Typically, when customers use and purchase financial services, they dModern factories operate at high speed, with tighter supply chains and rising expectations for real-time visibility. Yet many manufacturers still rely on disconnected systems, manual reporting, and delayed decision-making on the shop floor.
This gap is exactly where a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) becomes essential. Understanding what is MES manufacturing execution system is no longer a technical question. It is a strategic one for modern manufacturing.
This guide explains:
- What MES means in manufacturing
- How MES works on the shop floor
- Core MES functions and benefits
- Industries that rely on MES
- How to choose and implement MES successfully
Let’s explore!
What is MES manufacturing execution system?
A Manufacturing Execution System (MES) is software that monitors, controls, and records manufacturing operations in real time on the shop floor. In simple terms, MES manages the transformation of raw materials into finished products, based on actual production conditions rather than static plans.
From a systems perspective, MES acts as the execution layer between ERP and shop-floor operations:
– ERP defines what and how much to produce
– MES manages how production is actually executed
MES collects real-time data from machines, operators, and sensors to provide an accurate, live view of production status. This capability defines what is mes manufacturing execution system truly means in practice.
Why MES matters in modern manufacturing?
For many decision-makers, asking what MES mean is really about business value.
In today’s fiercely competitive and rapidly changing world, this is where understanding what is MES manufacturing execution system is becomes critical. Driven by industrial automation, regulatory requirements, and the comparatively low cost of MES deployment, industry predictions emphasize this significance; the worldwide MES market is expected to reach US$41.78 billion by 2032.
Manufacturers today face:
– Shorter production cycles
– Higher quality and compliance demands
– Increasing automation and data complexity
MES is important since it changes production from a reactive operation into one propelled by information. MES enables producers to track production with precision, spot bottlenecks early, minimize unexpected downtime, and react rapidly with data-backed decisions by offering real-time visibility into it.
For example, a leading automotive manufacturer achieved a 15% increase in throughput and reduced downtime after implementing a comprehensive MES to monitor production and optimize resources in real time. Another major pharmaceutical company reduced lead times by 30% and cut inventory costs by 20% by using MES to improve scheduling and inventory management. This is exactly what MES manufacturing execution system is and what it can do for your business.
On the production floor, MES links processes, people, and machines. One system helps with quality control, resource allocation, inventory tracking, and production scheduling. Thus, producers have the means to boost profitability and productivity independent of the sector or plant size.
Core functions and components of MES
To gain insight into what is MES manufacturing execution system, it is important to examine some of the primary activities which define the way MES works on the factory floor. The primary model of MES contains various activities to enable manufacturing execution systems (MES). All of these activities can be traced back to the MESA International Framework, which has been used for many years throughout different industries as a reference for the capabilities that MES have.
In essence, they explain what MES stands for in manufacturing from a functional perspective. The table below summarizes the key MES functions and their roles in modern manufacturing.
| Core function | Description |
| Operations/ Detailed scheduling | Plans and sequences production activities based on priorities, capacity, and constraints, helping manufacturers understand what is MES manufacturing execution system in real-world production planning. |
| Resource allocation and status | Tracks real-time status of machines, materials, and labour for effective allocation. |
| Dispatching production units | Manages and adjusts production tasks in real time on the shop floor. |
| Document control | Controls and distributes approved work instructions and production documents. |
| Data collection and acquisition | Collects real-time data from equipment, systems, and operators. |
| Labor management | Manages workforce availability, skills, and authorizations. |
| Quality management | Monitors quality checks, deviations, and compliance requirements. |
| Process management | Controls and monitors the production process from order release to completion, reinforcing that is MES manufacturing execution system is a core layer between planning and execution. |
| Maintenance management | Supports preventive and corrective maintenance to reduce downtime. |
| Product tracking and genealogy | Tracks product flow and full production history for traceability. |
| Performance analysis | Analyzes production performance against targets for continuous improvement. |
Key features of a MES system
These functions explain MES’s meaning as an execution-focused system rather than a planning tool.
How MES works: from raw material to finished product
Understanding how MES functions throughout the whole production life cycle helps you to appreciate what is MES manufacturing execution system is in practice. Real-time control on the shop floor, MES constantly gathers, analyzes, and uses data to direct production processes from raw material intake to finished products.

Learn how it works to understand what is MES manufacturing execution system
Step 1: Data collection on the shop floor
MES starts by gathering real-time data from several sources, including equipment, sensors, people, and networked systems such as ERP or PLM. Machine condition, production rates, inventory levels, and quality indicators are all covered by this data. Gathering data straight from the source guarantees that MES manufacturing execution guarantees that choices concerning production are based on actual shop-floor conditions rather than assumptions.
Step 2: Data integration and contextualization
To provide a single view of the manufacturing environment, all gathered data is analyzed and integrated throughout the MES platform. This stage is essential to understanding what an MES manufacturing execution system is, as MES processing turns raw data into a meaningful production context by connecting machines, materials, people, and orders into a single operating image that is always current.
Step 3: Production scheduling and planning
MES creates thorough production schedules based on production orders received from upper-level systems. Order priorities, machine capacity, material availability, and labour limitations are all taken into consideration in these schedules to guarantee practical and doable implementation plans.
Step 4: Work order execution and tracking
This is where what is MES manufacturing execution system becomes most visible on the shop floor. MES gives specific operators or workstations work orders along with explicit directions, specifications, and paperwork. The system follows every order in real time as work advances, updates work-in-progress status, and immediately flags delays or deviations.
Step 5: Machine and equipment integration
Sensors, PLCs, or established communication protocols link the system directly to equipment on the shop floor. This enables MES to immediately address equipment problems, automatically gather production data, and monitor machine performance.
Step 6: Quality control and compliance
Throughout production, critical data such as measurements, test results, and inspection outcomes are continuously recorded. This capability highlights what is MES manufacturing execution system is in practice, as MES helps preserve consistent product quality by enforcing standard quality processes, triggering alerts when issues arise, and logging data for traceability and analysis.
Step 7: Material and inventory tracking
MES tracks materials throughout the whole production process. This includes monitoring inventory, assisting with restocking as necessary, and ensuring that you have what you need when you need it. Time and material waste are reduced as a result.
Step 8: Performance analysis and reporting
At last, MES produces dashboards, reports, and performance indicators using real-time production analysis. These ideas promote informed decision-making and ongoing development. Manufacturers now understand what MES manufacturing execution system provides: controlled execution, total visibility, and data-driven manufacturing from beginning to end.
This end-to-end visibility defines what is MES manufacturing execution system in action.
Key benefits of implementing MES
The following manufacturing execution system benefits draw attention to the reasons why producers trying to increase quality, cost management, and efficiency have come to view MES as a vital solution.
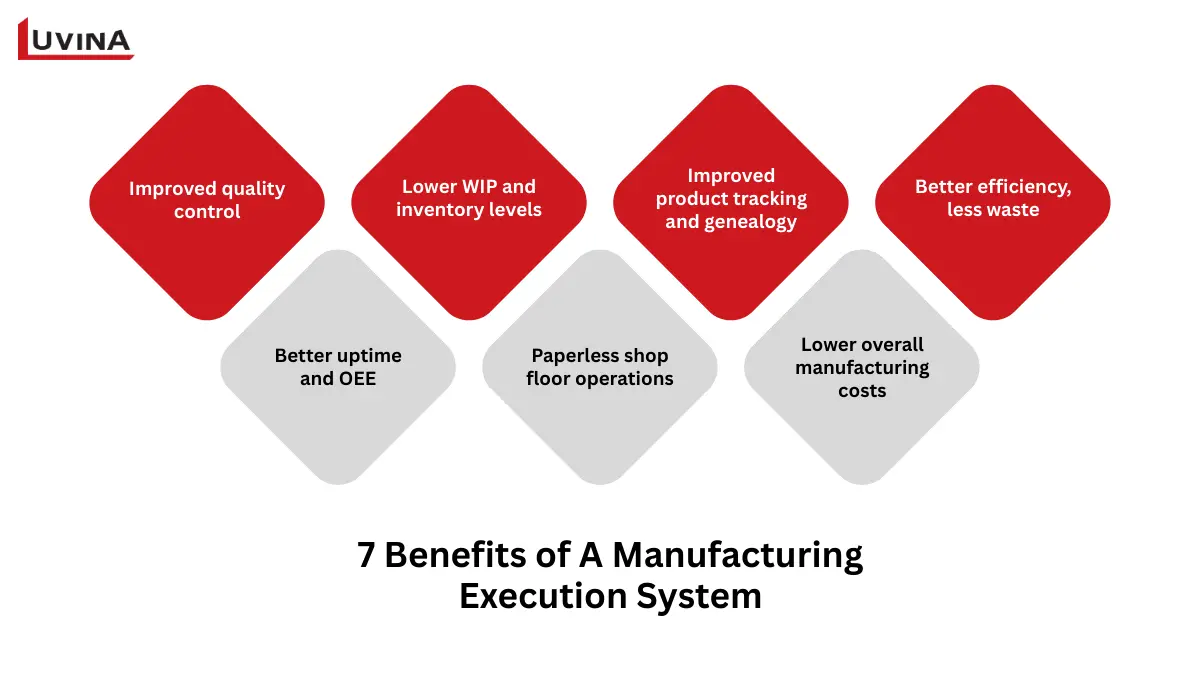
The MES system plays a major role in daily manufacturing operations
– Improved quality control: With real-time quality data and alerts, what is MES manufacturing execution system enables manufacturers to stop production immediately when defects or deviations are detected, thereby minimizing scrap, rework, and quality-related waste.
– Better uptime and OEE: An MES balances labor, materials, and equipment to make realistic production schedules that mesh with maintenance.
– Lower WIP and inventory levels: MES regularly updates inventory records for scrap, nonconforming materials, and production output. This real-time visibility reflects what is MES manufacturing execution system is in action, helping reduce surplus raw materials and work-in-progress inventories while lowering costs related to handling, storage, and inventory monitoring.
– Paperless shop floor operations: Reduce human error and guarantee quick availability of production data across linked systems by substituting manual paper with digital workflows.
– Improved product tracking and genealogy: Supporting complete traceability and simplifying regulatory compliance, what is MES manufacturing execution system connects products and batches with their process and quality data across the whole production cycle.
– Lower overall manufacturing costs: MES can cut manufacturing costs by making workflows smoother and reducing mistakes. This can lower costs related to things like labor, inventory, batch issues, delays, communication problems, waste, and following rules.
– Better efficiency, less waste: Seeing what’s happening as it happens lets manufacturers spot problems fast and fix them. This boosts efficiency and cuts down on waste and fixing mistakes.
These benefits explain why MES is widely adopted across regulated and high-volume industries.
Industries that commonly use MES
The most frequent users of MES are regulated sectors since they have to meet stringent governmental and industry requirements, including:
– Pharmaceuticals
– Food and beverage
– Medical devices
– Biotechnology
– Aeronautics and aerospace
– Defense
These industries all need to carefully track materials, steps, and what they produce in the end. A manufacturing execution system helps make sure everyone follows the same procedures. It also grabs production and quality info as it happens and keeps records right for checks.
Beyond daily operations, MES is important in scenarios where fast and precise recalls are required. By linking each product or batch to its full production history, manufacturers gain the visibility and control that define what is MES manufacturing execution system in regulated environments – enabling quick issue isolation, reduced compliance risk, and stronger protection of brand reputation.
Examples of MES systems and vendor typologies
To clearly understand what is MES manufacturing execution system in real-world operations and see how it works, checking out its use in different industries is a good idea. The main MES functions remain the same, but how each industry utilises them varies based on the products they manufacture, the regulations they must comply with, and what’s most important to them. Here are some MES system examples. They give you an idea of how MES fits into different manufacturing contexts.
| Industry | Description | Example MES applications |
| Automotive | Manages high-volume, multi-stage assembly with strict sequencing and quality control, clearly demonstrating what is MES manufacturing execution system is in discrete manufacturing environments. | – Track vehicle progress across workstations- Synchronize component availability in real time- Support quality checks and recall management |
| Pharmaceuticals | Enforces regulatory compliance and batch integrity throughout production. | – Manage electronic batch records (EBR)- Track batch genealogy and GMP compliance- Capture real-time quality data aligned with what is MES manufacturing execution system in regulated manufacturing |
| Food and beverage | Manages recipe-driven production and food safety controls. | – Track ingredients and lot numbers- Manage recipes and formulations- Support allergen control and food safety compliance |
| Electronics | Controls highly automated and component-intensive manufacturing processes. | – Manage BOMs and component traceability- Integrate with pick-and-place and testing equipment- Monitor equipment performance in real time |
| Aerospace and defence | Supports complex assemblies with strict documentation and traceability needs. | – Track part movement and assembly stages- Manage work orders and inspections- Document compliance with industry regulations |
| Consumer goods (FMCG) | Optimizes fast-paced production with frequent product and packaging changes, highlighting how what is MES manufacturing execution system supports agility at scale. | – Coordinate multiple production lines- Manage packaging variations- Track output, quality, and inventory levels |
| Textile and footwear | Controls flexible, order-based production with high labour involvement. | – Track order progress by process stage- Measure productivity by line and worker- Monitor defect rates and delivery timelines |
| Construction materials and metals | Focuses on process stability, energy use, and batch consistency. | – Track raw material and energy consumption- Monitor furnace and process parameters- Ensure consistent quality across batches |
| Cosmetics and personal care | Requires strict formula control and traceability similar to regulated industries. | – Manage formulations and mixing processes- Track quality by batch- Control labelling, lot numbers, and expiration dates to meet what is MES manufacturing execution system requirements |
Some MES systems examples in different industries
How to choose the right MES for your factory
Manufacturers must first know what is MES manufacturing execution system relates to their own operations to make the right choice when selecting the correct one. Then, to guarantee the system provides actual operational value, producers should assess a well-defined collection of requirements, including functional fit, industry alignment, integration capability, usability, scalability, vendor support, and long-term product vision.
The following are key steps to direct the choice process:

Follow these steps to choose the most suitable MES system
– Determine key business and operational needs: Identify where MES should create the most impact (operator efficiency, traceability, inventory visibility, quality control, or scheduling accuracy) based on a clear understanding of what is MES manufacturing execution system and how it supports shop-floor operations.
– Align MES capabilities with industrial demands: Verify that the system supports your production model and satisfies your requirements.
– Check integration and scalability: Verify perfect integration with ERP, equipment, and shop-floor systems and make sure the MES can scale over lines, factories, and future data volumes – key criteria when assessing what is MES manufacturing execution system beyond basic functionality.
– Evaluate configurability and usability: Choose a solution that operators will find natural, easy to set up, and straightforward to maintain. This is where the MES manufacturing execution system converts into everyday operational value.
– Check how well the vendor delivers and supports: Look at how they put things in place, how fast they roll things out, how good their training is, and the support they give after launch.
– See the product’s future and new ideas: Review the vendor’s long-term plans for Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT), data analytics, and artificial intelligence, ensuring the solution aligns with what is MES manufacturing execution system is today while supporting future smart manufacturing initiatives.
– Confirm with feedback and proof: Use what other customers say, user reviews, and trial projects to check how well it works in the real world before deciding.
Challenges and best practices when implementing MES
Although companies know precisely what is MES manufacturing execution system, they may still have difficulties with cost, integration, personnel, and long-term operation. Understanding what MES mean operationally helps companies forecast hazards early and use the appropriate best techniques to guarantee sustainable value from MES adoption.
The most frequent obstacles encountered when applying MES are listed below, with tested best solutions for each one.
| Challenge | Description | Best practices |
| Complex implementation and system integration | MES must be aligned with existing production processes and integrated with ERP and shop-floor systems. Poor planning can cause delays and operational disruption. | • Implement in phases, starting with critical lines or workshops• Define clear scope, objectives, and timeline early |
| Data integration and data quality issues | Inconsistent master data and weak integration between MES, ERP, and other systems lead to unreliable reports and decisions. | • Standardize data models and integration architecture early• Choose MES with proven ERP and shop-floor connectors |
| Resistance to change and low user adoption | Operators may resist shifting from manual processes to digital MES if the benefits are unclear. | • Conduct role-based training and continuous communication• Involve shop-floor users early in the design process |
| High initial investment cost | MES requires investment beyond software, including infrastructure, implementation, and training. | • Roll out MES in phases to spread costs• Consider cloud-based or SaaS MES to reduce upfront investment |
| Data security and operational reliability | MES handles critical production data, making security and system stability essential. | • Apply standardized integration and data governance• Select MES solutions with strong security and reliable data flows |
| Lack of continuous monitoring and improvement | Treating MES as a one-time project limits long-term value. | • Define KPIs and performance dashboards• Assign clear system ownership and conduct regular reviews |
Key challenges and recommended best practices for implementing MES
MES and the future: Industry 4.0, cloud & IoT integration
Modern producers view the MES manufacturing execution system as a key digital layer that connects equipment, data, and business systems in real time as Industry 4.0 speeds. This change lets MES enable more informed decisions, quicker reactions, and more linked operations throughout the whole manufacturing environment.
Understanding what is MES manufacturing execution system in this future-ready environment means also appreciating its contribution to cloud adoption, IIoT connectivity, and sophisticated analytics. Not just production control, MES is evolving into a tool for ongoing optimization.
Some of the main technological trends influencing the future of MES are:
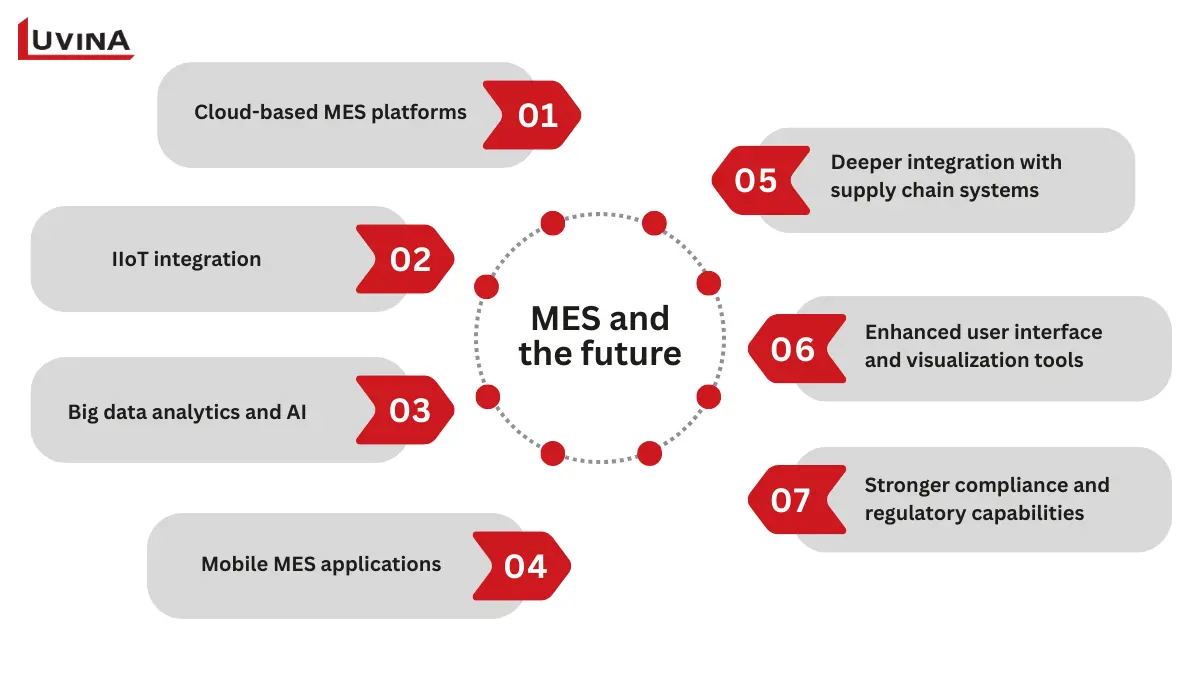
MES will continue to undergo many changes in the future
– Cloud-based MES platforms provide scalability, faster deployment, and lower infrastructure ownership costs while enabling multi-facility visibility and remote access to production data. These capabilities reflect the evolution of the MES manufacturing execution system within modern, distributed manufacturing environments.
– IIoT integration allows MES to collect real-time machine, sensor and connected devices data, which improves the monitoring, optimizing and predictive analytics of MES.
– Big data analytics and AI are used to analyze large volumes of manufacturing data, identify patterns, predict failures, and support smarter, faster decision-making on the shop floor.
– Mobile MES applications will provide real-time access to alerts, dashboards, and core MES functions via smartphones or tablets, reinforcing that MES is a manufacturing execution system as a real-time, connected platform rather than a standalone production tool.
– Deeper integration with supply chain systems will allow manufacturing companies to synchronize the production plan with demand, inventory, logistics and Supplier information, improving the planning and execution processes.
– Enhanced user interface and visualization tools that provide interactive dashboards and other advanced visual representations of production data allow users to more easily understand and act upon production data.
– Stronger compliance and regulatory capabilities, such as electronic records, audit trails, and automated documentation, support industries with strict regulatory requirements.
Together, these developments further define what is MES manufacturing execution system as a critical enabler of smart factories and Industry 4.0 transformation.
FAQ
1. What is a MES (Manufacturing Execution System)?
A MES is software that monitors, tracks, and controls production in real time to improve efficiency, quality, and traceability across the shop floor. This is the core idea behind what is MES manufacturing execution system.
2. What is the difference between MES and ERP?
MES focuses on executing and optimizing manufacturing operations, while ERP manages broader business functions such as finance, HR, and sales.
3. How do MES and ERP work together?
ERP defines what and how much to produce, while MES manages how production is executed efficiently on the factory floor using real-time data.
4. How much does it cost to implement an MES?
MES implementation costs vary depending on factory size, process complexity, and available resources, so there is no fixed price.
Conclusion
We hope this article has helped manufacturers clearly see what is MES manufacturing execution system is and why it has become a core component of modern production management. When applied correctly, MES can become a foundation for building smart factories, strengthening operational resilience, and maintaining sustainable competitiveness in an increasingly demanding market.
If your organization is considering MES as part of its manufacturing or digital transformation strategy, Luvina can support you with practical consultation and tailored solutions. Contact Luvina to explore how MES can be effectively implemented to match your production goals and business roadmap.
Glossaries
– Manufacturing execution system (MES): Software that monitors, controls, and optimizes manufacturing operations in real time.
– Shop floor: The physical production area where machines, operators, and manufacturing activities take place.
– ERP (Enterprise resource planning): A business system that manages planning, finance, inventory, and orders, and integrates with MES to align production with business operations.
– IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things): The use of connected sensors, machines, and devices to collect and exchange manufacturing data for real-time monitoring and analysis.
– OEE (Overall equipment effectiveness): A key metric used to measure equipment performance, availability, and quality in manufacturing.
Resources
- https://www.sap.com/products/scm/digital-manufacturing/what-is-mes.html
- https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/mes-system
- https://vti-solutions.vn/mes-la-gi-he-thong-dieu-hanh-san-xuat-mes/#5_Ung_dung_cua_MES_trong_cac_nganh_cong_nghiep
- https://www.ibm.com/think/insights/manufacturing-execution-systems-software
- https://www.infor.com/blog/choose-the-best-mes-system
- https://foodready.ai/blog/what-is-a-manufacturing-execution-system/
- https://www.meegle.com/en_us/topics/supply-chain/manufacturing-execution-systems?utm_source=chatgpt.com









Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter
Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter