The actual issue is not whether a legacy system should be replaced when it starts to limit company expansion, but rather how it should be managed. Rewriting everything from scratch is costly, risky, and time-consuming. Many businesses, therefore, are looking at other methods to learn about and improve their current software. This is where the argument over software reengineering vs reverse engineering enters.
Though both methods tackle current systems, they are occasionally misused or confused. Actually, every strategy tackles a different issue and yields a different result. Understanding the difference between software reengineering and reverse engineering helps teams to update legacy systems more quickly, prolong system life, and make wise technical decisions. The following article will discuss how these methods function, when to employ each one, and how they fit into a pragmatic software upgrading plan.
What is Software Re-Engineering
Before deep diving into the discussion of software reengineering vs reverse engineering, let’s get to know what software reengineering is.
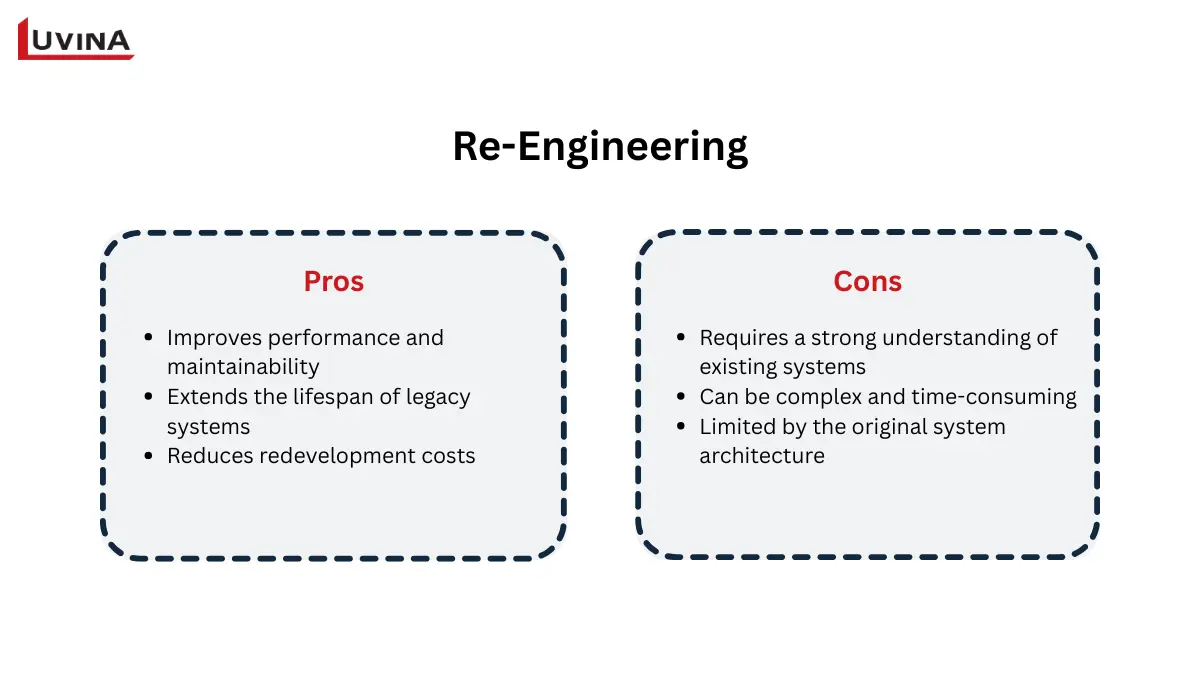
The pros and cons of software reengineering
According to Wikipedia, software re-engineering is “the examination and alteration of a system to reconstitute it in a new form.” Basically, software re-engineering is the technique of examining a current software system and then changing it to increase structure, performance, maintainability, or functionality without affecting its fundamental purpose. This also draws attention to the difference between software engineering and software reengineering, as the latter focuses on enhancing already developed systems rather than starting from the ground up.
In comparing software reengineering vs reverse engineering, commonly used on legacy systems, that still generate corporate value but are unable to satisfy contemporary technical or operational demands (for data migration), is re-engineering. It aspires to raise efficiency, minimize technical debt, and increase software lifetime while reducing expense and risk relative to total redevelopment.
What is Reverse Engineering
Reverse engineering is “a process through which one attempts to understand how a previously made system or piece of software works, often with little or no original documentation.” In essence, reverse engineering is the process of studying software to obtain its design, structure, and behavior without altering the system. It only emphasizes interpretation and discovery rather than rewriting or fixing the program, though.
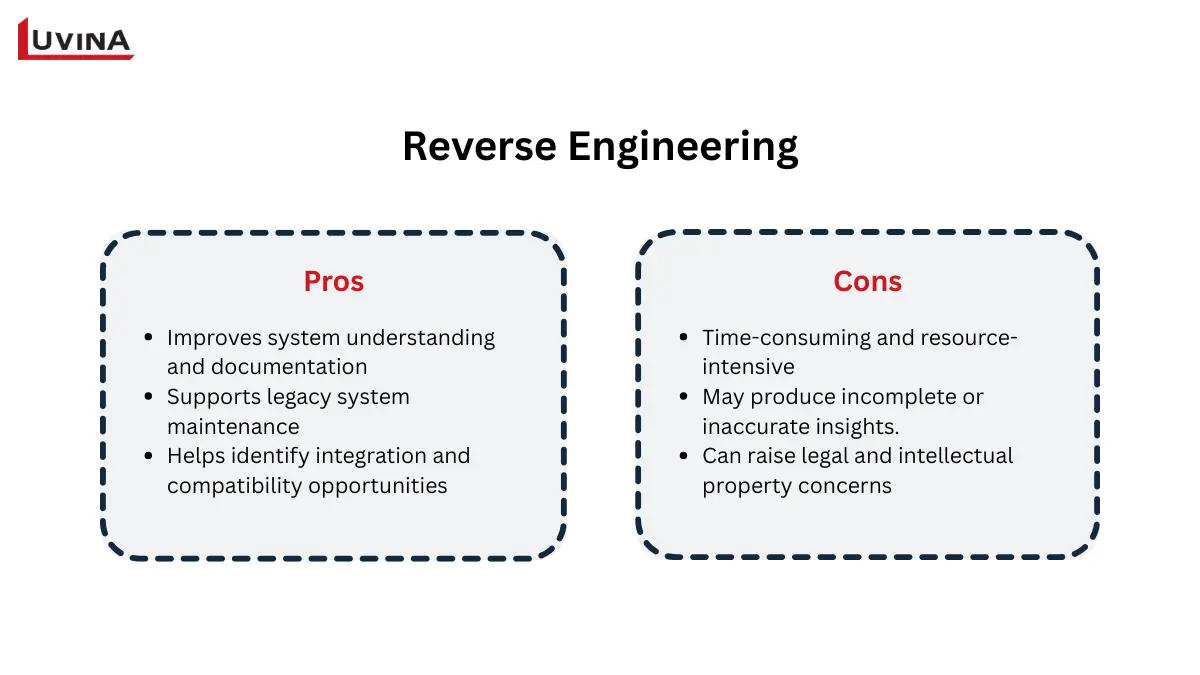
The pros and cons of reverse engineering
Reverse engineering is particularly helpful in preserving legacy systems, debugging difficult problems, or enabling compatibility with proprietary formats when comparing the two approaches.
Key Differences: Software Re-Engineering vs Reverse Engineering
Software reengineering vs reverse engineering may appear similar at first glance since both include existing systems. Still, they have quite distinct functions in reality.
While re-engineering seeks to alter a system to increase quality, performance, or adaptability, reverse engineering is mostly about comprehending the system as is. Particularly in maintenance of legacy systems, software migration, and modernizing efforts, acknowledging these differences is critical when assessing reverse engineering vs reengineering in software engineering.
The table below helps to clear up how software engineering distinguishes between reverse engineering and reengineering:
| Aspect | Reverse engineering | Software re-engineering |
| Primary goal | Understand system design, structure, and behavior | Improve, restructure, or modernize the system |
| Focus | Analysis and documentation | Modification and enhancement |
| Scope | Usually applied to specific components or systems | Often applied to the entire system or process |
| Methods | Code analysis, design recovery, and system inspection | Refactoring, redesign, and system reconstruction |
| Tools | Specialized analysis and inspection tools | Development and modernization tools |
| Legal considerations | May raise intellectual property concerns | Typically focused on internal improvement |
Quick comparison table: software reengineering vs reverse engineering
Learn how to plan and execute a successful software migration
When and Why Do We Need Each Approach
Choosing the best strategy – software reengineering vs reverse engineering -depends on the issue you are trying to address and the present state of the system. Teams seldom ask whether to use only one approach in isolation; rather, they consider when each method makes the most sense within a broader maintenance or modernization effort. The following sections describe when and why every method should be used.
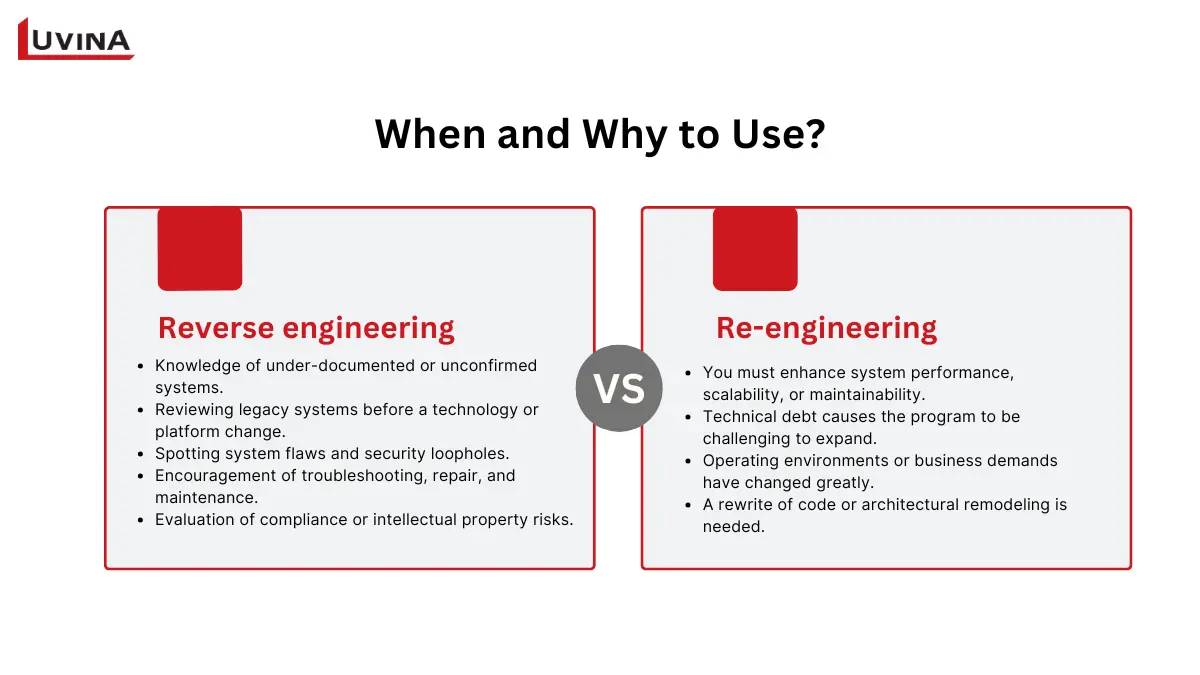
These two approaches are used in different scenarios
When and why to use reverse engineering?
Between software reengineering and reverse engineering, when knowledge about a system is either limited or absent, reverse engineering is required. Often, the first step in decision-making, it centers on understanding how code executes inside without changing its behavior.
Among the typical uses are:
– Knowledge of under-documented or unconfirmed systems.
– Reviewing legacy systems before technology or platform change.
– Spotting system flaws and security loopholes.
– Encouragement of troubleshooting, repair, and maintenance.
– Evaluation of compliance or intellectual property risks.
When and why to use software re-engineering?
When the system has to change to satisfy new technological or commercial needs, software re-engineering is used, comparing software re-engineering vs reverse engineering. This method reorganizes, enhances, or rebuilds the program to maximize long-run value rather than just analyze it.
Common selections are made in circumstances where:
– You must enhance system performance, scalability, or maintainability.
– Technical debt causes the program to be challenging to expand.
– Operating environments or business demands have changed greatly.
– A rewrite of code or architectural remodeling is needed.
Reverse engineering and reengineering are frequently used together in difficult projects. While re-engineering uses that knowledge to make changes, reverse engineering offers the knowledge needed to lower risk. In major projects of modernization where software reengineering vs reverse engineering must cooperate to produce long-lasting results, this combined approach is especially successful.
How Reverse Engineering Fits into the Software Re-Engineering Process
In actuality, reverse engineering is a crucial phase in the larger software re-engineering cycle rather than an independent project. The base for making safe and efficient modifications comes from knowledge of the inner functioning of a system. The relationship between these two techniques is best seen as consecutive rather than competitive.
Usually, in the software re-engineering process, reverse engineering follows the next flow:
– System evaluation: Examine the present software to spot bottlenecks, limitations, and elements needing work
– Reverse engineering: Study source code and internal architecture to reveal the workings of the system without changing its behavior.
– Improvement planning: Define a new structure or design that addresses performance, maintainability, or functional gaps identified earlier.
– Implementation changes: Refactor or rebuild sections of the code base to put into effect the intended improvements.
– Quality validation: After modifications, thoroughly test the new system to guarantee correctness and stability.
– Knowledge consolidation: Revise technical documentation to match the revised system design and behavior.
Software Reuse vs Software Re-Engineering
Besides the software reengineering vs reverse engineering comparison, the comparison between software reuse and software reengineering is also remarkable. Software reuse and software re-engineering are both cost-effective strategies, but they address different challenges.
– Software reuse focuses on accelerating development by leveraging existing components.
– Re-engineering concentrates on improving or modernizing an existing system that no longer meets current requirements.
The table below highlights the key difference between software reuse and software reengineering.
| Aspect | Software reuse | Software re-engineering |
| Primary purpose | Reduce development time by reusing existing components | Improve and modernize an existing software system |
| Main focus | Productivity and consistency across projects | Maintainability, performance, and adaptability |
| Key activities | Using libraries, frameworks, and reusable modules | Restructuring architecture, updating code, and redesigning systems |
| Impact on functionality | Reuses existing functionality without changes | May improve or extend system functionality |
| Documentation | Emphasizes clear usage guidelines for reusable components | Requires updated documentation for the re-engineered system |
| Complexity handling | Manages complexity through modular and standardized components | Reduces complexity by transforming outdated structures |
| Typical use cases | New projects that can leverage proven components | Legacy systems that are hard to maintain or extend |
| Main drawback | Risk of dependency on outdated or poorly designed components | Can be time- and resource-intensive |
The differences between software reuse and software reengineering
Examples
By looking at practical cases, it becomes easier to see how software reengineering vs reverse engineering is applied. The examples below illustrate how each approach delivers value in different contexts.
Examples of software re-engineering
When companies want to update systems to boost performance, scalability, or operational efficiency, software re-engineering is used.
– PayPal: Using the Go programming language, PayPal re-engineered elements of its system for better scalability, cleaner code, and improved performance for high-traffic workloads.
– UPS: Employing Agile and DevOps, modernised its traditional package tracking system to provide ongoing interface change, lowering operational costs and customer attrition.
– Walmart: To enhance inventory accuracy, in-store operations, and fulfillment efficiency, rebuilt supply chain systems using data-driven software and automation.
Examples of reverse engineering
Usually used in software reengineering vs reverse engineering, reverse engineering lets teams first grasp the functioning of a system before fixing, securing, or improving it.
A grand example comes from the efforts of the U.S. military to update nuclear weapons control systems originally developed in the 1970s. Using outmoded equipment and unsupported components, engineers reverse-engineered essential elements of the system to ascertain their operation and guarantee secure modernization.
FAQ
1. Is reverse engineering the same as software re-engineering?
No. Software reengineering vs reverse engineering are different. Reverse engineering focuses on understanding how a system works, while software re-engineering focuses on modifying and improving that system.
2. Do I always need reverse engineering before re-engineering?
Not always, but it is essential when the system lacks documentation or is poorly understood.
3. Which approach is better for legacy system modernization?
In most cases, combining both works best: reverse engineering to gain insights, then re-engineering to implement improvements.
Conclusion
Comparing definitions, processes, and examples makes it evident that while complementary, each serves a unique goal at various phases of a software system’s life cycle; reengineering and reverse engineering are not interchangeable.
Hopefully, after reading this article, you know the distinction between software reengineering and software engineering. Feel free to contact Luvina for custom advice and expert assistance if you are thinking of reverse engineering, software re-engineering, or more general system upgrading projects and require professional consultation.
Resources
- https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Introduction_to_Software_Engineering/Reengineering
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/software-engineering/software-re-engineering/
- https://www.institutedata.com/blog/pros-and-cons-of-software-engineering/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Reverse_engineering
- https://solutionshub.epam.com/blog/post/what-is-reverse-engineering-in-software-engineering
- https://www.scaler.com/topics/reverse-engineering-in-software-engineering/
- https://www.ipqcco.com/blog/differences-between-reengineering-and-reverse-engineering-when-to-use-reverse-engineering
- https://www.institutedata.com/blog/refactoring-and-reengineering/
- https://prepinsta.com/software-engineering/software-re-engineering/
- https://acropolium.com/blog/software-reengineering/
- https://builtin.com/articles/reverse-engineering









Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter
Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter