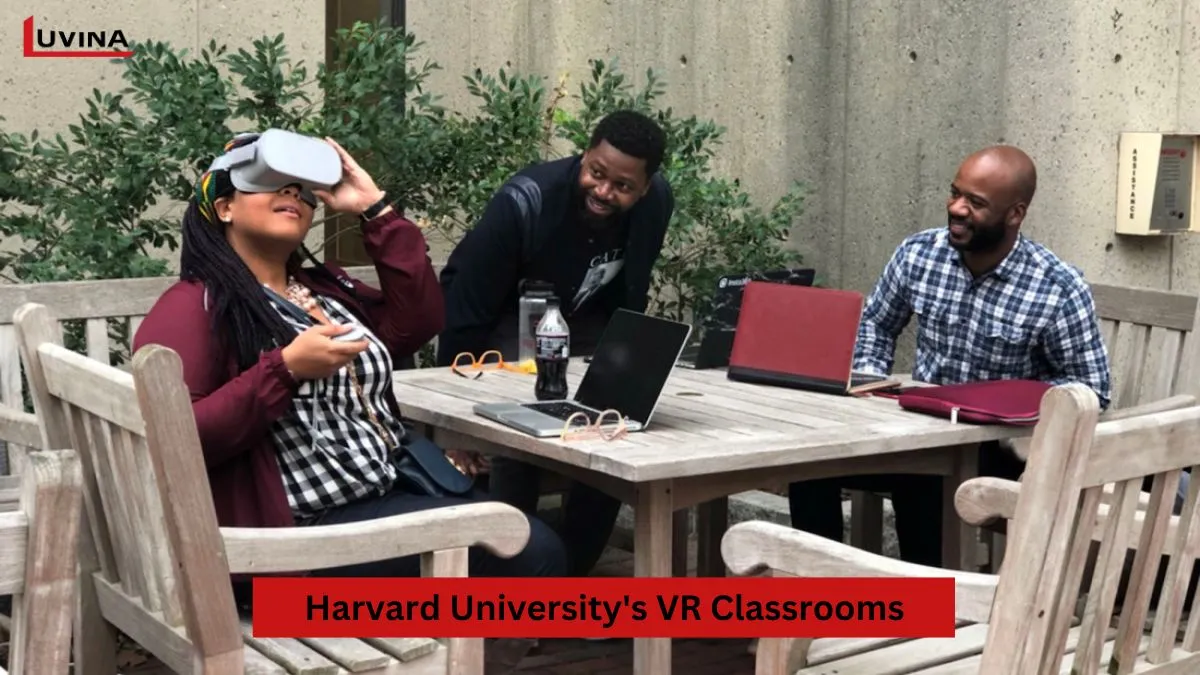
1. Harvard University’s VR Classrooms
Harvard University has embraced the use of augmented reality in education through offering its most beloved computer science course, CS50, in fully immersive VR. Students watch lectures in virtual classrooms from wherever they are, creating an additional level of engagement to virtual education. Harvard’s innovation has attracted over three million students worldwide, confirming the power of AR VR in the classroom to transform traditional learning.

2. 3D Printing and AR at Bader Intermediate School
At Bader Intermediate School in Auckland, the learners are discovering new methods with the use of augmented reality. With the use of AR and 3D printing together, learners can create things in the virtual world and physically print them as objects in reality. Both technologies used together introduce creativity and enable students to understand abstract ideas, and consequently, augmented reality in the classroom is very effective.
3. SkyView App
The SkyView app utilizes AR to make it possible for students to observe the night sky by identifying stars, constellations, and planets. This interactive tool interacts with students when learning astronomy and elicits the power of augmented reality in educational settings through the projection of abstract notions in tangible terms.
4. Microsoft HoloLens: Use of Augmented Reality in Education
Holographic education with Microsoft’s HoloLens is a huge advance in augmented reality healthcare education. Its mixed reality interface lets students learn detailed human anatomy, explore the circulatory system, and even do things with organs as if it’s real and one is indeed in an actual-body simulation. It’s a game changer in augmented reality in medical education and training, offering real-life, interactive simulations for learning by hands.
5. Immersive historical learning with the 1943 Berlin Blitz
The immersive VR experience “1943 Berlin Blitz in 360°,” produced by Immersive VR Education, allows students to experience a real-life historical event. Immersive VR Education’s “1943 Berlin Blitz in 360°” virtual experience places students inside a realistic history situation. The AR/VR lesson demonstrates students firsthand what being on the battlefield is like during wartime, fully immersed, a demonstration of bringing history to life for students where textbooks cannot.
6. Virtual field trips with Google Expeditions
Google Expeditions allows teachers to take students on virtual field trips to locations like Mount Everest or the Louvre Museum, providing immersive educational experiences that would be impossible to organize in real life. This is a prime example of AR and VR in the classroom, giving students access to global landmarks from the safety and comfort of their classroom.

7. Improving public speaking with virtual speech
VirtualSpeech offers an innovative VR experience that allows students to practice public speaking in front of a virtual audience. By replicating real-life situations, students can refine their presentation skills in a controlled, virtual environment, demonstrating the power of VR for soft skills training and boosting confidence.
8. Steam’s VR museum of fine art
Using augmented reality in education has never been more immersive than with the VR Museum of Fine Art. This platform allows students to explore world-class artwork, such as the Mona Lisa, up close and personal, without the limitations of crowds or barriers. It’s a unique way to integrate art history with technology, enriching the learning experience.
9. Training law enforcement with VR
Police departments are using VR simulations to train officers on how to handle riots, arrests, and other critical situations. This use of AR VR classrooms for professional training demonstrates how VR can be applied outside traditional classrooms to enhance practical skills and ensure safer communities.
10. Language learning with Mondly VR
Mondly’s VR language learning software provides an immersive environment where students can engage in real conversations with virtual characters, making language learning more interactive and effective. This example shows the potential of augmented reality in education sector by helping students learn and practice languages in realistic settings.
>> Read more: Customize virtual LMS: Flexible eLearning solutions
Conclusion
In essence, AR and VR in education are powerful instruments changing how we learn and teach; they are more than just fads. VR AR education allows students to investigate difficult ideas and interact with material in ways formerly unthinkable using immersive and interactive experiences. These tools could help to remove obstacles to learning so that education is more engaging, available, and useful to pupils worldwide.
The road to adopting AR/VR learning in mainstream education is not paved. However, the phenomenal benefits that these technologies bring to learning—ranging from personalization and flexibility to the provocation of curiosity and enhanced understanding—far outweigh the above drawbacks. Going forward, we must continue innovating, conducting research, and collaborating to fully harness the power of VR and AR in learning.
Related Posts:









Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter
Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter