Accounting software development is becoming an essential factor in modern business operations. The global accounting software market was valued at $24.48 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach $29.8 billion by 2032, reflecting the rising demand for better and more accurate financial management. Since businesses are prone to human errors in manual accounting, adopting the digital way will help the industry streamline processes and avoid costly mistakes.
The guide below details some important steps in developing successful accounting software, from understanding business requirements to integrating essential features. It will help you learn how to build a solution that will enhance your business by making it more financially efficient.
What is accounting software?
Accounting software is a computerized tool that helps a business entity automate and manage the whole function of its financial operation. Invoicing, expense tracking, payroll processing, financial reporting, and inventory are all easily manageable. This tool supports a companywide system to track and process information regarding financial transactions, and by this means, prepares accurate financial statements, enables the management of projects, and allows timely filings for taxes.

Accounting software development therefore allows the creation of tailor-made solutions for the specific needs a company may have, increasing efficiency and accuracy in the management of financial activities. The development of accounting software offers several advantages, including saving time by automating repetitive tasks, minimizing human errors, and showing real-time insights into the financial status of a company. It helps an enterprise make qualified decisions, hedge risks, and ensure growth.
Types of accounting software
If you approach the building accounting solutions journey for your business, it’s worth considering 2 major ways of classification: by target audience and by development process. Both of these approaches will lead you in the selection of the best software solution, tailored for the specific needs of your business.
Types by the target audience:
- Personal accounting software: This software is typically used by individuals for simple tasks like tracking income and expenses, creating budgets, and generating basic reports. While it can be useful for personal finance management, it lacks the functionality required for handling complex business accounting needs.
- Accounting software for small and medium enterprises (SMEs): It is designed for small to medium-sized businesses; it provides features such as accounts payable, accounts receivable, payroll, and inventory management. Examples include QuickBooks, Xero, and Sage. Most SMEs develop accounting software to cater to their specific needs and have better integration with increased efficiency.
- Accounting software for large enterprises: Large organizations need accounting software that can perform multi-currency transactions, consolidate data from different subsidiaries, and follow international accounting standards. Examples include Oracle for large enterprises, but SAP can also be an option businesses choose for their needs via custom accounting software development.

Types by the development process:
- Custom accounting software: The accounting software development process is directed toward the development of customized software that can precisely meet all those financial management requirements a business needs. Such a custom solution allows flexibility in covering all necessary features and integration within existing systems smoothly. It would, therefore be wise to create a financial management tools company to come into play for designing and implementing such systems, which ensure a boost in efficiency and accuracy.
- Ready-made accounting software: These are off-the-shelf, cloud-based solutions meant to provide businesses with basic accounting functions. Even though this ready-made software is convenient and cost-effective, it can lack the personalization opportunities required by some businesses with special needs. In such cases, customized accounting software development services offered by specialized companies often prove to be better suited.
Accounting software development process
Accounting software development implies a structured process of creating high-performance and very user-friendly solutions that target the meeting of specific business needs. Be it the development of a custom platform or the enhancement of existing tools, each phase of this process ensures the resulting product will be efficient, secure, and scalable. The key steps involved in developing accounting software include:
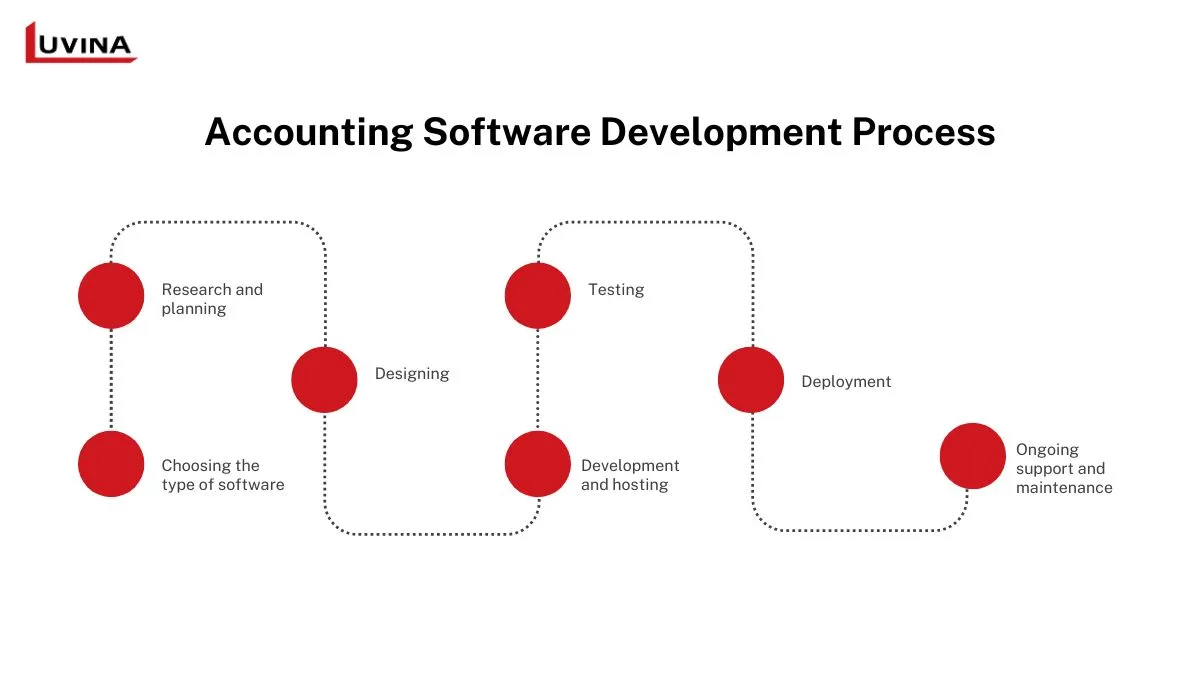
Step 1 – Choosing the type of software
In this regard, its development process is initiated by the choice of what type of software is to be developed, namely enterprise systems, custom solutions, and specialized software. All these choices do depend significantly on what features and scalability and what other integrations it shall be about with the final result. Appropriate software would have to be selected as such so the business goals can be oriented accordingly.
Step 2: Research and planning
Thorough research is the very foundation of any effective accounting software development. It should start with deep market analysis to find gaps, trends, and user expectations. A business should analyze the solutions that competitors offer to establish what makes their solution unique to ensure theirs stands out. This step will also involve the identification of pain points in the ongoing processes and the determination of essential features to solve the issues.
A developer creating property development accounting software, for example, targets those features around project budgeting, tracking of expenses, and financial reporting relevant to the property industry. The gathered information provides insight during the next step – planning.
Planning transforms research data into a phased project plan involving scope, milestone, budget assignment, and timeframe. Teams align expectations with their stakeholders and make sure that stakeholders’ priorities have been confirmed. The choice of the right model, waterfall, or hybrid – will ensure that the development is approached in an organized and flexible manner about change. With proper research and planning, a project will not only be clear as to what it needs to deliver but also limit risks that allow for a smooth accounting software development process.
Step 3: Designing
This is the point where the vision starts to take shape. During this stage, much attention is paid to creating a user-centered interface and smooth user experience. The designers create wireframes to visualize the structure of the software and then make prototypes that can simulate the user’s journey. These low-fidelity prototypes help the stakeholders to visualize the layout, navigation, and overall feel of the product.

After the approval of wireframes, the focus has to shift towards visual design. The interface is to be according to branding, including clarity and ensuring users’ ability to work with complicated functions without hassle. Such features as dashboards, logs of transactions, and reporting features should intuitively be placed to be found easily for maximum efficiency. A well-thought-out design limits confusion and is the foundation for smooth accounting software development.
Step 4: Development and hosting
The development stage brings the ideas to life. Here, the development of the software’s back-end and front-end functionality should be coded. Usually, developers do an MVP in which only core features are targeted for the software’s workability testing. For instance, an MVP for developing accounting software might include expense tracking, invoicing, and payroll management functionalities.
One of the important decisions to be made at this stage is choosing the hosting type. The options available to a business could be on-premises hosting, Web-based hosting, or Cloud hosting. Once the hosting option is chosen, the development team integrates the APIs, develops the security measures, and complies with the data. Rigorous coding standards and version control are maintained to build a stable and reliable product.
Step 5: Testing
The purpose of quality assurance is to ensure that the software maintains standards of performance, security, and functionality. Testing is aimed at bug finding, optimizing workflows, and confirming that compliance exists with user requirements. This phase, testing, consists of several layers of testing to find and eliminate potential issues before product deployment: functional, performance, security, and user acceptance testing. Fixing issues at this stage means that the business will deploy reliable and high-performance software.
Step 6: Deployment
The release phase of accounting software development is where the actual deployment of the software for real use is done, first by soft release. It allows a few selected users to try out the product in real conditions, providing their valuable feedback for further improvements. Also, onboarding materials, such as tutorials or user guides, are transparent, ensuring that its adoption is smooth because users can master the features and functionalities of the software with ease.

It is very important that after the release, user feedback be gathered on minor issues or additional needs. The developer should be in a position to make timely updates to enhance performance and user satisfaction. Marketing at this stage is of utmost importance, which will introduce the software to a bigger audience, highlighting its unique features and benefits.
Step 7: Ongoing support and maintenance
Ongoing support and maintenance would keep the software functional, safe, and current according to evolving business needs. In other words, bug fixes over time, some performance enhancements, or the integration of new features due to user input are all probable inclusions.
In addition, monitoring current industry trends and emerging technologies allows you to stay competitive with the software either through enhanced functionality or meeting updated regulatory requirements. It’s about proactive customer support, offering quick resolutions and 24/7 assistance, which will play a very important role in long-term user trust and satisfaction.
Developing Accounting Software with Luvina
When it comes to accounting software development, Luvina stands out as a trusted partner with over 20 years of experience delivering high-quality solutions to clients worldwide. With a dedicated team of 750+ skilled professionals, Luvina leverages cutting-edge technologies and proven methodologies to create software tailored to meet your business’s unique requirements.
By choosing Luvina, you can access a development process designed to save time and enhance efficiency. Our agile development approach ensures faster delivery without compromising quality, while rigorous testing guarantees error-free and reliable software. In addition, proactive support on our side—24/7—will ensure that your software remains competitive and timely for capturing market demand.
It also extends the developing accounting software journey of collaboration with Luvina in streamlining your financial processes for higher productivity and profitability.
Conclusion
Developing accounting software can change how your business deals with money: automate processes and enhance workflows. However, such tool development requires a high level of expertise and a deep understanding of your very specific needs, which makes the choice of the right accounting software development company crucial.
Luvina provides accounting software development services for your business objectives. Contact us today to explore how our custom solutions can drive your business forward.
FAQ
Examples of accounting software
Many accounting software solutions have become industry benchmarks, for example, QuickBooks Online for small businesses, NetSuite ERP for businesses of all sizes, and Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central for medium-sized businesses,…
How much does the development of accounting software cost?
The cost of accounting software development depends on various factors such as the type of software, desired features, and developer expertise.
Here’s a general cost breakdown:
Large enterprises: $100,000 – $625,000.
Small businesses: $1,250 – $30,000
Mid-sized businesses: $60,000 – $100,000









Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter
Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter