Japan has earned international renown for high quality, and Japanese quality standards have found their way into industries well outside of the country. Since Japan ranks among the top 20 on the World Economic Forum’s Global Competitiveness Index for innovation and business sophistication (2025), it shouldn’t be surprising that companies everywhere compete to adopt these high standards. But how is it that these quality systems are so potent? In this article, we’ll break down the key quality management systems, and the impact of Japan’s quality-driven approach to foreign companies. Keep reading to discover!
Top 3 Key Quality Management Systems in Japan
Maintaining product quality and business performance has been a high priority in Japan for decades. Japanese quality standards are founded on well-organized quality management systems that promote innovation, enhance global competitiveness, and reassure consumers. Below, we introduce 3 key systems that define Japan’s quality management system: Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS), ISO Standards, and Total Quality Management (TQM).
1. Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS)
Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS) provides a scientific way of ensuring quality, safety, and efficiency in industries from electronics to construction. JIS, which was first introduced in 1949, has played a huge role in industrial growth in Japan through specific standards for materials, sizes, and performance criteria. JIS meets domestic requirements in Japan with relatively strict standards. It is a prestigious certification highly regarded worldwide.
Products certified by JIS are awarded the JIS Mark, a seal of quality certification. The standards are continuously updated to catch up with technological advancements and global regulations, including ISO and IEC standards. This integration allows Japanese companies to remain competitive in overseas markets without compromising on Japanese quality standards.
2. ISO Standards
Japan adopts ISO standards proactively to be compliant with the global platform and to maintain high-quality manufacturing processes. International standards make companies more efficient, customer-oriented, and environmentally sustainable. The most critical standards are ISO 9001 for quality management, ISO 14001 for environmental responsibility, and ISO 45001 for workplace safety.
In addition to general quality standards, Japan also applies industry-specific ISO certifications. For example, IATF 16949 supports automotive manufacturing, ISO/IEC 27001 ensures information security, and ISO 22000 regulates food safety.
3. Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management (TQM) is Japanese business culture’s fundamental philosophy, with emphasis on continuous improvement and collective responsibility. Toyota and Sony are some of the corporations that have successfully embraced TQM and instilled all their levels with a passion for quality. The system prioritizes customer satisfaction while encouraging incremental process improvement under Japanese quality standards.
TQM focuses on principles such as Kaizen (constant improvement), workers’ involvement, and data-driven decision-making. Rather than fixing individual errors, it optimizes whole processes to enhance effectiveness and eliminate waste.
Japanese Quality Standards by Industry
Japan has set rigorous Japanese quality standards in various industries to ensure product safety, efficiency, and competitiveness on the world stage. Every industry has guidelines that address certain challenges and technological advancements.
1. Japan’s software quality standards
Japan has adopted sophisticated software quality standards to ensure the reliability and effectiveness of software products. The frameworks blend global best practices with industry-specific requirements, having stringent standards for software engineering and IT development.

Key software quality standards in Japan:
- – ISO/IEC Standards: Includes ISO/IEC 25010 (software quality models) and ISO/IEC 12207 (software lifecycle processes).
There are also tight regulations in Japan on software utilized for key industries. For example:
- – Medical Software Regulations: The PMD Act (Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act) ensures compliance with international safety standards like GHTF (Global Harmonization Task Force).
- – Industry-Specific Standards: Tailored software quality requirements apply to fields like automotive and electronics to ensure precision and reliability.
2. Automotive industry quality standards
Japan’s automotive sector is renowned for its meticulous quality control, driven by stringent Japanese quality standards tailored to vehicle safety, performance, and innovation. These regulations ensure that automobiles manufactured in Japan maintain superior reliability and durability.

Key frameworks include:
- – Japanese Automotive Standards Organization (JASO): Sets technical requirements for automotive components such as engine oils and lubricants.
- – Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS): Regulates automotive technologies, ensuring consistency and quality in production.
- – IATF 16949: An international quality management standard specifically for the automotive industry. It sets requirements for a Quality Management System (QMS) to ensure continuous improvement, defect prevention, and waste reduction in the supply chain. It is based on ISO 9001 but includes additional requirements tailored to the automotive sector.
3. Food industry quality standards
Japan enforces strict food quality control to provide consumer protection, product wholesomeness, and compliance with global food standards. They regulate food production at every stage from farm to packaging, including cultivation, processing, labeling, and distribution.

Key food industry standards in Japan:
- – Japanese Agricultural Standards (JAS): Established by the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries to regulate product quality, production processes, and distribution.
- – Food Sanitation Act: Governs food safety legislation, including laws on additives, contaminants, and labeling.
- – Organic JAS: Verifies organic farm products and processed foods according to Japan’s organic agricultural and production standards.
- – Food Labeling Standards: Ensures transparency in allergen information, nutritional information, and expiration date.
Step-by-Step JIS Certification Process for Foreign Companies
Foreign companies wishing to acquire JIS certification must go through a methodical evaluation process to demonstrate that their products meet Japan’s stringent standards of safety, performance, and reliability. Certification not only enhances credibility within the Japanese market but also shows conformity with globally accepted quality assurance systems.
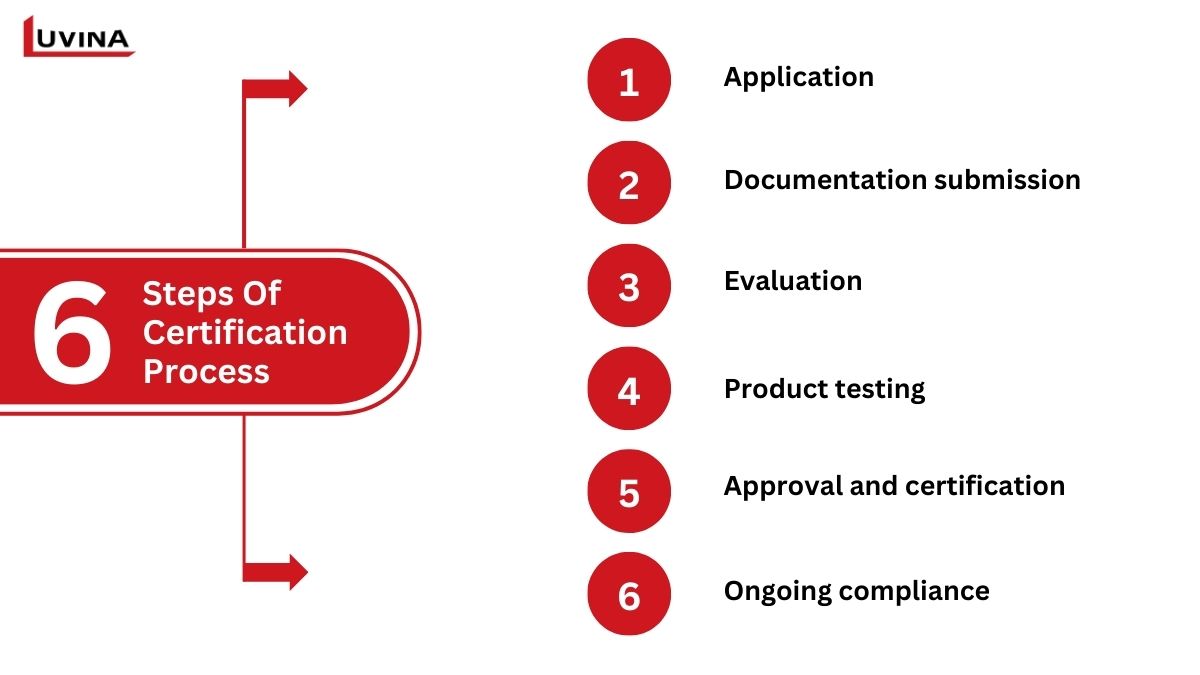
The certification process consists of several key steps:
- Application: Foreign companies must apply through a recognized certification body that undertakes testing of their products against JIS standards.
- Documentation submission: Organizations are required to submit complete documentation, which may include guides for quality management, product descriptions, and testing reports. Such documents need to be translated into Japanese for the majority of them.
- Evaluation: The certifying agencies review the documents presented and audit factories to verify compliance with JIS standards and ISO/IEC 17065 requirements.
- Product testing: Testing can be conducted either at the certification body’s laboratory or at the applicant’s facility, according to agreement, to fulfill Japanese quality standards.
- Approval and certification: The company is certified and eligible to label the product with the JIS Mark if the product meets all the requirements.
- Ongoing compliance: Periodically, certified companies must be audited to maintain their certification and demonstrate ongoing compliance with JIS standards.
Foreign companies aiming to obtain JIS certification should work with local consultants or legal representatives familiar with Japan’s regulatory framework to ensure a smooth certification process.
Conclusion
Lastly, familiarity with Japanese quality standards is required for any business firm that wants to flourish in Japan’s highly competitive business environment. Given Japan’s image of precision and consistency, adherence to these standards can help businesses gain the confidence and support of Japanese consumers.
With a long history of working with Japanese counterparts, Luvina is quite familiar with such requirements and is ready to assist global businesses navigate the complexities of this nation. Whether as a newly built company or as an established firm, Luvina can be capable of aiding you in terms of adhering to such specifications as well as promoting your visibility in such a lucrative economy. Call Luvina today for personalized guidance and to begin the process of entering Japan’s business environment successfully.









Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter
Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter