Machine learning for predictive analytics is accelerating as data grows, enabling faster and more informed decisions across industries.
Machine learning and predictive analytics together are becoming a necessary strategy for businesses as they continue to work through increasingly complex and diverse datasets. This article will look at how machine learning and predictive analytics work together, their importance, and their effects on the next generation of data-driven intelligence.
What is Predictive Analytics and Why Machine Learning Matters
The subject of using past and present data to forecast future events is predictive analysis. Statistical methods, data mining, and predictive modelling are all used to find patterns that enable businesses to project consumer behaviour, market changes, operational hazards, or new possibilities.
Datasets are now too large and complex for classical statistics. Machine learning fills this gap by learning patterns automatically and improving over time. ML presents adaptive algorithms that learn from data, improve their predictions over time, and manage patterns too intricate for hand analysis.
Machine learning for predictive analytics improves this section in several significant ways:
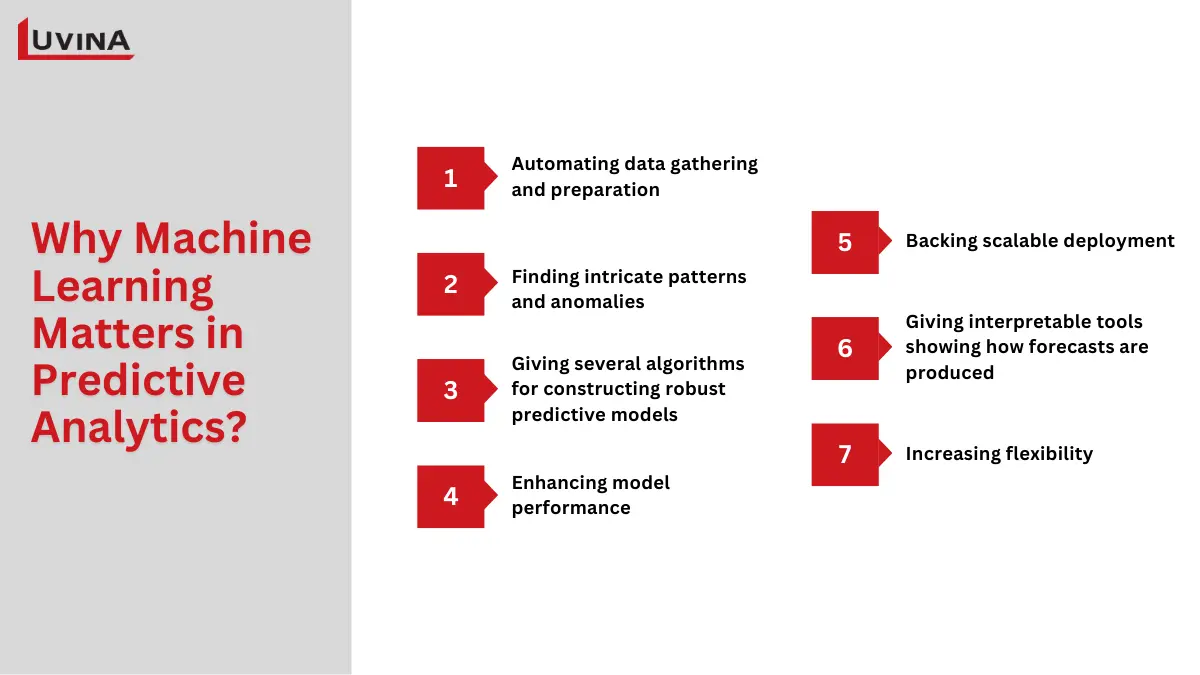
– Across several sources, automating data gathering and preparation.
– Finding intricate patterns and anomalies that conventional approaches could miss.
– Giving several algorithms for constructing robust predictive models.
– Enhancing model performance by means of automatic hyperparameter tuning.
– Backing scalable deployment across on-premise, cloud, and edge settings.
– Giving interpretable tools that show how forecasts are produced.
– Increasing flexibility as models change with fresh data allows more accurate machine learning estimates.
Information Sets Used in Machine Learning for Predictive Analytics
Datasets, also called information sets, form the foundation of predictive analytics because models learn patterns from these inputs. To find patterns and predict outcomes, training, verification, and testing of models depend on these data sets. For successful projects, knowing how to organize and apply these datasets efficiently is a crucial first step.
Usually separated by role in the machine learning process, predictive analytics data is:
– Training set: The majority of data, employed to instruct the model how input attributes interact with target outcomes.
– Validation set: During training, a smaller subset is employed to adjust model parameters and avoid overfitting finely.
– Test set: Employed to assess its ultimate performance and real-world accuracy, the test set consists of previously unseen data for the model.
By structure and kind, datasets can also be sorted, hence affecting which algorithms are most appropriate:
| Data type | Description | Format | Use case |
| Structured data | Highly organized, table-based data | CSV, SQL, Excel | Regression, classification, forecasting (e.g., sales or customer records) |
| Unstructured data | Free-form data without predefined structure | Text, images, audio, video | Sentiment analysis, image recognition, speech processing |
| Semi-structured data | Partially organized data with tags or keys | JSON, XML, HTML, system logs | Web data mining, metadata analysis, and log processing |
| Time-series data | Sequential data points indexed by time | Specialized databases, CSV with timestamps | Forecasting stock prices, weather patterns, and customer churn |
Classification of datasets based on their type and structure
Key data points within these datasets include numerical data (quantitative values like age or price), categorical data (labels or classifications), and text data (written language transformed into numerical formats). Proper preparation and handling of this information sets used in machine learning and predictive analytics ensures that machine learning for predictive analytics models can deliver precise and actionable predictions.
ML Algorithms for Prediction in Predictive Analytics
Selecting the appropriate algorithm is key to generating machine learning models for prediction that are reliable and accurate. There are many different ML algorithms; each is suited to perform certain tasks due to the specific data type and the prediction objectives of the task.
The following table summarizes key machine learning algorithms for prediction. These algorithms form the backbone of machine learning for predictive analytics projects.
| Algorithm | Description | Pros | Cons |
| Linear regression | Identifies correlations between variables | Easy to understand; clearly shows key drivers | Too simple for complex relationships; can overfit |
| Logistic regression | Adapted linear regression for classification | Easy to understand | Sometimes too simple; may overfit |
| Decision tree | Splits data into branches based on feature values | Easy to implement; interpretable | Not powerful enough for complex data; prone to overfitting |
| Random forest | Aggregates many decision trees to improve predictions | High-quality results; fast training | Slower prediction; hard to interpret |
| Gradient boosting | Sequential trees that focus on hard-to-predict cases | High-performing; accurate | Sensitive to small data changes; complex interpretation |
| Neural networks | Deep learning models mimicking brain structure | Handles extremely complex tasks; best for image/text | Resource-intensive; slow to train; hard to interpret |
| Support vector machines | Separates data with optimal margins | Robust for classification; effective in high-dimensional spaces | Hard to tune; less effective for large datasets |
| K-means clustering | Partitions data into clusters based on similarity | Simple and fast; useful for pattern discovery | Requires a predefined number of clusters; sensitive to outliers |
Key algorithms of machine learning for predictive analytics
Types of Machine Learning Models for Predictive Analytics
Machine learning models for prediction can be roughly divided into supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning, each one catering to various demands depending on the kind of data and the predictive challenge.

3 main machine learning models for prediction
Supervised learning
In machine learning for predictive analytics, supervised learning is a form whereby labeled data is used to train algorithms, guiding the model to improve predictions over time by input-output pairings. This approach is frequently employed in predictive analytics since it lets models forecast outcomes based on past data. Applications include forecasting stock prices, customer behavior, patient readmissions, or email classification. Some common machine learning prediction models in supervised learning include:
– Linear regression: Finds straight-line correlations between variables, appropriate for forecasting continuous results like sales or pricing trends.
– Logistic regression: Was adapted from linear regression and uses a different approach (logit function) for classifying (predicting) discrete outcomes like spam or loan approval.
– Decision trees: Are structured like flow charts and used to partition the data based on certain features (variables). Once the model has made these partitions, an individual can classify (or predict) outcomes based on simple rules.
– The random forest: Uses multiple decision trees (classifiers) to produce one final prediction and is useful for classifying (or predicting) when complex datasets are present and using a robust set of decision trees reduces overfitting.
– Neural networks: Use multiple layers of interconnected nodes to identify patterns in large amounts of high-dimensional data such as images, text, and sensor data.
– Support vector machines (SVM): Can be effectively used to classify (or predict) when the classes can be separated by an optimal decision boundary.
Unsupervised learning
One of the models of machine learning for predictive analytics is unsupervised learning, which
helps models to find underlying patterns and structures without a clear direction by means of unlabeled data.
Unsupervised learning supports predictive analytics by identifying segments, anomalies, and hidden patterns in large datasets. They can find groups, trends, or outliers that might not be immediately obvious, therefore giving companies useful information from data that cannot be classified or grouped in advance.
Reinforcement learning
Guided by rewards and punishments, reinforcement learning instructs models via trial and error. This is among the machine learning models for prediction best fitted for situations where every movement influences future outcomes, including training autonomous robots, creating adaptive systems, or designing artificial intelligence game agents. Learning from comments throughout time allows reinforcement learning systems to improve their decision-making techniques and performance in changing situations.
Examples & Use-Cases of Machine Learning for Predictive Analytics
Using machine learning for predictive analytics allows companies to forecast market trends, detect anomalies before they become worse, and forecast consumer behavior.
Initially, machine learning models for prediction not only allow businesses to utilize predictive analytics in real-time but also to reduce their liabilities. Examples of where businesses have successfully implemented machine learning prediction would include: fraud detection; customized product suggestions to improve customer retention and ROI; optimizing inventory and forecasting customer demand.
The following segments represent some of the ways that machine learning for predictive analytics has been implemented in various industries:

Machine learning prediction is having a strong impact across every industry
Banking and financial services
Machine learning for predictive analytics is used in the banking and finance industry to identify investment opportunities, evaluate market risks, and detect fraud. While unsupervised models identify abnormalities in real time, improving operational efficiency and security, supervised learning models examine historical transaction patterns to highlight suspicious activity.
Predictive models help financial institutions as well as forecast sales cycles, revenue, and possible losses. By means of machine learning prediction, businesses include past information and predictive analytics to make wise choices, reduce hazards, and maximize profit.
Retail and e-commerce
Machine learning for predictive analytics enables retailers and online retailers to analyse data related to potential customers, forecast demand, and improve inventory management (including replenishment). By analysing browsing and purchase data, retailers can build personalized product recommendations and improve engagement.
Customer service
Based on interaction and purchasing patterns, machine learning algorithms divide consumers. ML models for prediction let companies foresee customer needs before they occur, therefore proactively tackling customer churn, customizing deals for several segments, and hence boosting general satisfaction.
Healthcare and medical diagnostics
In the health industry, using machine learning for predictive analytics, data relating to past behaviours and health histories of patients are analysed in order to provide timely and accurate medical diagnoses. ML helps predict patient volume so hospitals can plan staffing and allocate resources more accurately.
Sales and marketing
The sales and marketing segments use machine learning models for prediction to rate leads, rank prospects, and project future marketing results. The combination of former customer activities with known market trends allows for more accurate marketing strategies, improved audience segmentation, and increased rates of conversion.
Cybersecurity
In cybersecurity, predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms are used to monitor network traffic, detect abnormalities, and anticipate potential cyber attacks. Using machine learning for predictive analytics also allows organizations to analyze structured and unstructured data in real-time and prevent security breaches before they happen.
Best Practices & Pitfalls
Using machine learning for predictive analytics can provide organizations with an opportunity to understand potential challenges and develop proven strategies to obtain accurate and reliable results from predictive analytics. Before applying proven practices, organisations must understand the various pitfalls that can impair a model’s performance and reliability.
– Overfitting and underfitting: Models that learn from noise versus actual patterns will be able to predict only training data well, but poorly for future samples because they are not using the actual trends.
– Bias of aata quality: Poor data quality will create biased predictions, which will affect the user’s level of confidence in the predictions.
– Ethical/compliance issues: If predictive models are not utilised properly, predictive models can be used in a discriminatory manner, as well as creating privacy/security violations and non-compliance with regulations.
– Resources: In most cases, using and implementing machine learning for predictive analytics will require significant computing power and highly skilled personnel, which may create barriers to organisations wishing to use ML in predictive analytics.
Organizations can use established approaches to avoid these traps:
– Select the most pertinent features to guarantee the model picks up accurate and significant information; manually clean and normalize the data.
– Choose models that fit the business problem and evaluate them using metrics like MAE, MSE, R², or F1-score.
– To grasp why a model produces particular predictions even in complicated situations, use interpretable models or execute methods like LIME and SHAP.
– Regularly monitor the results of models and change them as new data or shifting economic circumstances present themselves to keep forecasts correct across time.
Future Trends in Machine Learning for Predictive Analytics
The discipline of machine learning for predictive analytics is growing at a remarkable rate. Several major trends are helping to define predictive analytics’ future as technologies develop. Together, these patterns suggest a future wherein predictive analytics driven by machine learning not just offers more thorough insights but also enables more moral and wise company choices.
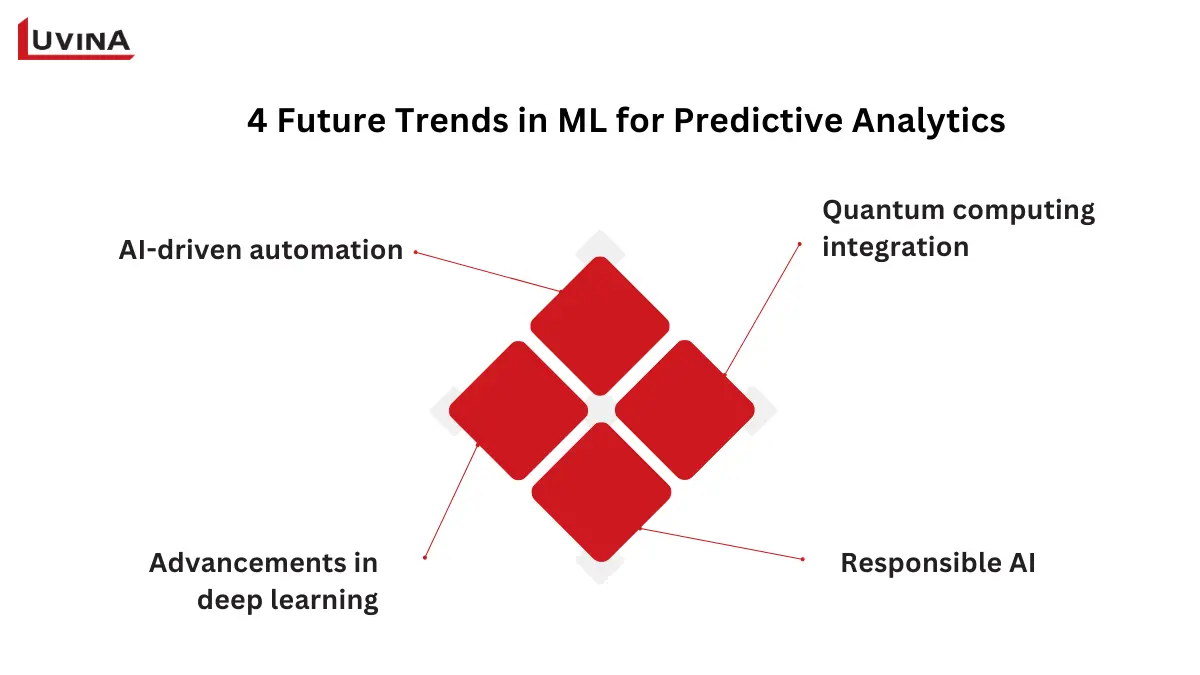
4 trends predicted to shape machine learning in predictive analytics
– AI-driven automation: Automation powered by artificial intelligence enables real-time responses and increased productivity by progressively automating predictive decision-making in sectors.
– Advancements in deep learning: Better deep learning algorithms are improving computational efficiency and model accuracy for sophisticated predictive applications.
– Quantum computing integration: Faster processing rates made previously impossible big-scale data analysis possible.
– Responsible AI: Emphasis on fairness, openness, and ethical AI helps to keep predictive analytics responsible and credible.
FAQ
1. What is predictive analytics in machine learning?
Predictive analytics uses historical data and algorithms to forecast future outcomes. It helps organizations make informed decisions based on past patterns.
2. Is machine learning essential for predictive analytics?
Yes, machine learning for predictive analytics is crucial as it analyzes data, detects patterns, and improves prediction accuracy.
3. Can machine learning only predict outcomes?
No, machine learning also supports classification, clustering, and pattern recognition beyond just prediction.
4. What is the difference between predictive analytics and forecasting?
Forecasting relies mainly on time trends, while predictive analytics uses multiple variables and machine learning for predictive analytics to predict specific results.
5. Can small businesses use predictive analytics?
Yes, small businesses can leverage cloud tools and structured data to run predictive models without large budgets.
Glossary
– Predictive analytics: Involves analyzing past events or trends to predict future events and assist with making a data-driven decision about how to make a product, provide a service or improve customer experience.
– Machine learning: A distinct area of computer science in which algorithms are developed to be able to recognize and make predictions or decisions without needing explicit programmatic instructions.
– Supervised learning: Training a model using known data, where the model is provided with labeled data points (values and results) and attempts to make accurate predictions based on the label of the input data.
– Unsupervised learning: Similar to supervised learning, but the model uses only the input data to find similarities or groupings, and does not have access to any information regarding which group or label the items belong to.
– Reinforcement learning: Allows a machine learning model to learn through trial and error, as a result of receiving feedback regarding its performance based on successful or unsuccessful actions.
– The training set: The collection of data used to establish a set of patterns or relationships for a particular problem, so that the model can identify those patterns in new data.
– The validation set: The collection of data used to validate the accuracy of a trained model and to help prevent overfitting.
– The test set: A collection of data that a trained model has no prior exposure to, and is used to evaluate how well the model performs.odels match consumer preferences, safety standards, and moral issues.mails.
Conclusion
The use of machine learning in combination with predictive analysis is changing the manner in which businesses analyze and apply their data. By employing machine learning for predictive analysis, businesses can identify trends and hidden patterns, and thereby, leverage data to help make decisions based on factual data and results to enhance productivity and improve overall success.
Mastering machine learning prediction prepares companies to stay competitive, maximize operations, and leverage their data’s entire potential as data gets volume and complexity.
Resources
- https://www.sas.com/en_gb/insights/articles/analytics/a-guide-to-predictive-analytics-and-machine-learning.htm
- https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/role-machine-learning-predictive-analytics-o-johnson-taiwo-mba-1101e/
- https://www.domo.com/learn/article/ml-vs-pa
- https://www.dsstream.com/post/data-science-in-action-the-role-of-machine-learning-in-predictive-analytics#types-of-machine-learning-methods
- https://www.pecan.ai/blog/machine-learning-in-predictive-analytics/#how-pecan%E2%80%99s-automated-machine-learning-platform-addresses-best-practices-and-challenges
- https://marutitech.com/machine-learning-predictive-analytics/
- https://dev.to/raajaryan/the-role-of-machine-learning-in-predictive-analytics-427n
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/396447138_Machine_Learning_for_Predictive_Analytics_Models_Methods_and_Use_Cases
- https://morsoftware.com/blog/information-sets-used-in-machine-learning
- https://www.phaedrasolutions.com/blog/information-sets-used-in-machine-learning#:~:text=Information%20sets%20used%20in%20machine%20learning%20are%20structured%20collections%20of,B)%20Types%20of%20information%20sets
- https://www.ibm.com/think/topics/predictive-ai#:~:text=Subscribe%20today-,How%20predictive%20AI%20works,trust%20with%20users%20and%20stakeholders.
- https://valanor.co/machine-learning-for-predictive-analytics/
- https://medium.com/@webadmin_46735/top-machine-learning-algorithms-for-predictions-a-short-overview-5ed1ff6942ffl









Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter
Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter