When people ask what is frontend, they often think of visuals and UI design. In reality, the frontend is the entire layer that users see, touch, and interact with when using a digital product – from page layout and navigation to responsiveness, speed, and usability.
Frontend plays a critical role in how users perceive performance, usability, and brand credibility. A well-built frontend ensures that applications are intuitive, visually consistent, and optimized across devices and browsers.
What is Frontend development?
Front-end development is the labor that transforms ideas and requirements into interactive experiences that consumers can interact with and utilize, such as page layout, navigation, buttons, and visual components. This layer – also referred to as the web front end/front end application – directly influences how users engage with a website or application and how natural that experience feels,
To fully understand what is frontend development, you need to look at its core responsibilities:
– Writing and maintaining website interface codes
– Page design, structure, layout, and user paths
– Designing interactive user interface components and evaluating their performance
– Improving websites for SEO, reliability, security, and speed
Frontend Programming Languages/Techstacks
To understand what the frontend is, you need to consider the technologies that support the user-facing level of a website or program. Frontend development depends on an organized technology stack that converts design ideas into interactive experiences consumers can view and engage with. Simply put, what does front end means is how content is arranged, formatted, and made interactive on the web front end using the right mix of tools and languages.
Based on their function in constructing the frontend layer, frontend technologies can be divided into several groups.
Core front-end programming languages (the foundation)
These are the universal technologies supported by all modern browsers and form the base of every frontend project.
| Language | What for? |
| HTML | Defines the structure of a page, determining where content sections appear. |
| CSS | Controls presentation, including layout, colors, fonts, spacing, and visual effects that make interfaces appealing. |
| JavaScript | Adds interactivity and logic, allowing pages to respond to user actions like clicks, scrolling, or form input. |
3 most-used frontend programming languages
Together, these three languages explain what is frontend at its most fundamental level: structure, style, and behavior working as one.
Frameworks and libraries (speed and scalability)
On top of core languages, frontend developers rely on frameworks and libraries to build interfaces faster and more consistently.
| Framework | What for? |
| CSS frameworks (Bootstrap, Tailwind CSS,…) | Streamline layout and styling |
| JavaScript frameworks (React, Vue, Angular,…) | Manage complex UI logic and state in modern applications. |
Popular frontend frameworks overview
These tools are important when building scalable interfaces and help clarify what is frontend development in real-world, production environments is.
Supporting tools and workflows (quality and collaboration)
Beyond coding, frontend teams use tools that support development and maintenance. Version control systems track changes, testing tools help catch errors, and browser developer tools allow teams to debug and optimize performance. Responsive design techniques, including flexible layouts and media queries, ensure the interface works across devices.
What Is Frontend Service?
Front-end services are a service suite of professional design, development, and maintenance of website or application user-facing layers (i.e., “the front end”). Companies can engage with a front-end service provider to ensure that their application/website has a unified visual appearance, is intuitive to navigate, and interacts well with the company’s overall goals/strategy. Most front-end service providers provide support for multiple devices, front-end coding, interface design, and ongoing support as needed.
Then, what is front end service benefits? Organizations use frontend services to get access to experienced experts who can convert needs into polished digital experiences rather than creating and managing an internal team. This method enables companies to quickly launch, maintain quality, and successfully change their frontend in accordance with changing user needs and market demands.
Frontend vs Backend vs Full Stack
Understanding what is frontend requires contrast with backend and full-stack development. Each of these areas of development is a distinct level in the architecture of a complete digital solution. The backend is responsible for how logic and data flow through an application, while the frontend is responsible for how users interact with and experience an application. A complete software product is a combination of both the backend and frontend. Knowing this difference also clarifies the front-end service’s meaning in actual projects.
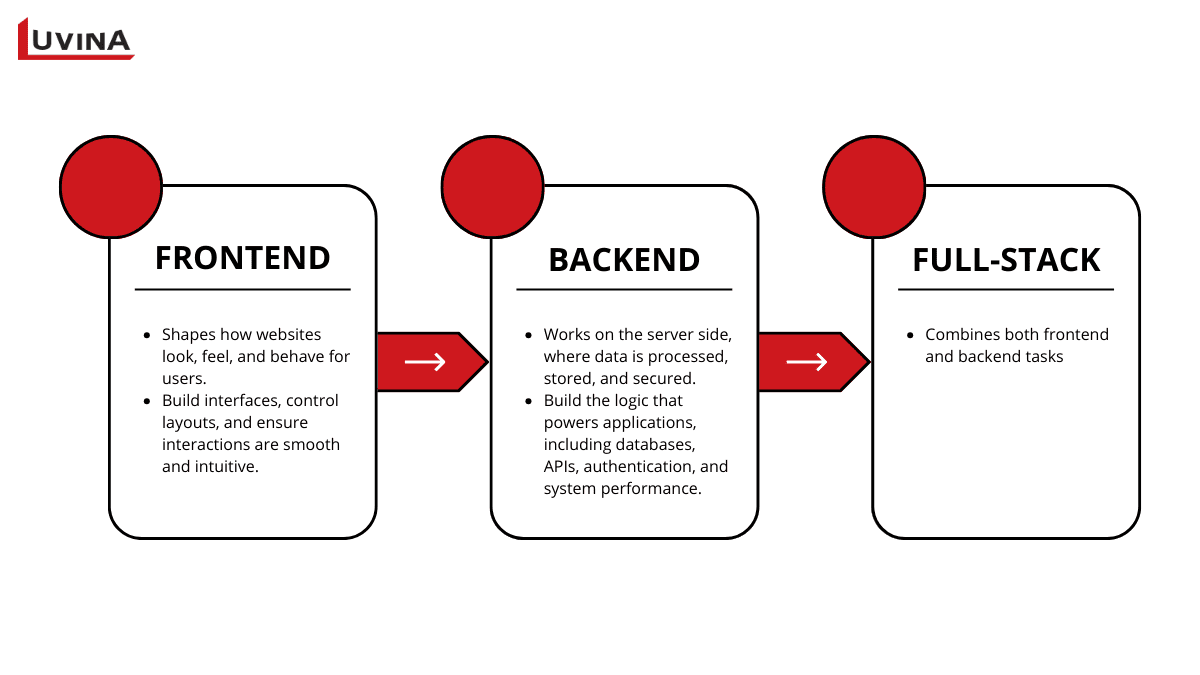
Understanding what is frontend helps differentiate these 3 definitions
Frontend development
The client-side experience is the main emphasis of what is frontend. Simply said, frontend development is the effort made to influence the look, feel of front-end websites, and behavior of consumers of front-end websites. Frontend developers make certain interactions are fluid and intuitive; they create interfaces, manage layouts, and guarantee smoothness. They are in charge of creating designs into useful interfaces and of the first impressions users have. When individuals ask again what is frontend, the response always goes back to user experience and graphical interface.
Backend development
On the server side, where information is processed, kept, and secured, backend development operates. Backend developers create the logic that drives complex business systems like ERP, CRM, or POS software, handling databases, APIs, and system performance. Though users do not visibly see this layer, backend systems power every activity on the front end to operate reliably and consistently.
Full-stack development
Full-stack development combines both frontend and backend tasks. A full-stack developer knows what is frontend development, how to manage data, server-side logic, and frontend design. Flexibility is usually prized in this role since full-stack developers may create, connect, and keep a whole application from interface to infrastructure.
The distinctions among frontend, backend, and full-stack development are summarized below in a high-level comparison:
| Aspect | Frontend development | Backend development | Full-stack development |
| Main focus | User interface and experience | Server logic and data processing | End-to-end application |
| What users see | Layout, visuals, interactions | Not visible to users | Both frontend and backend |
| Core technologies | HTML, CSS, JavaScript, React, Vue, Angular | Python, Java, PHP, Node.js, C#, SQL/NoSQL databases | A combination of frontend and backend technologies |
| Key responsibilities | UI implementation, responsiveness, usability | APIs, databases, security, performance | System integration, full product delivery |
| Typical use case | Building engaging front-end websites | Powering and scaling applications | Owning the full application lifecycle |
Comparison table: Frontend vs Backend vs Full stack
Performance, Security, and SEO in Frontend Development
To fully understand what is frontend, it’s important to look beyond visuals and focus on how frontend quality impacts real business outcomes. Frontend directly affects user experience, trust, and engagement across front-end web pages and digital products. This perspective helps clarify what is frontend in today’s development landscape: a critical bridge between users, technology, and business goals.
Performance in frontend development
Rendering methods, asset loading, and browser-side processing all influence performance. Slow or unresponsive interfaces increase bounce rates and reduce conversions, especially on front-end websites where users expect instant feedback. From this angle, what is frontend development is closely tied to optimizing how interfaces are delivered and experienced in real time.
Security considerations on the frontend
The initial link between the system and users is the frontend. Frontend aids in lowering risks, including data exposure, cross-site scripting, and incorrect authentication flows, even though it does not replace backend security. Knowing what is frontend also means appreciating its supportive function in overall application security by upholding secure interaction patterns and safeguarding user-facing components.
SEO impact of frontend implementation
The frontend structure has a direct impact on how search engines index and crawl pages. Good rendering strategies, a clear page structure, and semantic HTML help visibility in search results. Although indirect, accessibility and performance are significant SEO signals.
Best practice in frontend development starts with creating clean, organized frontend code that benefits both search engines and users without sacrificing speed or security.
– Employ semantic HTML, modify images and fonts, remove extra JavaScript, and implement lazy loading
– Choose appropriate rendering methods and manage resources carefully when developing frontend software.
– Adhere to safe authentication processes, confirm and cleanse user inputs, and stay away from showing sensitive data on the client side.
– Although it helps minimize data leakage and XSS, the frontend should never be solely in charge of fundamental security logic.
– Use clear page hierarchy, meaningful headings, and accessible navigation
– Balance user experience, security, and search visibility from the start instead of optimizing them separately later.
Future Trends in Frontend Development
Instead of focusing only on visuals, Modern frontend teams must balance speed, usability, security, and visibility on search engines, redefining what is frontend in real-world business contexts.
Key trends defining the future of frontend development include:
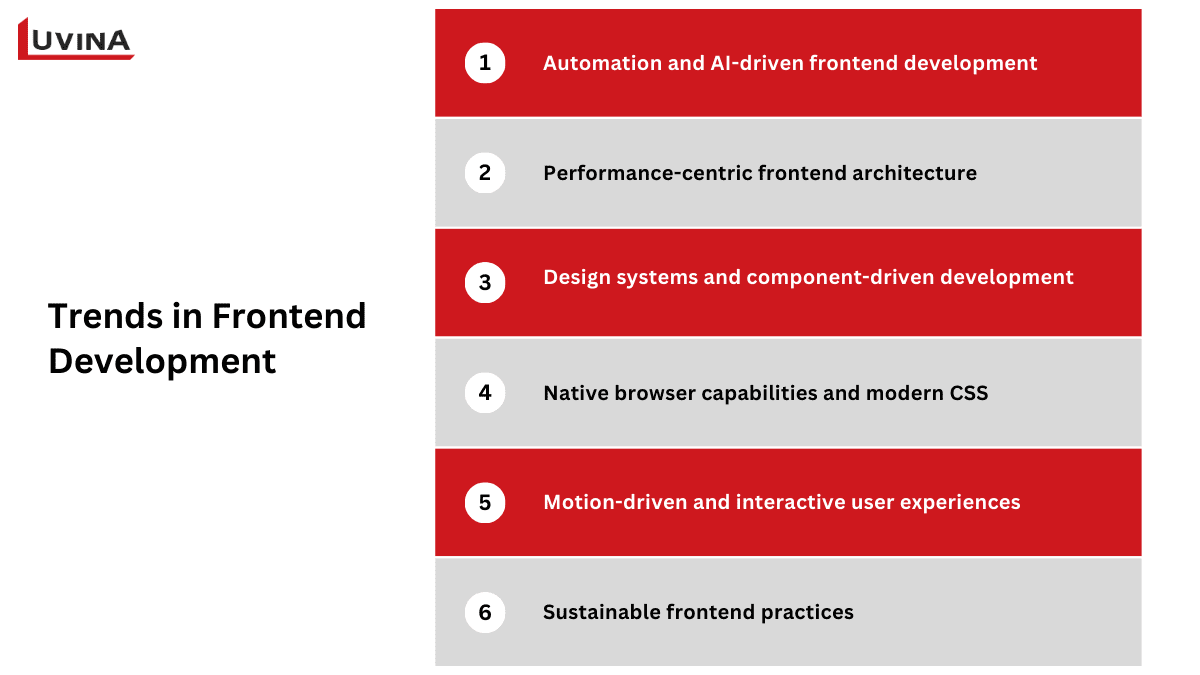
Some emerging trends in frontend development
– Automation and AI-driven frontend development: AI instruments are speeding daily operations, including code generation, testing, and quality inspections, therefore changing what is frontend work by enabling designers to pay more attention to architecture and user experience.
– Performance-centric frontend architecture: Techniques like server-side rendering, static generation, and edge delivery are currently conventional while developing sophisticated front-end websites, where speed directly affects user retention and conversion.
– Design systems and component-driven development: Scalable UI libraries help standardize front-end web pages, making front-end easier to maintain while guaranteeing accessibility and visual consistency.
– Native browser capabilities and modern CSS: Teams depend less on big libraries with sophisticated layout, animation, and responsive features, therefore redefining expectations for frontend implementation quality.
– Motion-driven and interactive user experiences: Small animations and micro-interactions improve usability and participation without degrading performance.
– Sustainable frontend practices: Lean codebases and effective asset delivery help to lower environmental impact and resource consumption.
FAQ
1. What is frontend development?
Frontend development focuses on building the user-facing interface of a website or application.
2. What is the difference between frontend, backend, and full stack?
Frontend handles the UI, backend manages server logic, and full stack covers both.
3. Why is understanding frontend important for businesses?
Knowing what is frontend helps improve user experience, performance, and conversion rates.
Conclusion
This article makes it clear what front-end development actually entails. The aim was to enable readers not just to grasp what is frontend at a conceptual level but also to recognize why frontend has become a strategic layer that clearly influences consumer experience, scalability, and corporate performance.
Luvina is here to help if you want more thorough advice, technical clarification, or hands-on assistance to design, create, or scale a frontend product. Contact Luvina to explore how we can help your frontend development path or to go over your needs.
Glossaries
– Frontend: The part of a website or application that users directly see and interact with in their browsers.
– Backend: The server-side layer that processes data, handles logic, and supports frontend functionality.
– JavaScript Framework: A toolset used to build and manage dynamic, interactive frontend interfaces efficiently.
– Semantic HTML: The practice of using meaningful HTML elements to clearly define content structure, improving accessibility, SEO, and maintainability of front-end code.
– Responsive design: An approach that ensures frontend layouts adapt smoothly to different screen sizes and devices.
Resources
- https://airfocus.com/glossary/what-is-a-front-end/
- https://www.coursera.org/articles/what-is-front-end-development
- https://www.hpe.com/emea_europe/en/what-is/front-end-applications.html
- https://webcapitan.com/blog/what-is-front-end-service-and-development/#Front-End-Development-Technologies
- https://viblo.asia/p/phan-biet-giua-front-end-back-end-va-full-stack-WAyK8RGnlxX
- https://talentsprint.com/blog/frontend-vs-backend-vs-full-stack-development
- https://talent500.com/blog/future-of-frontend-development-2025/
- https://medium.com/@ignatovich.dm/frontend-development-trends-in-2025-bef95f50aa2e









Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter
Read More From Us?
Sign up for our newsletter