Manufacturing is entering a new age driven by generative AI in manufacturing. The U.S. GenAI manufacturing market exceeded USD 70M in 2022 and is projected to surpass USD 2.1B by 2032, a 41% CAGR that captures the rapid change of manufacturers.
From detecting high-value uses and conquering deployment difficulties to creating a sustainable roadmap, this guide outlines practical best practices manufacturers can adopt to implement GenAI effectively.
Let’s jump in if you want to know how these technologies transform processes and enable genuine performance increases.
Key use-cases of generative AI in manufacturing
The emergence of generative AI in manufacturing has moved the industry away from classical automation workflows towards responsive, adaptable, and exceptionally inventive workflows. Below are the leading real generative AI applications in manufacturing:
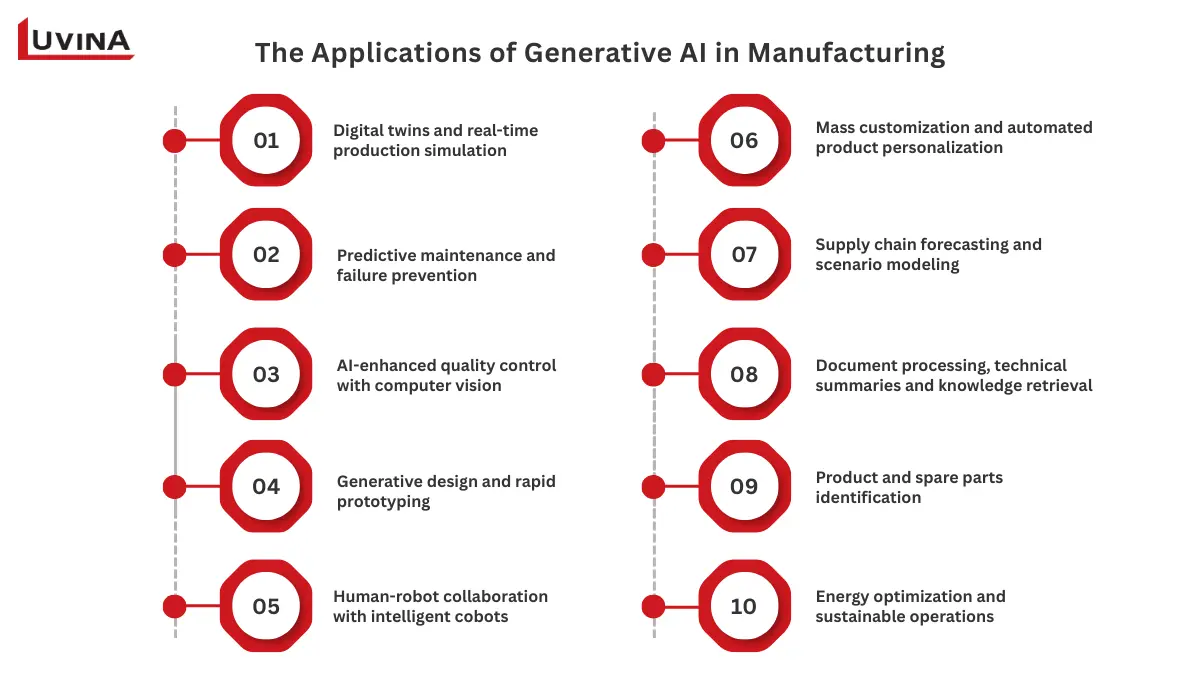
1. Digital twins and real-time production simulation
Digital twin technology creates virtual replicas of equipment, production lines, and even entire plants using IoT sensors, PLC data, and advanced AI models. This is one of the most significant applications of GenAI in manufacturing. These digital worlds enable manufacturers to evaluate production modifications, simulate disturbances, and forecast performance without contacting the physical asset by means of real-time data updating.
2. Predictive maintenance and failure prevention
Predictive maintenance is a major application of GenAI. AI analyzes real-time sensor data to detect subtle machine anomalies before they appear as failures. It provides early warning, such as vibration changes or rising temperatures, allowing operators to schedule repairs and avoid unplanned downtime.
This is a departure from the former “wait until it breaks” model, and reinforces a brand new idea of a proactive, self-monitoring system that eliminates or greatly reduces unplanned downtime.
3. AI-enhanced quality control with computer vision
For quality inspection, generative AI in manufacturing enhances the process considerably, especially when combined with computer vision systems to inspect every product in milliseconds and identify even the tiniest defects. The AI-powered inspection systems can indicate a misalignment, surface defect, or assembly issue faster and more reliably than human inspectors or traditional rule/method-based systems.
This delicate aspect of inspection is made viable because, by utilizing prior knowledge from examining thousands of defects from numerous suppliers, the AI can identify anomalies immediately and stop defective products at the earliest indication, preventing defective products from proceeding down the line.
4. Generative design and rapid prototyping
One of the most revolutionary methods of generative AI in manufacturing, speeding product development, is generative design. Then generates several optimized design options within seconds by AI that examines restrictions, including materials, performance targets, durability demands, and cost constraints.
Rather than spending weeks waiting for each prototype iteration, engineers can quickly assess a broad range of ideas at once, allowing R&D cycles to happen more quickly and with less wasted materials. This gives manufacturers of products in the automotive, aerospace, and electronics industries the ability to get better products to market faster, with better performance and reduced risk of producing them.
5. Human-robot collaboration with intelligent cobots
Using cobots with generative AI in manufacturing also adds adaptive intelligence on the factory floor that allows for safe and intelligent collaboration with human workers. Cobots learn from their environments, change actions in real-time, and work on highly precise, physically demanding, or repetitive tasks without impeding lines. This partnership increases productivity, lowers job injuries, and enables employees to concentrate on innovative and strategic work.
Demonstrating how generative AI use cases in manufacturing improve both human potential and automation capacity inside the same workflow, cobots are an essential component of the future intelligent factory paradigm.
6. Mass customization and automated product personalization
One of the most breakthrough AI solutions for manufacturing is the ability to produce personalized products at mass-production speed. AI interprets customer preferences, generates tailored configurations, and translates them into manufacturable instructions, all without disrupting production flow. It adapts designs in real time, ensuring that each custom order fits quality standards and system constraints.
7. Supply chain forecasting and scenario modeling
An additional intricate facet of generative AI in manufacturing presents itself in terms of supply chain optimization, in which generative AI evaluates supplier performance, logistical constraints, seasonal demand trends, and external factors to simulate real-time planning scenarios. Generative AI will forecast stockouts or shortages, suggest stock modifications, and determine optimal shipping routes. Generative artificial intelligence also simplifies purchasing communication and order management, therefore enhancing cooperation between suppliers and distributors.
8. Document processing, technical summaries, and knowledge retrieval
Technical documentation is especially important in manufacturing settings; generative AI in manufacturing streamlines this by rapidly handling manuals, schematics, maintenance records, and compliance reports. Natural-language inquiries made by engineers can yield quick summaries or certain data gleaned from lengthy papers.
Key insights from artificial intelligence include knowledge repository organization and the reduction of the often-needed manual search, cross-reference, or interpretation of complicated documents. Faster problem-solving, more effective training, and easier communication throughout production, maintenance, and engineering teams are all supported here.
9. Product and spare parts identification
Staff can characterize a component based on appearance or purpose rather than needing precise codes or names. The artificial intelligence deciphers the description, locates appropriate items, recommends appropriate substitutions, or examines submitted photos to determine the right component. This speeds up maintenance chores, lowers ordering errors, and lowers downtime during repairs.
10. Energy optimization and sustainable operations
With generative AI in manufacturing, energy management gets much more effective as AI identifies hidden inefficiencies by monitoring consumption patterns across machines, HVAC systems, and production environments. It finds pointless loads, suggests best operating times, and offers practical ideas to cut electricity bills and minimize trash.
By reducing the carbon footprint, this ongoing development strategy enables manufacturers to reduce energy expenses and promotes sustainable production objectives. The system continually recomputes and modifies such that every watt is properly used without compromising output.
Business benefits of generative AI in manufacturing
By adopting generative AI in manufacturing, organizations can not only enhance productivity, minimize costs, strengthen safety, and boost sustainability, but they can also capitalize on the following primary business benefits associated with generative AI within operations:
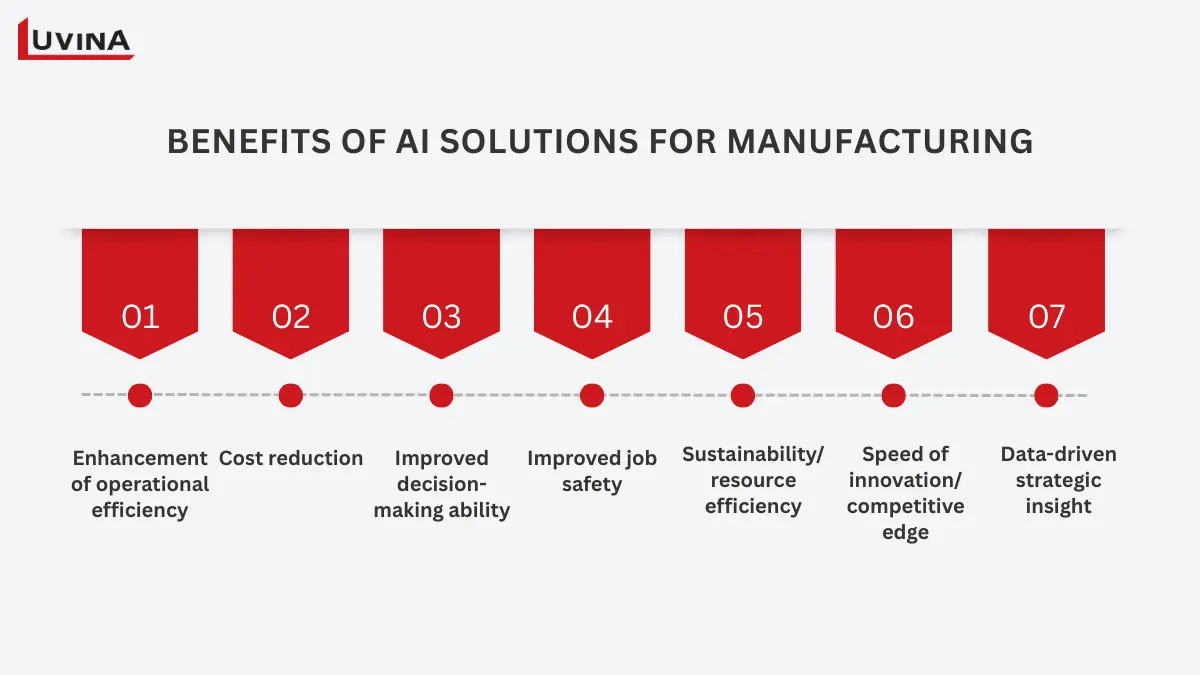
– Enhancement of operational efficiency: By leveraging automation and AI capabilities to precisely perform repetitive tasks, generative AI within manufacturing minimizes the risk of human error and enables continuous improvement to manufacturing processes.
– Cost reduction: Generative AI in manufacturing drives cost savings by minimizing labor and operational costs through predictive maintenance, automated and AI quality checks, and energy optimization; reducing material waste and eliminating unplanned downtime.
– Improved decision-making ability: Managing real-time data and utilizing digital twin simulations enables management to anticipate implications of scenarios, review scenarios for production, and identify opportunities to reduce risk before changes are made.
– Improved job safety: AI-enhanced cobots and monitored systems can take over risky jobs or jobs requiring ergonomics that can generate risk for injury in the workplace.
– Sustainability/resource efficiency: AI-enabled algorithms and systems with smart sensors reduce energy use, help in waste minimization, and maximize business resources.
– Speed of innovation/competitive edge: Generative AI in manufacturing greatly increases the speed of design and prototyping, generating multiple variations of the product in seconds, allowing a team to review ideas and move concepts forward, with a general perception of a reduction in the time to get a product to market of better quality.
– Data-driven strategic insight: AI continually analyzes vast amounts of operating data to identify trends, drive improved processes, and inform production decisions. Companies become more agile, allowing better forecasting and rapid adjustment to the market conditions.
Key considerations before implementing GenAI in manufacturing
Using generative AI in manufacturing effectively calls for strategic insight. The major factors to be considered for a seamless and efficient deployment are as follows:
– Determine ROI: Evaluate whether a GenAI use case will solve a substantial problem and provide quantifiable ROI, therefore guaranteeing that resources are directed to projects with actual commercial effect.
– Evaluate data availability and quality: Find out if your organization possesses sufficient, accurate, and trusted data to support generative AI in manufacturing use cases, and whether or not there continues to be new data available to improve AI performance.
– Automate lower-value tasks first: Focus on leveraging AI for heavy-lifting, time-consuming tasks so that employees can engage in more valuable analysis and decision-making versus manual data processing.
– Plan for scalability: While expecting possible workforce opposition, make sure you have the talent, capital, and change management approaches required to grow AI solutions for manufacturing throughout corporate divisions.
– Guarantee ethical use of data: Since the performance of generative artificial intelligence is directly correlated to the integrity and ethical nature of the data it is utilizing, employ clear, unbiased, and trusted data.
– Make the data easy to use: Employees need to be able to readily learn and utilize the AI solutions.
– Implement across the enterprise: Create GenAI solutions capable of being implemented across multiple departments, with flexibility for varying levels of digital capability, and to create uniformity throughout the enterprise.
– Plan for continuous improvement: Think about how a GenAI application may grow with more high-quality data to make sure it gets more and more useful for the company, planning for continuous improvement.
Challenges, risks, and best practices for deploying Gen AI in manufacturing
Implementing generative AI in manufacturing presents enormous promise, but it also presents several problems that businesses have to overcome to succeed. The primary obstacles and realistic remedies for using artificial intelligence effectively in industrial activities are listed here.
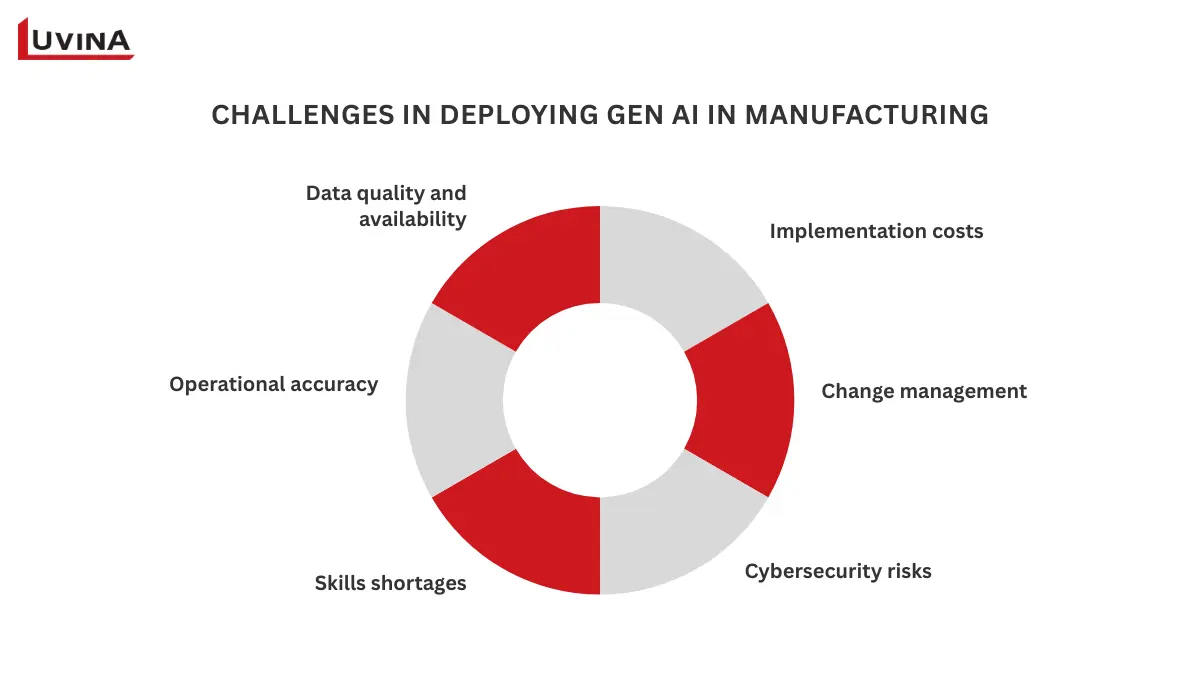
Data quality and availability
Although producers often have problems with imperfect or inconsistent datasets, artificial intelligence systems depend on accurate, organized, and pertinent data. This may cause erratic ideas in fields like predictive maintenance or quality control.
Solution: Automate sensor and manufacturing line data collection and repeatedly check and clean datasets.
Operational accuracy
While some generative artificial intelligence systems are still growing and may not have the dependability required for important operations, production environments need great accuracy.
Solution: Pilot projects concentrating on reduced-risk activities like workflow optimization or non-critical equipment monitoring can confirm performance before full-scale implementation.
Skills shortages
Companies find it challenging to fully use generative artificial intelligence in manufacturing because there are not enough data science, machine learning, and artificial intelligence experts available.
Solution: Provide operations, engineers, and managers with workforce training programs emphasizing real-world applications of AI solutions for manufacturing in everyday activities.
Cybersecurity risks
Increased digital connectivity created by artificial intelligence integration provides new vulnerabilities that may impact sensitive manufacturing processes.
Solution: To secure processes underpinned by AI, implement modern cybersecurity solutions, including network monitoring, access controls, and regular audits.
Change management
Employees could object to using artificial intelligence out of worry about job stability or fresh processes, therefore slowing down its adoption.
Solution: Clearly communicate, include staff in artificial intelligence planning, and provide retraining to show how generative AI in industrial systems enhances instead of replacing human labor.
Implementation costs
Implementing artificial intelligence comes with high levels of technology and infrastructure investment, which can be a hurdle for small to mid-sized manufacturers.
Solution: Start with high-value, low-risk pilots such as predictive maintenance, track the results, and then scale slowly based on ROI.
Roadmap for getting started
Implementing generative AI in manufacturing is not a trivial matter or a quick process. Following this path helps to minimize risk and aptly embed artificial intelligence into the operations of the manufacturer.
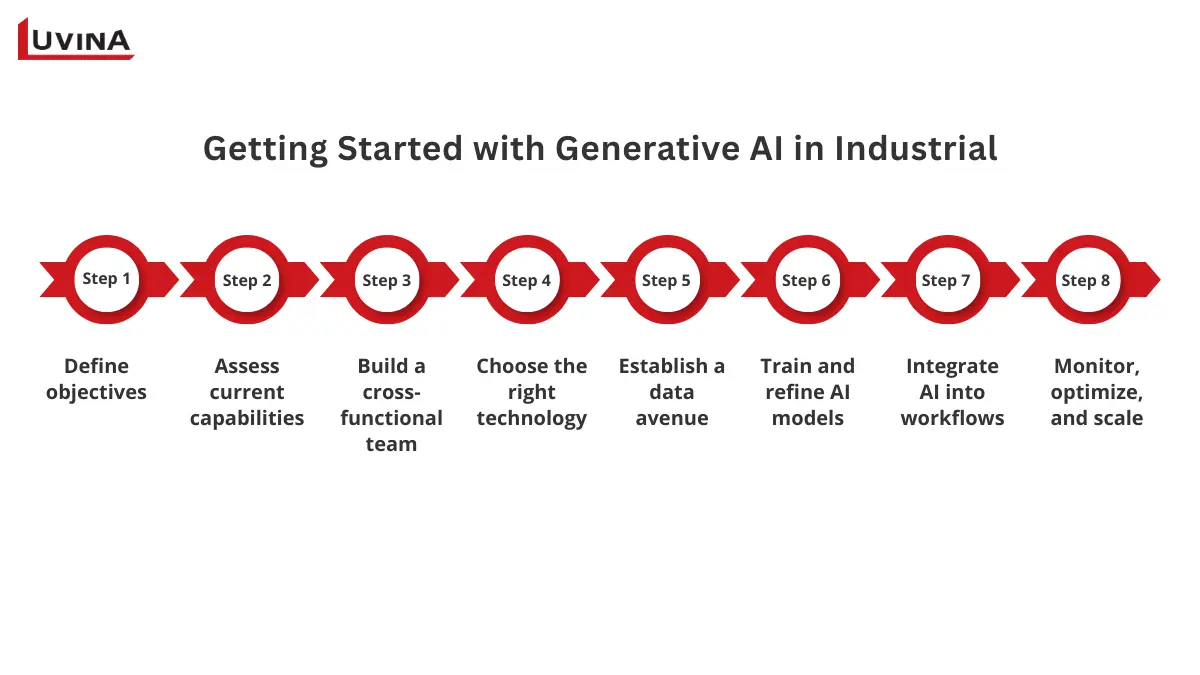
Step 1: Define objectives
Clearly define which problems you want to solve (reducing downtime, increasing quality of the product, increasing complexity of supply chains,…). Including people from several departments helps to guarantee congruence with the general company plan. The efficacy of generative AI in manufacturing projects is assessed using quantifiable goals like lowering lead time by 20% or raising defect detection by 30%.
Step 2: Assess current capabilities
Evaluate your technology stack, data sources and quality, and workforce capabilities now. Verify if the sensors, logging systems, and ERP systems available to you provide the right and sufficient data, because generative AI in manufacturing depends on good data quality.
Step 3: Build a cross-functional team
Working with AI requires engagement outside of IT. Find a way to engage functions such as operations management, subject matter experts, engineers, and data science professionals. This important engagement establishes affinity to solutions are not only technically viable but also practical in production environments. Foster a team environment by promoting open discussion, setting proper expectations, and encouraging engagement from the shop floor to drive iteration of models for AI.
Step 4: Choose the right technology
Choose the AI platforms and tools that fit all the goals you are aiming for, along with how you are planning to scale and use existing systems. Ease of integration, user-friendliness, and level of vendor support are all considerations. Pilot a number of the AI solutions for manufacturing on the shop floor to assess which fits best. While some factors are self-explanatory, some considerations may include cloud deployment versus on-premise, evaluation of any IoT sensor, and whether the AI solution supports simulations for digital twins.
Step 5: Establish a data avenue
There should be a clear idea of how to collect, store, curate, and govern your company’s data. Aggregating data from hardware (machines), sensors, production logs, and supply chain systems ensures that the AI models will be developed on accurate, high-quality data. Models should be validated on an ongoing basis to ensure that good data is used.
Step 6: Train and refine AI models
Historical and diverse datasets to train your generative AI in industrial applications. Each team should continue to refine the models based on a defined set of performance assessment metrics and input from the stakeholders. Ultimately, well-trained AI models should be able to anticipate the failure of machinery, optimize workflows, and potentially design new products.
Step 7: Integrate AI into workflows
Create user-friendly interfaces and give hands-on instruction so staff members can confidently engage with artificial intelligence systems. Real-time insights are made possible by Link AI’s output to production planning, inventory management, and quality control systems.
Beyond technical preparation, is your company culturally ready? Encourage awareness of artificial intelligence advantages; deal with staff worries; and offer continuous training. Only when teams use artificial intelligence tools daily, understand and trust it can adoption be successful. Generative AI in manufacturing promises long-lasting effects only in a society willing to adapt.
Step 8: Monitor, optimize, and scale
Generative AI in manufacturing implementation is continuous. Regularly keep an eye on indicators like quality improvements, lowering of downtime, and production. Change models and processes as needed using fresh information to improve forecasts. Increase effective use cases across departments over time to maximize ROI.
Future trends of AI-integrated factory
Future factories will boost production, efficiency, and inventiveness by fusing human imagination with artificial intelligence. Important trends affecting generative AI in manufacturing include:
– Assistance systems: Generative artificial intelligence automates activities like PLC code generation and records expert knowledge, freeing engineers to concentrate on difficult problem-solving.
– Enhanced recommendation systems: Real-time instructions and spare part suggestions provided by AI-driven advice for predictive maintenance let even less-experienced engineers to effectively maintain equipment.
– Autonomous systems: Robots that move supplies and production equipment can operate without help. They read instructions and perform tasks with minimal human supervision.
– Hyper-personalization and product development: Producers can make extremely personalized products to customer preferences and current use through mass customization and fast prototyping produced by generative AI in manufacturing contexts.
– Integration with new technologies: AI allows near real-time decisions, virtual testing of designs, and process optimization that combines work with edge computing, digital twins, and augmented reality.placing them.
Conclusion
By now, you should be able to grasp and see the changes that generative AI in manufacturing can bring to your operations.
Ready to adopt GenAI at scale? Talk to Luvina’s industrial AI experts to build your production-ready GenAI roadmap.
Resources
- https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/ai-in-manufacturing
- https://appinventiv.com/blog/generative-ai-in-manufacturing/
- https://frostbrowntodd.com/using-generative-ai-in-manufacturing-three-key-considerations/
- https://www.leewayhertz.com/generative-ai-for-manufacturing/#How-can-you-transform-manufacturing-operations-with-ZBrain
- https://customerthink.com/how-to-implement-generative-ai-in-manufacturing-a-step-by-step-approach/
- https://www.pwc.com/us/en/industries/industrial-products/library/gen-ai-in-manufacturing.html









Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter
Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter