As AI transforms industries, understanding ML learning types helps you choose the right method for each project. Using AI technology would not apply one model to every one of the individual use cases for a given niche. No single learning methodology would work for all applications. Every learning approach educates machines differently; selecting the suitable one among different types of machine learning will determine your project’s success or failure.
This guide explains each ML learning type and shows when to use them effectively.
What Are the Main Types of Learning in Machine Learning?
In ML, learning refers to how models analyze data, discover patterns, and improve over time. Each gives a different means for systems to analyze data and make decisions without being explicitly trained for every step; these learning methods build the basis of current machine learning techniques.
The 3 main categories of machine learning are commonly used as a basis for practitioners to understand what are the 5 types of machine learning. These 3 categories are: supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning. Semi-supervised and self-supervised learning have developed from the combination of the categories mentioned above.
Supervised Learning: How It Works, Algorithms & Use Cases
Supervised learning uses labeled examples to teach models how to map inputs to correct outputs. During training, the model will look at all the labeled examples, learn how to relate the features of an input to the expected result, and then be able to apply what it has learned in order to ‘predict’ (i.e., make a guess) on new, ‘unseen’ inputs.
Supervised learning is one of the most excellent types of ML models for which a clear record of previous ‘successes’ or ‘failures’ from using certain features will be available.
As one of the types of learning in machine learning, supervised learning is organized into 2 main categories:
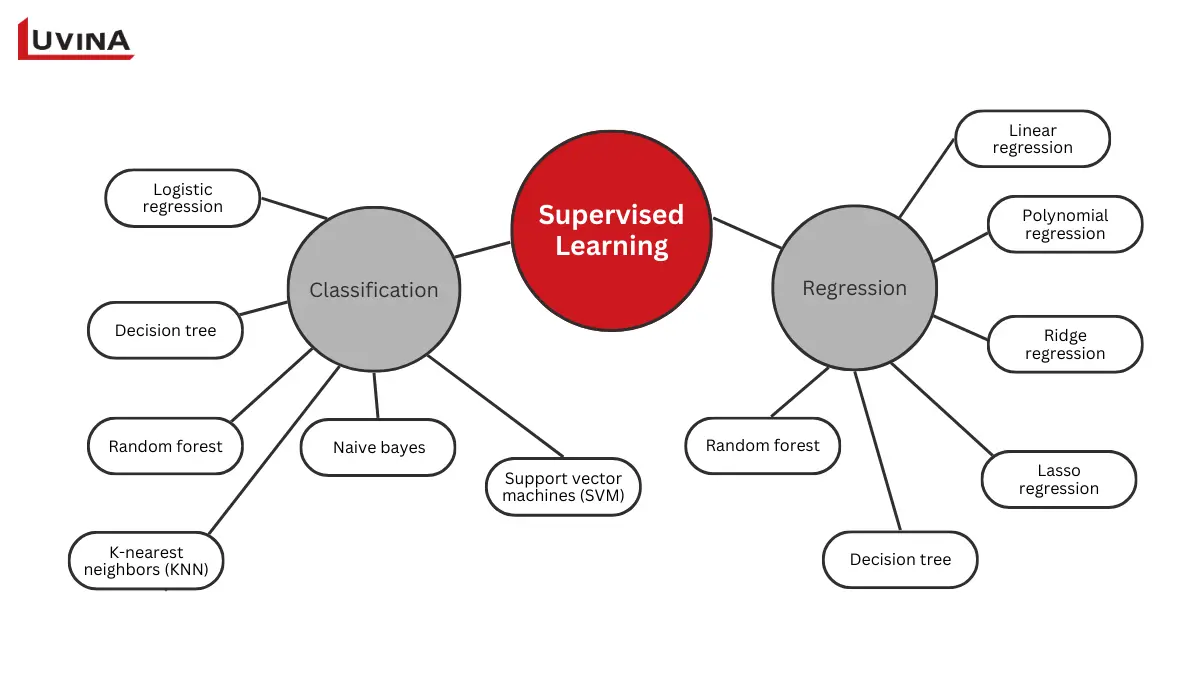
Supervised learning uses labeled data to teach models how to make predictions
– Classification (predicts the classification of the input, e.g., spam vs. not spam) includes: Logistic regression, decision tree, random forest, k-nearest neighbors (KNN), naive bayes, support vector machines (SVM).
– Regression (predicts the continuous value of the input, e.g., house price or sales forecast) includes: Linear regression, polynomial regression, ridge regression, lasso regression, decision tree, and random forest.
This is one of the types of learning in machine learning that is widely used when accurate predictions matter. It powers image recognition, speech processing, sentiment analysis, fraud detection, credit scoring, medical diagnosis, recommendation systems and predictive analytics.
Types of Learning in Machine Learning – Unsupervised Learning
Unsupervised learning finds hidden patterns in unlabeled data and supports exploratory data analysis. By exposing patterns that would be challenging to recognize by hand, this method sometimes supplements other types of m models.
3 separate subgroups of unsupervised learning exist, which are as follows:
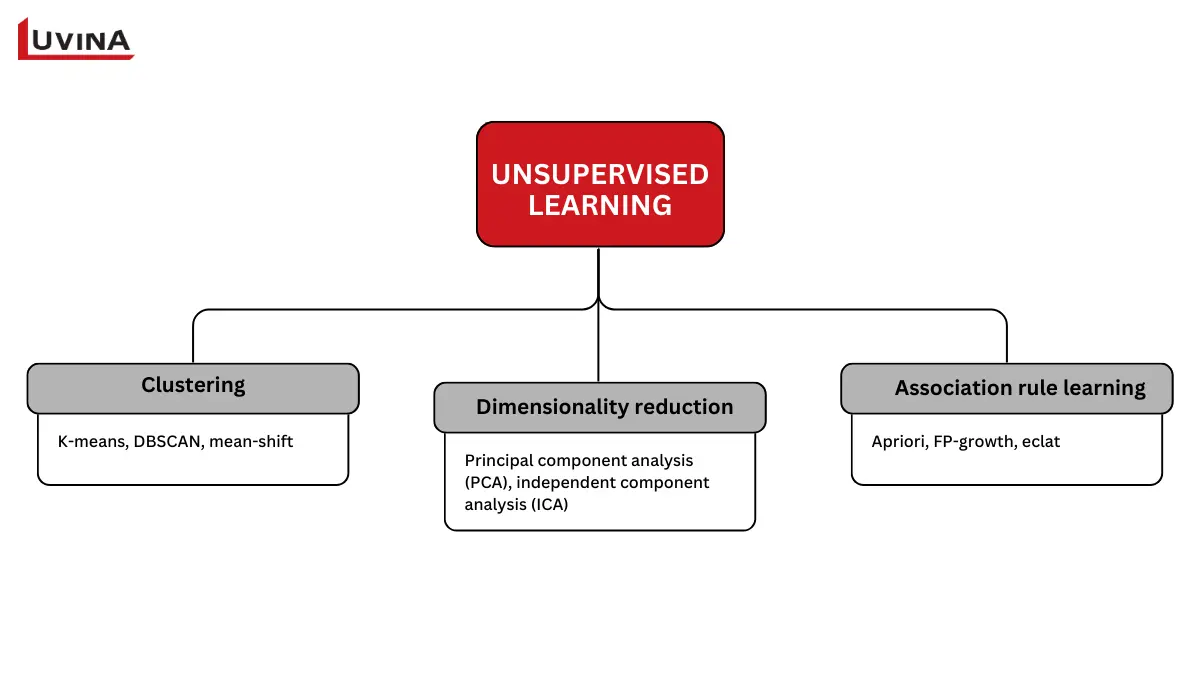
Unsupervised learning is a type of learning in machine learning that finds patterns in data
– Clustering (Various methods of partitioning similar points into a common group based on commonality): K-means, DBSCAN, mean-shift.
– Dimensionality reduction (Techniques to reduce the complexity of a dataset to its most basic level while retaining the important features of the data.): Principal component analysis (PCA), independent component analysis (ICA).
– Association rule learning (Methods for discovering relationships between items in large datasets.): Apriori, FP-growth, eclat.
All 3 methods are often used for customer segmentation, fraud detection, recommendation systems, marketing analytics, and data preprocessing.
Semi-Supervised, Self-Supervised & Hybrid Approaches
Hybrid methods combine aspects of supervised and unsupervised approaches, hence lying between the types of learning in machine learning. Rather than depending on a single learning style, modern systems in use combine several approaches to solve difficult problems; hence, these methods reflect how they operate.
Among the most significant categories in this hybrid environment are semi-supervised learning and self-supervised learning, both of which are assuming more and more importance across different types of machine learning models.
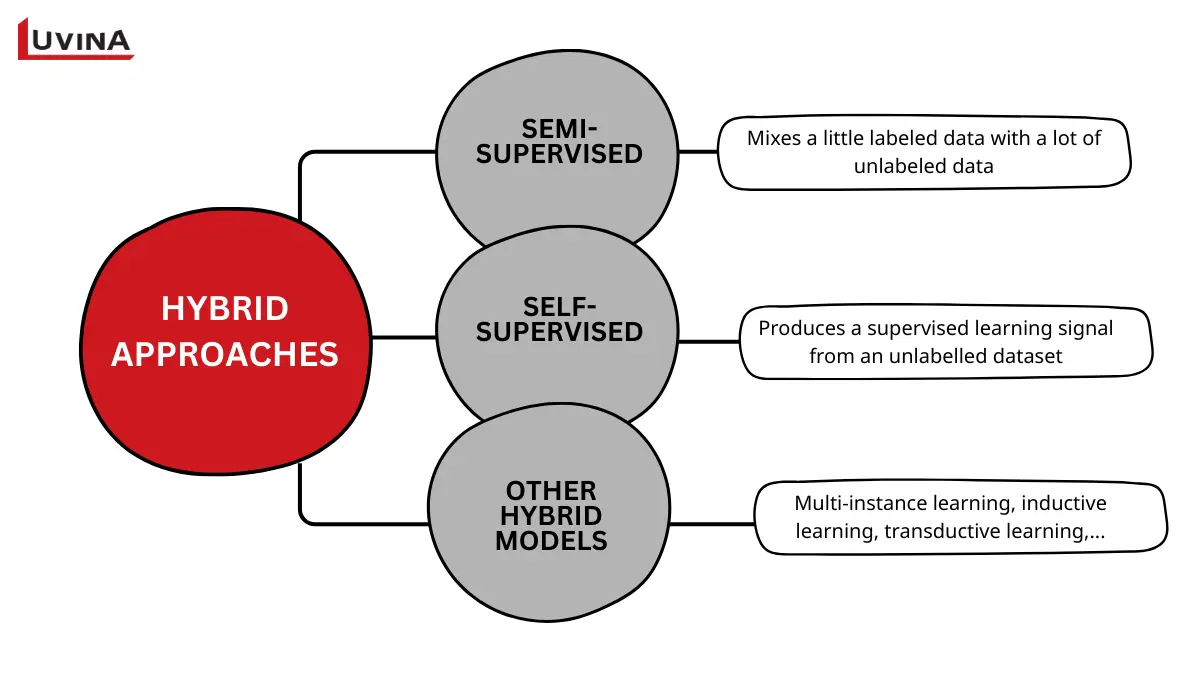
Hybrid learning combines machine learning methods to solve complex tasks
Semi-supervised learning
Semi-supervised learning combines limited labeled data with large unlabeled sets to improve accuracy.
By means of unsupervised steps, models can find patterns or clusters, then use supervised signals to improve them. Graph-based learning, label propagation, co-training, self-training, and generative adversarial networks (GANs) are among the often-used methods.
Particularly when unlabeled data still has important information, semi-supervised learning is one of the types of learning in machine learning often used in picture classification, NLP, speech recognition, recommendation systems and medical imaging.
Self-supervised learning
Self-supervised learning generates its own training labels, making it ideal for large audio, vision, and text tasks.
Popular techniques include masked modeling, contrastive learning, autoencoders and predictive coding. Among types of learning in machine learning, self-supervised learning powers modern NLP systems, computer vision pipelines, speech recognition tools and the pre-training of large AI models.
Beyond these core categories, other hybrid fields also contribute to the broader landscape of hybrid ML approaches. For example:
– Multi-instance learning focuses on labeling groups of instances rather than individual samples.
– Inductive learning creates general rules from specific examples.
– Transductive learning predicts outcomes for specific cases without requiring full generalization.
Reinforcement Learning and Other Advanced Learning Paradigms
Among the most dynamic types of learning in machine learning is reinforcement learning (RL). RL emphasizes trial-and-error behavior instead of depending on labeled data as in other machine learning categories. The agent progressively refines its tactics over time by receiving bonuses for good deeds and punishments for bad ones. Frequently found in reinforcement learning from human input (RLHF), this incentive-driven mechanism lets the system repeatedly practice decisions until it reaches the targeted outcome.
Reinforcement learning powers robotics, gaming, automation, and autonomous vehicles through trial-and-error learning.
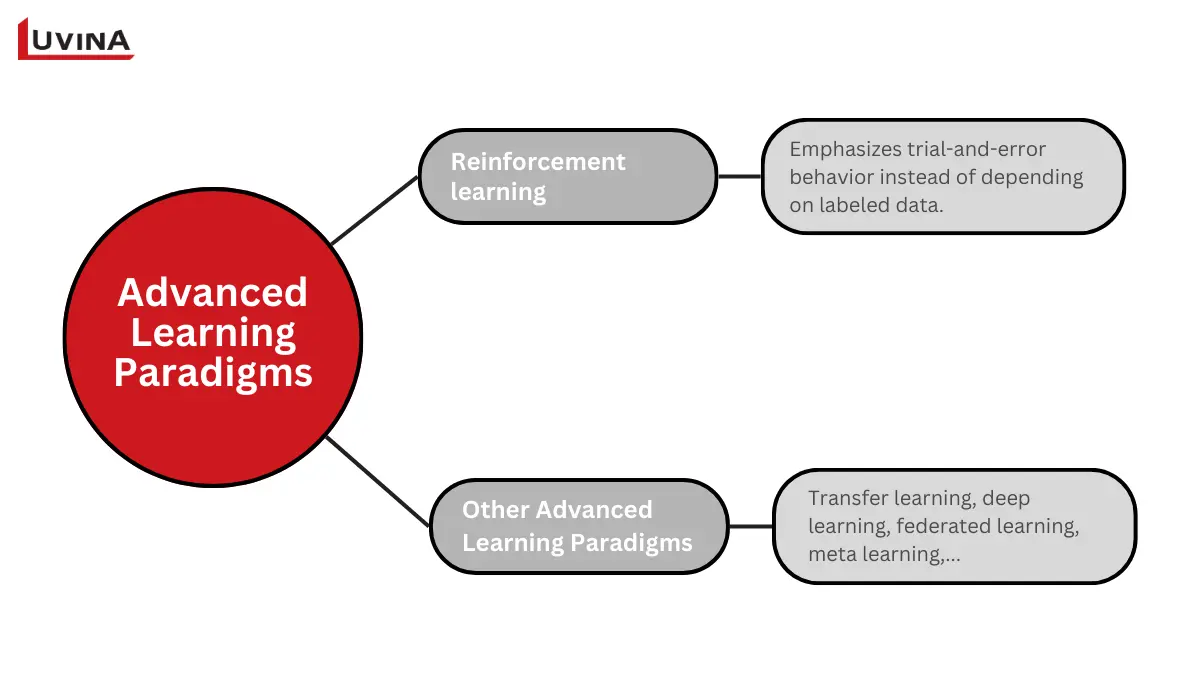
Reinforcement learning is generally considered an advanced machine learning model
Usually relying on essential algorithms like Q-learning, SARSA, and Deep Q-learning, developers help RL run. Positive reinforcement, which rewards wanted conduct, or negative reinforcement, which removes unwanted consequences when the appropriate action is taken, can be used to incorporate RL.
Beyond reinforcement learning, several advanced types of learning in machine learning extend the landscape of sophisticated learning approaches:
– Transfer learning is concerned with the application of knowledge gained from training on one specific task to another similar task.
– Deep learning makes use of deep multilayer neural networks.
– Federated learning is about creating models on many interconnected devices, without aggregating the data from these devices into one central data repository.
– Meta learning (“learning to learn”) lets models rapidly fit fresh assignments using insights from prior learning events.
Criteria for Choosing the Right Types of Learning in Machine Learning
Choosing the best learning method starts with knowing how the types of learning in machine learning operate in actual situations. Every approach has its own merits; thus, the best one for you will rely on your computational resources, data, and job needs. The major criteria below should guide your choice of the method best suited for your project.

3 key criteria to help you choose types of ML models
Data landscape
The characteristics of your data, including the size, structure and complexity of your dataset, will determine what you can do and also will have a significant impact on the types of learning in machine learning that will be most successful.
– Datasets size: Smaller data sets allow for “easier” overfitting (high bias) models. Larger data sets enable more complex modelling, e.g., neural networks and gradient boosting.
– Datasets structure: Tree-based models work well with structured/tabular data, while deep learning works best for images, sound, and text.
– Pattern complexity: Nonlinear patterns/relationships require flexible models (SVM, neural networks, boosted trees), whereas linear patterns/relationships can be modelled with linear models.
Matching the method to the problem
Particularly while striking accuracy, openness, and legal requirements, different tasks call for different types of learning in artificial intelligence.
– Explainability: If a model is being used for performance-based purposes, then a “black box” model (e.g., deep learning) is typically acceptable. In regulated cases, the model used must be easy to interpret (e.g., linear regression, decision trees).
– Task type: Depending on whether the problem is classification, regression or clustering, different types of learning in machine learning will be effective.
– Workflow fit: Each data scientist may employ multiple learning approaches, such as unsupervised learning to identify patterns, a supervised learning approach for training and a reinforcement learning based method for fine-tuning.
Balancing performance with practical constraints
Even powerful machine learning approaches must align with your available resources, infrastructure and deployment expectations.
– Training & inference speed: Simple models offer fast training and quick predictions; deep models may train slowly but still deliver fast inference. Instance-based methods like k-NN predict slowly despite zero training time.
– Computational & budget limits: Deep neural networks often require GPUs and long training cycles. Lightweight models run efficiently on standard hardware and support rapid experimentation.
Emerging Trends in Learning Types: What’s Next in ML Paradigms?
New trends are developing among several sectors as machine learning advances, changing how companies use different types of learning in machine learning to tackle real-world issues. Each influencing how future machine learning methods will develop, the following are the major trends pointing to the direction of the next wave of innovation:
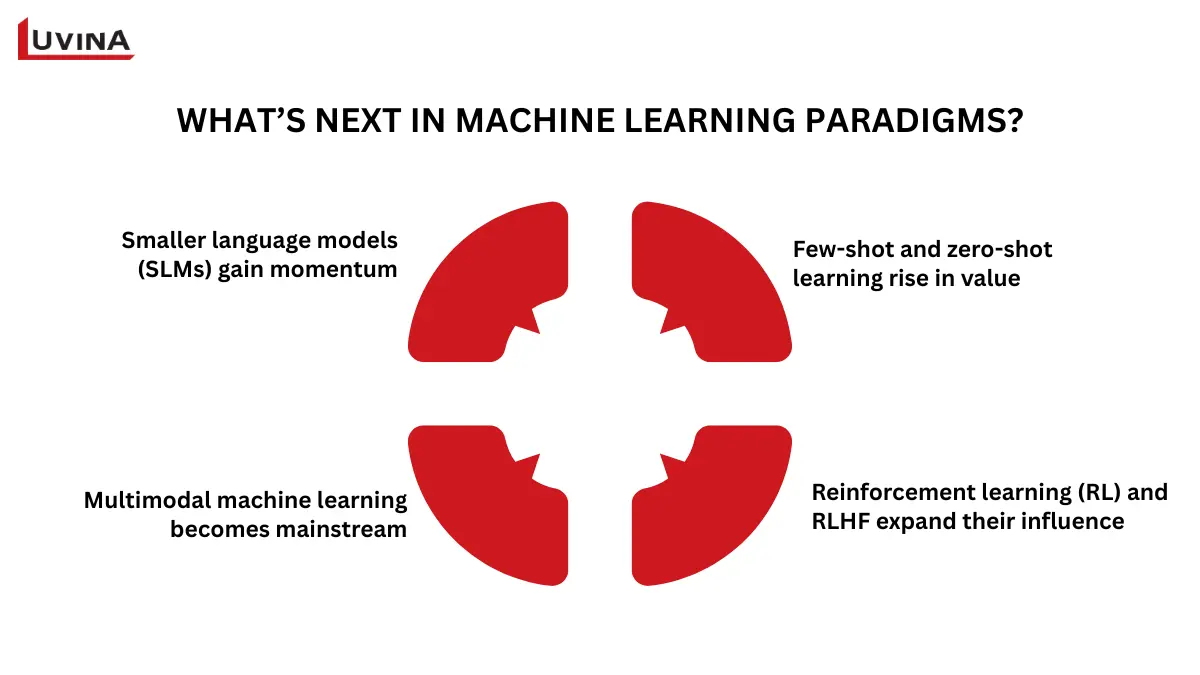
The different types of machine learning are expected to continue evolving in the future
Smaller language models (SLMs) gain momentum
SLMs like Qwen and Pythia show that high performance doesn’t always require massive scale. These types of learning in machine learning offer faster inference, lower cost and improved accessibility, making them ideal for IoT devices, edge computing and sustainable ML workloads. This shift also broadens the use of lightweight solutions across various types.
Multimodal machine learning becomes mainstream
Simultaneous comprehension of text, pictures, and audio allows multimodal systems to reason more richly and more like humans. Pushing artificial intelligence toward whole decision-making, they run systems for visual question answering, document analysis, and unified image-text search.
Few-shot and zero-shot learning rise in value
Offering great benefits in data-scarce settings, these approaches enable different types of learning in machine learning to accomplish new jobs with few or no labeled examples. Industries such as customer service and healthcare depend on them to change rapidly without extensive data gathering or reskilling.
Reinforcement learning (RL) and RLHF expand their influence
By letting agents learn via contact, RL keeps driving advancements in robotics, autonomous systems, finance, and gaming. RLHF provides human supervision that helps models match consumer preferences, safety standards, and moral issues.
FAQ
1. What are the main types of machine learning?
The 3 core types of learning in machine learning are supervised learning, unsupervised learning and reinforcement learning. They differ in how models learn from data.
2. How is supervised learning different from unsupervised learning?
Supervised learning trains on labeled data to predict specific outcomes, while unsupervised learning analyzes unlabeled data to uncover hidden patterns such as clusters or associations.
3. When should a business use supervised learning?
Supervised learning is best when clear outcomes are required and labeled historical data is available, for tasks like fraud detection, churn prediction or demand forecasting.
4. What are common use cases for unsupervised learning?
Among types of learning in machine learning, Unsupervised learning is useful for exploratory tasks such as customer segmentation, anomaly detection or discovering purchasing patterns without predefined categories.
5. How can companies decide which learning approach fits their project?
They should evaluate the type of data they have (labeled or unlabeled), the goal of the project (prediction or discovery), required model transparency and available computational resources.
Glossary
– Machine learning (ML): A field of artificial intelligence that enables computers to learn from data and make predictions or decisions without being explicitly programmed.
– Supervised learning: A learning approach that uses labeled datasets to train models for tasks such as classification or regression.
– Unsupervised learning: A method that analyzes unlabeled data to uncover hidden patterns, clusters, or relationships without predefined outcomes.
-Reinforcement learning: A learning paradigm where an agent interacts with an environment and improves its performance through rewards and penalties.
– Clustering: An unsupervised learning technique that groups similar data points based on shared characteristics.
– Classification: A supervised learning task that categorizes data into predefined groups, such as spam vs. non-spam emails.
Conclusion
Understanding the types of learning in machine learning gives businesses a clear view of how each approach supports different objectives. By recognizing the strengths of each learning method above, you can choose solutions that align with their goals and make better use of their data as AI technologies continue to evolve.
Ready to bring machine learning into your next project? Contact Luvina for expert support.
Resources
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/machine-learning/types-of-machine-learning/
- https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/machine-learning-types
- https://machinelearningmastery.com/types-of-learning-in-machine-learning
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchenterpriseai/tip/Types-of-learning-in-machine-learning-explained
- https://www.digitalocean.com/resources/articles/types-of-machine-learning#core-types-of-machine-learning
- https://www.devoteam.com/expert-view/a-practical-guide-to-machine-learning-model-selection/
- https://www.esds.co.in/kb/machine-learning/









Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter
Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter