When people talk about building a website, they usually refer to two distinct layers working together. One layer handles logic, data, and performance behind the scenes, while the other focuses on what users see and interact with.
In simple terms, backend and frontend serve different roles in a website’s architecture. This article explains the difference between backend and front end, what tools they use, and how they work together in real-world projects.
What is backend vs. front end in simple terms?
Generally speaking, a website is divided into two main sections: the back-end and the front-end. These two sections include different types of technologies as well as layers of software that serve the user. This simple separation helps explain how websites function without relying on technical jargon.
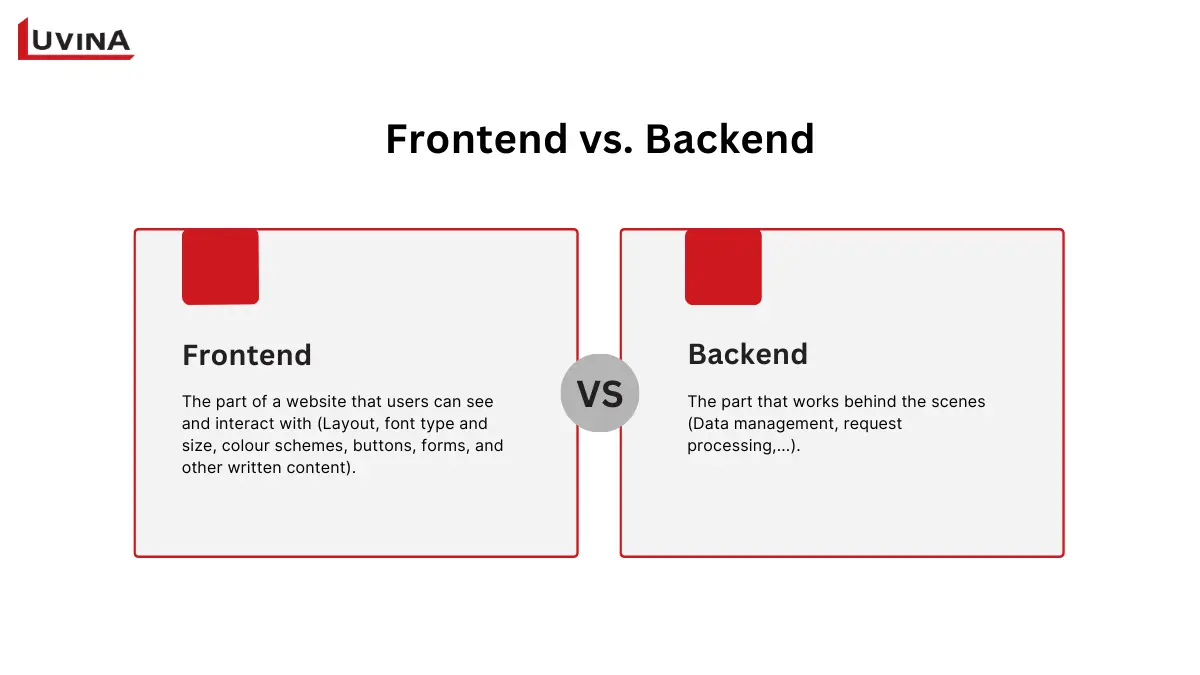
Backend and frontend are two parts of a website or application
The frontend is the part of a website that users directly interact with, including layout, buttons, forms, and visual elements. Its main goal is to ensure users can navigate the site easily and complete actions smoothly, such as submitting forms or clicking links.
The backend handles data management, request processing, and ensures that frontend features run smoothly. The backend controls the data and logic needed to fulfill those events – that is, when a user logs in, submits a form, or loads a page.
In simple terms, the frontend is what users see and click, while the backend is what processes data and makes everything work behind the scenes.
Consider an automobile to represent the frontend and backend in website development. While the engine within (backend) determines how well the vehicle really runs, the outside design (frontend) is the first thing people notice.
Source: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/what-difference-between-frontend-back-end-full-stack-ferland
Core Differences Between Frontend and Backend Development
The difference between backend and front end lies in responsibility. The frontend handles user interface and interactions in the browser, while the backend manages server-side logic, data processing, and system performance.
It is helpful to analyze the difference between backend and front end according to important features to more clearly see these functions in action.
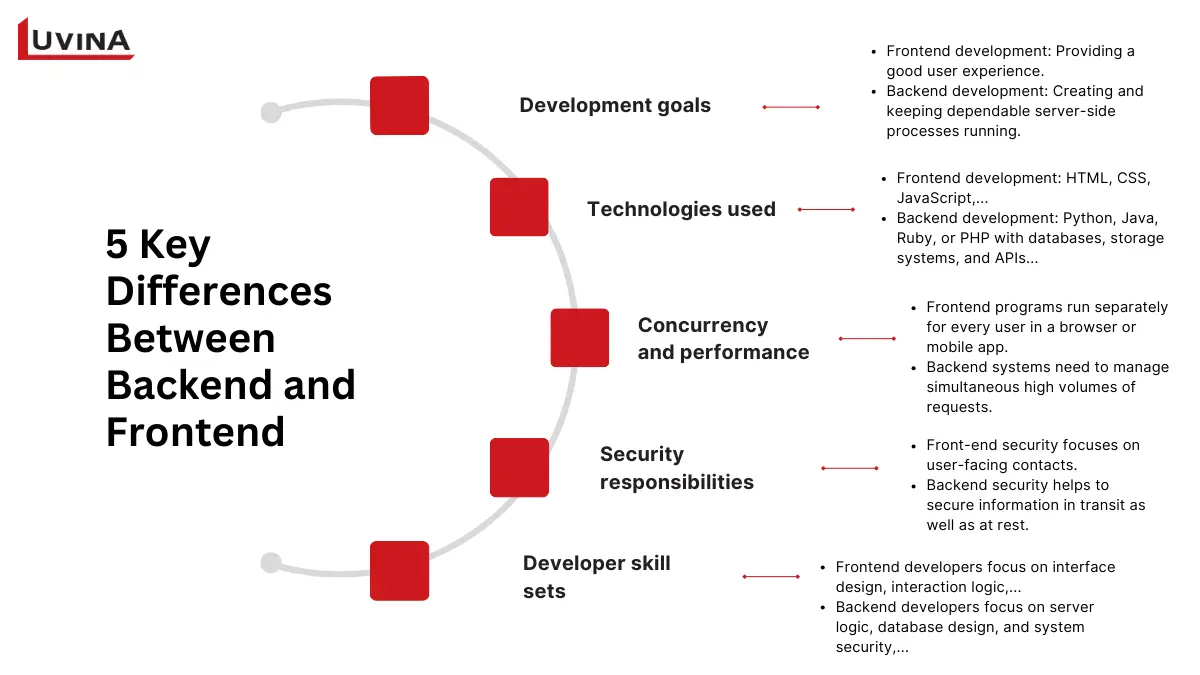
These criteria help define the difference between backend and front end
1. Development goals
Frontend development is motivated by the objective of providing a good user experience. Frontend developers focus on accessibility, responsiveness, and performance. Their goal is to deliver a consistent and user-friendly interface across devices. How natural and easy the interaction appears determines its success.
By contrast, backend development focuses on creating and keeping dependable server-side processes running. Backend developers build stable systems that handle requests accurately, meet security requirements, and scale efficiently. When setting project results, this divergence in priorities clearly mirrors the difference between backend and front end.
2. Technologies used
One other important difference between backend and front end is in the tools each side employs.
– Along with frameworks that aid in structure and UI development speed up, frontend development depends on browser-based languages like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
– Backend development combines server-side languages like Python, Java, Ruby, or PHP with databases, storage systems, and APIs that enable complex systems like ERP, CRM, or POS to properly interact.
3. Concurrency and performance
From a performance point of view, the difference between backend and front end is especially visible in how concurrency is handled. Frontend performance mainly affects individual users, as each interface runs independently in the browser.
Backend systems must handle many users at the same time, requiring careful management of requests to maintain speed and reliability.
4. Security responsibilities
Front-end security focuses on user-facing contacts. This covers verifying input, stopping harmful scripts, and encouraging safe authentication processes like multi-factor authentication. Certain features depend on user behaviour; for instance, devices or passwords need protection.
Backend security helps to secure information in transit as well as at rest. Across databases, APIs, and services, it handles authentication, authorization, access control, encryption, and safe server-side coding. Another major key difference between backend and front end is the split in security concerns.
5. Developer skill sets
Frontend developers specialize in building interfaces, managing layouts, and optimizing user interactions in the browser.
Backend developers focus on server-side logic, databases, APIs, and system security to ensure applications run reliably.
The table below summarizes the difference between backend and front end development across key criteria:
| Aspect | Frontend Development | Backend Development |
| Main focus | User interface and user experience | Server logic and data processing |
| Where it runs | Browser (client-side) | Server (server-side) |
| Core technologies | HTML, CSS, JavaScript, frontend frameworks | Python, Java, PHP, APIs, databases |
| Concurrency | Each user runs independently | Handles many users simultaneously |
| Caching | Browser or client-side caching | Server-side or CDN caching |
| Security focus | Input validation and UI-level security | Authentication, authorization, data protection |
| Developer skills | UI design, responsiveness, performance | System architecture, databases, scalability |
A short comparison table of the difference between backend and frontend development
Source: https://aws.amazon.com/vi/compare/the-difference-between-frontend-and-backend
Frontend and Backend Tools & Frameworks
One of the most sensible approaches to grasp the difference between backend and front end is by examining tools and frameworks. Though both layers serve the same purpose, they employ distinct technologies to manage user interaction and system logic. Starting from the frontend and progressing to the backend, the chapters below clearly divide this.
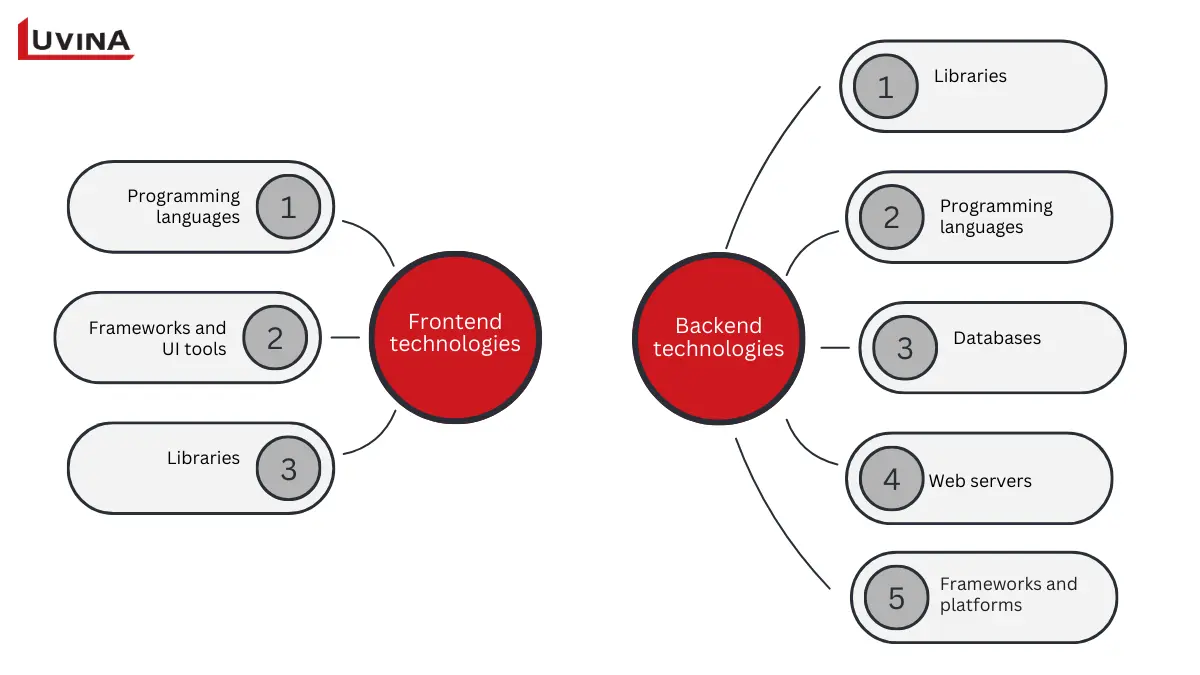
Frontend and backend tools differ significantly
1. Frontend technologies
Frontend tools focus on layout, styling, and interactivity in the browser.
Programming languages
– HTML: Provides page content and structure
– CSS manages responsiveness, colours, fonts, and layout
– JavaScript: Adds dynamic behavior and interactivity
Frameworks and UI tools: React, Angular, Vue.js, Bootstrap, Tailwind, Semantic UI, Foundation, Flutter, Ember.js, Backbone.js
Libraries
– jQuery: Simplifies DOM manipulation and interactions
– SASS: Enhances maintainability and organization of CSS
2. Backend technologies
Backend tools support data storage, server logic, and application scalability.
Programming languages: Python, Java, Ruby, PHP, C#, JavaScript (Node.js)
Databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, SQLite
Web servers: Apache, Nginx, IIS
Frameworks and platforms: Django, Ruby on Rails, Express.js, Spring Boot, Laravel, Node.js (runtime environment for server-side JavaScript)
Libraries: Mongoose, Socket.io, JDBC, Pandas
Together, these tools support different responsibilities and show how frontend and backend work together within a complete system.
Source: https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/blogs/frontend-vs-backend
Front-end Developer vs Back-end Developer
Among the most frequent decisions for those new to web development is which between frontend and backend jobs to take. Though both help create the same good, their obligations, abilities, and daily activities are rather distinct. Decisions about which route best fits your interests and strengths are made much easier by an awareness of the difference between backend and frontend positions at the job level.
Although their daily duties differ greatly, front-end and back-end developers work closely with one another.
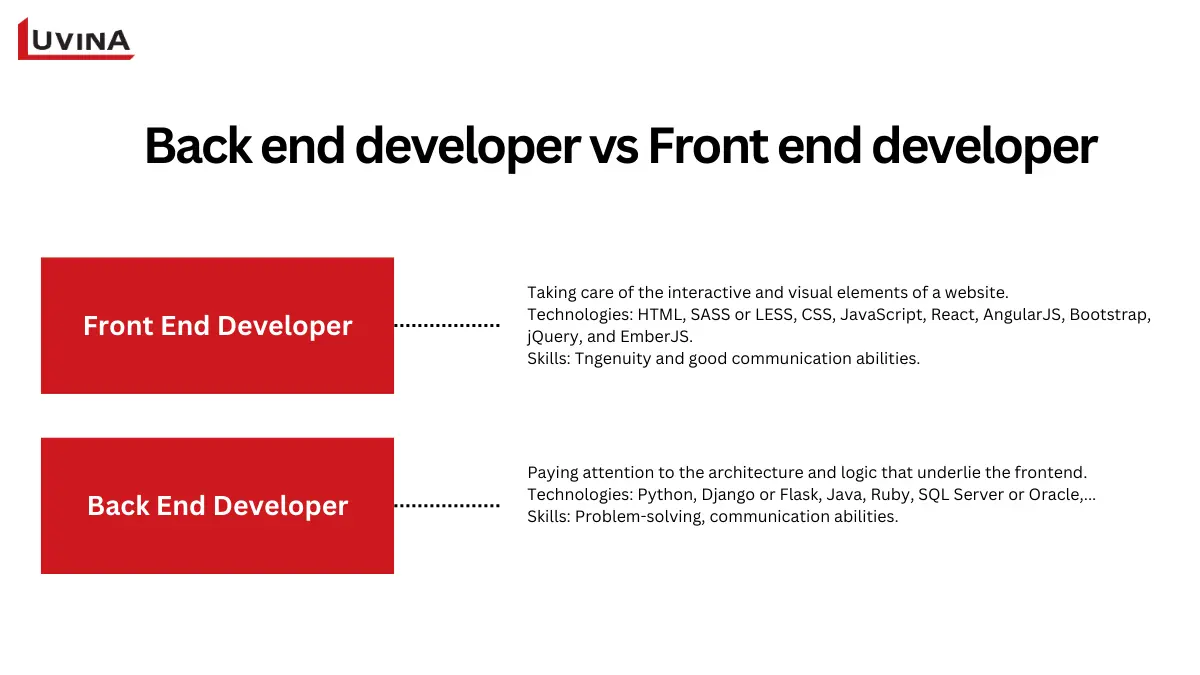
The comparison between back-end developers and front-end developers is quite common
Frontend developers
The interactive and visual elements of a website belong to front-end developers. Their work dictates how customers interact with a product; therefore, end users see the difference between backend and front end.
Using core frontend technologies, they construct interfaces:
– HTML to arrange the elements of a page
– Often using preprocessors such as SASS or LESS, CSS to manage responsiveness, colors, typeface, and layout.
– JavaScript for interactivity, including animations, forms, sounds, and video.
– Frontend developers use frameworks and libraries like React, AngularJS, Bootstrap, jQuery, and EmberJS to enhance efficiency and consistency.
Apart from technical expertise, front-end developers need ingenuity and good communication abilities to work with designers, backend teams, and clients – particularly when justifying design or usability choices. At the role level, this user-facing emphasis underlines a fundamental difference between backend and front end.
Backend developers
Backend developers pay attention to the architecture and logic that underlie the frontend. The difference between backend and frontend development in reality is reflected in their construction of systems that manage requests, process data, and guarantee dependable application operation.
Common backend abilities and technologies comprise:
– Python for data processing, as well as frameworks such as Django or Flask
– Java for platform-independent, scalable apps.
– Ruby for quick development, especially in settings with high traffic
– Databases are handled using tools like SQL Server or Oracle to guarantee applications satisfy security and performance needs.
The role revolves around problem-solving because backend operations often include debugging, system optimization, and complex workflow management. Working with frontend developers, product teams, and business stakeholders requires great communication abilities. Talks of front end vs back end engineers sometimes draw parallels among these obligations.
Source: https://www.coursera.org/articles/front-end-vs-back-end
What Is Full-Stack Development?
Developing both the server and client side of a web app is full-stack development. Full-stack developers manage the entire product rather than only one layer; thus, they must know the difference between backend and front end and how these two components cooperate in actual use.
Full-stack developers connect many tasks throughout the stack in daily work into one complete system:
– Frontend tasks: Developing user interfaces with HTML, CSS, JavaScript, and frameworks like React or Angular
– Backend tasks: Building server logic and APIs using frameworks like Django, Spring, or Node.js as well as languages like Python, Java, Ruby, or PHP.
– Data and infrastructure: Working with databases (SQL or NoSQL), version control tools such as Git, and simple server or deployment configurations
For smaller products or non-tech-focused companies where flexibility and speed count, full-stack development is most suited. In such cases, a full-stack developer can deliver an application faster by handling both frontend and backend tasks. One drawback is that full-stack developers might be less specialized, therefore limiting big, very complicated systems.
Source: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/what-difference-between-frontend-back-end-full-stack-ferland
How Frontend and Backend Work Together?
Every contemporary web application runs on a continuous stream of requests and answers that help front-end and backend to collaborate. While users only see the interface, data processing and logic happen behind the scenes, highlighting the different roles of frontend and backend.
Typically, this cooperation proceeds in a basic order:
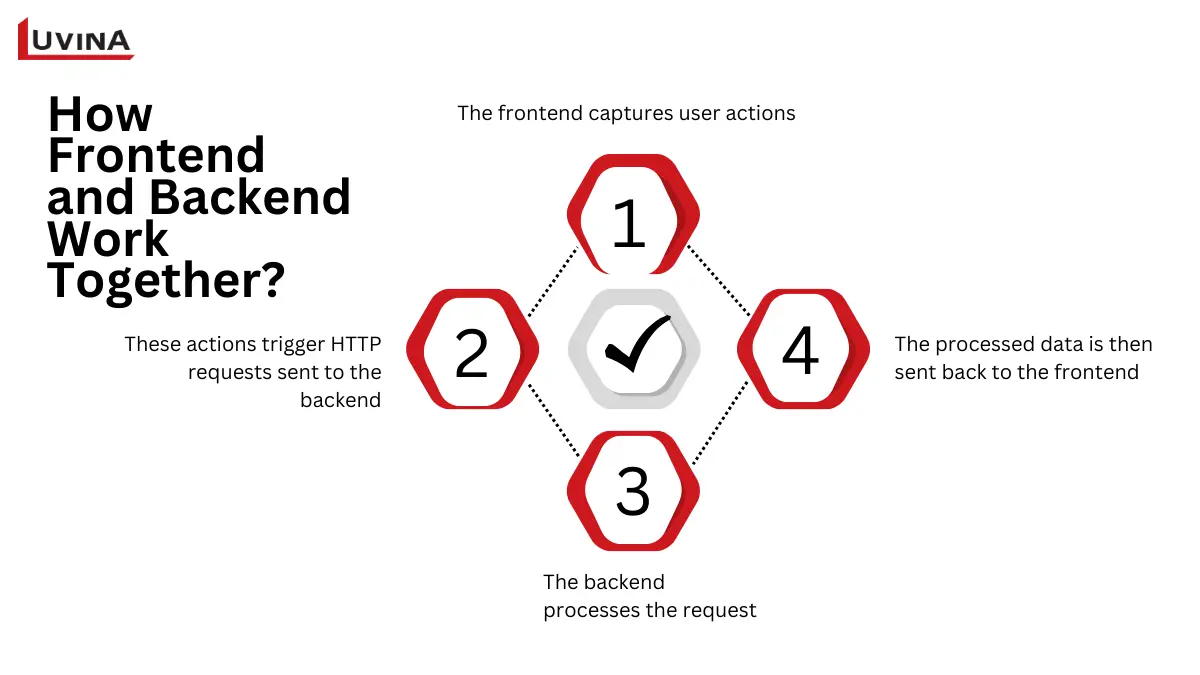
Backend and frontend operate in close coordination
– Using HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, the frontend records user activities, including form submissions, clicks, or page interactions.
– These events start backend HTTP queries meant to get or send data.
– The request is processed at the backend, business logic is applied, databases are engaged with, and security and data correctness are guaranteed.
– Then sent back to the frontend, the processed data dynamically updates the interface without having to reload the page.
Imagine buying groceries online for delivery. You click “Place Order” on the frontend to pick a meal. This action stores your order in the database, validates the request, and computes the delivery time by sending your order details to the server (backend). The backend then returns a confirmation, and the frontend immediately shows your order status and estimated arrival time.
Choosing which side to give top priority in actual projects depends on the objectives of the product.
– Frontend development gets first attention if the emphasis is on user experience, visual design, and smooth interactions.
– Backend development gets more important if the program depends significantly on data processing, APIs, authentication, or complicated business logic.
Knowing how these two levels interact helps to clear the difference between backend and frontend development and why both are crucial for creating scalable, high-performing web apps.
Source: https://mdevelopers.com/blog/frontend-backend-tech-integration
FAQ
1. Is JavaScript Frontend or Backend?
A MES is software that monitors, tracks, and controls production in real time to improve efficiency, quality, and traceability across the shop floor. This is the core idea behind what is MES manufacturing execution system.
2. Is React Frontend or Backend?
MES focuses on executing and optimizing manufacturing operations, while ERP manages broader business functions such as finance, HR, and sales.
3. Is PHP Frontend or Backend?
ERP defines what and how much to produce, while MES manages how production is executed efficiently on the factory floor using real-time data.
Conclusion
Frontend and backend work together to deliver complete digital experiences. While each layer serves a different purpose, both are essential for building scalable and high-performing applications.
With the right architecture and development approach, businesses can align user experience with system reliability to support long-term growth. Contact Luvina today to build your scalable frontend and backend systems.
Resources
- https://aws.amazon.com/vi/compare/the-difference-between-frontend-and-backend/
- https://www.computerscience.org/bootcamps/resources/frontend-vs-backend/
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/blogs/frontend-vs-backend/
- https://mdevelopers.com/blog/frontend-backend-tech-integration









Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter
Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter